|
|
You are not currently logged in. Are you accessing the unsecure (http) portal? Click here to switch to the secure portal. |
Difference between revisions of "Angelo Viggiani dal Montone"
| Line 2,019: | Line 2,019: | ||
| {{section|Page:Cod.10723 96r.jpg|3|lbl=96r.3}} | | {{section|Page:Cod.10723 96r.jpg|3|lbl=96r.3}} | ||
| {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/156|6|lbl=66r.6}} | | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/156|6|lbl=66r.6}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | rowspan="3" | | ||
| + | | rowspan="3" | <p>CON: I’m watching, but I cannot settle this right leg with the body well, and if I lift the heel of my left foot, I cannot support myself on it well, nor have my right leg extended and somewhat raised. </p> | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:Cod.10723 96r.jpg|4|lbl=96r.4}} | ||
| + | | class="noline" | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/156|7|lbl=66r.7}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | {{section|Page:Cod.10723 96r.jpg|5|lbl=96r.5}} | ||
| + | | class="noline" | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | {{section|Page:Cod.10723 96r.jpg|6|lbl=96r.6|p=1}} {{section|Page:Cod.10723 97r.jpg|1|lbl=97r.1|p=1}} |
| − | + | | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/156|8|lbl=66r.8}} | |
| − | | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/156| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 2,030: | Line 2,039: | ||
| <p>ROD: I would not know how to do it otherwise; it seems that nature forms such a figure finding yourself in that place with your right side forward, and wanting to throw that ''rovescio'' quite high, as much as can be done, without pivoting or turning the hand; but do it several times, paying attention to all the particulars of which I have told you. </p> | | <p>ROD: I would not know how to do it otherwise; it seems that nature forms such a figure finding yourself in that place with your right side forward, and wanting to throw that ''rovescio'' quite high, as much as can be done, without pivoting or turning the hand; but do it several times, paying attention to all the particulars of which I have told you. </p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/156| | + | | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/156|9|lbl=66r.9}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 2,036: | Line 2,045: | ||
| <p>CON: Look. </p> | | <p>CON: Look. </p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/156| | + | | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/156|10|lbl=66r.10}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 2,043: | Line 2,052: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| − | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/156| | + | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/156|11|lbl=66r.11|p=1}} {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/157|1|lbl=66v.1|p=1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 2,070: | Line 2,079: | ||
| <p>CON: I know why it is called “''guardia alta''”, but I do not know the reason why you call it “''offensiva''” and “''perfetta''”. </p> | | <p>CON: I know why it is called “''guardia alta''”, but I do not know the reason why you call it “''offensiva''” and “''perfetta''”. </p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/159|1|lbl=67v.1}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 2,077: | Line 2,086: | ||
<p>ROD: I will tell it to you: every guard formed on the left side will be called “''difensiva''”, and all of those on the right side will have the name “''offensiva''”; accordingly any time that the sword will be found on the left side (with the right foot in front, nonetheless, which we always assume, as much in ''guardia larga'', as in ''stretta''), still, whether the arm be found higher, or less narrow, or lower than it between the ''stretta'', and the ''larga'', that will be understood as a defensive guard, and will be for defense; and all the times in which the sword will be found by the right side (also with the right foot forward) both in ''guardia alta perfetta'' and in ''imperfetta'', both in ''guardia stretta'' and in ''larga'', either were it then among the ''alta'', and the ''stretta'', or between the ''stretta'', and the ''larga'', provided that the sword should be by the right side, such a guard will always be understood as offensive, and will be in order to offend. This will be our rule, and hold it fixed in your memory. </p> | <p>ROD: I will tell it to you: every guard formed on the left side will be called “''difensiva''”, and all of those on the right side will have the name “''offensiva''”; accordingly any time that the sword will be found on the left side (with the right foot in front, nonetheless, which we always assume, as much in ''guardia larga'', as in ''stretta''), still, whether the arm be found higher, or less narrow, or lower than it between the ''stretta'', and the ''larga'', that will be understood as a defensive guard, and will be for defense; and all the times in which the sword will be found by the right side (also with the right foot forward) both in ''guardia alta perfetta'' and in ''imperfetta'', both in ''guardia stretta'' and in ''larga'', either were it then among the ''alta'', and the ''stretta'', or between the ''stretta'', and the ''larga'', provided that the sword should be by the right side, such a guard will always be understood as offensive, and will be in order to offend. This will be our rule, and hold it fixed in your memory. </p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/159|f1|lbl=-}} |
| + | |||
| + | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/159|2|lbl=67v.2}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| <p>CON: I would ground it better in my memory, if I understood the basis of these “''alte''”, “''strette''” and “''larghe''” guards of yours. </p> | | <p>CON: I would ground it better in my memory, if I understood the basis of these “''alte''”, “''strette''” and “''larghe''” guards of yours. </p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/159|3|lbl=67v.3}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 2,090: | Line 2,101: | ||
<p>ROD: We will do them all soon, and then you will better understand the rule. This ''guardia alta'' is accordingly offensive, the sword being on the right side. </p> | <p>ROD: We will do them all soon, and then you will better understand the rule. This ''guardia alta'' is accordingly offensive, the sword being on the right side. </p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/159|f2|lbl=-}} |
| + | |||
| + | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/159|4|lbl=67v.4}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 2,096: | Line 2,109: | ||
| <p>CON: Why is it called “''perfetta''”? </p> | | <p>CON: Why is it called “''perfetta''”? </p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/159|5|lbl=67v.5}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 2,102: | Line 2,115: | ||
| <p>ROD: Because the point of the sword uncovers the enemy more, and looks more toward him in this form, than in some other in which one can be; this ''guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta'' is born from the ''rovescio'', the doing of which you have in the drawing forth of the sword. </p> | | <p>ROD: Because the point of the sword uncovers the enemy more, and looks more toward him in this form, than in some other in which one can be; this ''guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta'' is born from the ''rovescio'', the doing of which you have in the drawing forth of the sword. </p> | ||
| | | | ||
| − | | | + | | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/159|6|lbl=67v.6}} |
|- | |- | ||
| Line 2,109: | Line 2,122: | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| + | {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/159|7|lbl=67v.7|p=1}} {{section|Page:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) 1575.pdf/160|1|lbl=68r.1|p=1}} | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 04:06, 27 November 2023
| Angelo Viggiani dal Montone | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Died | 1552 Bologna (?) |
| Relative(s) | Battista Viggiani (brother) |
| Occupation | Fencing master |
| Genres | Fencing manual |
| Language | Italian |
| Notable work(s) | Lo Schermo (1575) |
| Manuscript(s) | Cod. 10723 (1567) |
| Translations | Traduction française |
Angelo Viggiani dal Montone (Viziani, Angelus Viggianus; d. 1552) was a 16th century Italian fencing master. Little is known about this master's life, but he was Bolognese by birth and might also have been connected to the court of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor.[1]
In 1551, Viggiani completed a treatise on warfare, including fencing with the side sword, but died shortly thereafter. His brother Battista preserved the treatise and recorded in his introduction that Viggiani had asked him not to release it for at least fifteen years.[1] Accordingly, a presentation manuscript of the treatise was completed in 1567 as a gift for Maximilian II (1527-1576), Holy Roman Emperor. It was ultimately published in 1575 under the title Lo Schermo d'Angelo Viggiani.
Treatise
Note: This article includes a very early (2002) draft of Jherek Swanger's translation. An extensively-revised version of the translation was released in print in 2017 as The Fencing Method of Angelo Viggiani: Lo Schermo, Part III. It can be purchased at the following link in softcover.
Illustrations |
Presentation manuscript (1567) |
Lo Schermo (1575) | |
|---|---|---|---|
Illustrations |
Presentation manuscript (1567) |
Lo Schermo (1575) | |
|---|---|---|---|
Illustrations |
Draft Translation (from the 1575) |
Presentation manuscript (1567) |
Lo Schermo (1575) |
|---|---|---|---|
Third Part Persons introduced in this discussion:
|
[78r.1] TERZA PARTE Persone introdotte nel ragionamento l'Illustrissimo Signor CONTE d'Agomonte, l'Illustrissimo Signor ALUIGI Gonzaga detto RODOMONTE et l' eccellente Messer LODOVICO Boccadiferro :~ |
[51v.1] TERZA PARTE. Persone introdotte nel Ragionamento. L'ILLUSTRISSIMO SIGNOR ALUIGI GONZAGA DETTO RODOMONTE, L'ILLUSTRISSIMO SIGNOR CONTE D'AGOMONTE, ET L'ECCELLENTISSIMO MESSER LODOVICO BOCCADIFERRO FILOSOFO. | |
ROD: Since we want to exercise ourselves for half an hour, Signor Conte, |
[78r.2] CONTE. VOGLIAMO noi andare di sotto nella stanza, ad essercitarci per un hora, Signor Aluigi? |
[51v.2] RODOMONTE. POI che noi vogliamo essercitarci per meza hora (Signor Conte) | |
[78r.3] ROD. Di gratia Conte, questo istesso desideravo io da voi, fra tanto il Dottore si riposerà. |
|||
[78r.4] CON Nel vero, Signor mio che hò presa gran consolatione hoggi, di quella sì honorata disputa, che insieme havete havuto. |
|||
|
[78r.5] ROD. Vi prometto, Conte, ch'egli hà fatto hoggi, contro di me gran resistenza con i suoi for= [78v.1] tissimi argomenti, e'bellissime risposte, et anchio mi pigliavo gran contento vederlo alle volte montar in colera, et in furore. |
|||
[78v.2] CON. Hò udito dire, che quanto più gli huomini dotti sono assaliti dal furore: tanto dicono cose piu belle. |
|||
Fury is of use to the lettered, and to soldiers, although it arises from choler. first I would desire that we were seized by that fury, which took Homer, Virgil, l’Ariosto, and every other most excellent poet: they said supernatural things; and by which are moved all those lettered men, discussing or writing, that say things rare and excellent; and by which we others accordingly are accustomed to make blows worthy of Mars, whose fury is born of choler. |
[78v.3] ROD. E gli è quel furor poetico, dal quale furon rapiti Homero, Virgilio, l'Ariosto, et ciascun altro Eccellentissimo Poeta; Et nui (ditemi Conte) quando siamo in furore, non ci soviene nella mente sempre qualche disusato capriccio? |
[51v.3] in primi desidererei, che sossimo assaliti da quel furore, dal quale rapiti Homero, Virgilio, l'Ariosto, & ciascun'altro Eccellentissimo Poeta; hanno detto cose sopranaturali: & dal quale mossi tutti i letterati, disputando, ò leggendo dicono cose rare, & Eccellenti; & noi altri perciò siam soliti fare colpi degni di Marte, il qual furore nasce dalla colera. | |
Objection that choler hinders the soldier from perturbing the enemy. CON: How is not better to find oneself without choler? Because as the spirit that is quiet speaks better, and succeeds better in letters, thus also is it in the handling of arms: the spirit being more reposed, the knight is able to better put in execution thoughtful and learned blows, while choler instead impairs reason, taking the same from man, causing him to function without knowing the why and the how. |
[51v.4] CON. Come, non è meglio il ritrovarsi senza colera? perche [52r.1] si come l'anima ch'è quieta, meglio discorre, & riesce nelle lettere meglio; cosi anco nell'armeggiare, sendo l'anima piu riposata, puo un Cavalliero meglio ponere in essecutione i colpi pensati, & imparati, ove la colera ci impedisce il discorso, leva di se stesso l'huomo, & lo fa operare senza sapere il perche, & il come. | ||
Response to the objection, to wit, that intemperate choler hinders, and the temperate is of use. ROD: If you propose to me a furious choler, that deprives one of intellect and speech, I would not differentiate among a choleric, and a furious, and an unreasoning animal, and then I would say that it would be detrimental, and that it would not suit our proposition. But if it were to be a temperate choler such as completely obscures reason, I tell you that it would be very useful; because choler is a fire of the blood around the heart, which, being temperate, temperately ignites the heart, and in consequence the ignited humors are temperately elevated, so that they give superior agility and force to the motive spirit, and they work more quickly in the function of every sense, and ultimately the speech, and therefore I must say that a little bit of choler is of use to the soldier, as well to whomever would practice in arms. |
[52r.2] ROD. Se voi mi date una colera furiosa, si che lievi l'intelletto, & il discorso; io non farò differenza tra un colerico, & un furioso, & un'animale irragionevole, & all'hora dirò che sia nociva, & che non si ricerchi al proposito nostro. Ma se sarà una colera temperata tale, che oscuri in tutto la ragione; dicovi che serà di molto giovamento: perche la colera è un incendio del sangue circa al core, la quale, sendo temperata accende temperatamente il core, & per consequente temperatamente si inalzano gli spiriti accesi, che danno maggior agilità, & forza all'anima motiva, & fanno piu presto nelle operationi ogni senso, & ultimamente il discorso, & perciò si puo dire, che un poco di colera giovi al soldato, & anco achi vole essercitarsi nell'armi. | ||
Difficulty of doing two mandritti tondi without pause, such that one lands no higher than the other. CON: This is certainly the cause that one day, while exercising with the conte di Mega, rather moved by the fury of choler, I performed two mandritti tondi, the one after the other without any pause, so that I did not elevate one above the other (and indeed you know, Rodomonte, how hard it would be to do it) whereat the conte was amazed, saying that he had never been able to do it, although he had studied all of the strokes of the sword. |
[78v.4] CON. Vi giuro Signore Aluigi, che tal volta mi son trovato si infuriato, che non havrei ceduto al cielo, et in quella caldezza tai colpi mi sono usciti dalle mani, che non li harrebbe fatto (dirò così) con ogni studio suo il valoroso Marte. Voi sapete bene quanto sia difficile il menare dui mandritti tondi l'un dopo l'altro senza indugio alcuno, talche l'uno non si innalzi più dell'altro, et pur giocando alli passati giorni con il CONTE DI MEGA mi vennero fatti, et non sò come; onde il Conte mezo attonito disse; Credo, che siate il Mastro di coloro, che sanno; io mai a' di miei non gli hò possuto fare, et penso che ricercasse tutti i tratti della spada, nè mai gli colse, et è pur [79r.1] Cavallier al pari di ogni altro valoroso, |
[52r.3] CON. Questa fu certo la cagione, che un giorno essercitandomi co'l Signor Conte di Mega, mosso alquanto dal furore della colera; feci due mandritti tondi l'un dopo l'altro senza indugio alcuno, tal che l'uno non s'inalzò piu dell'altro, & pur sapete Rodomonte quanto sia difficile a farli, onde il Conte restò maravigliato dicendo non haverli mai potuto fare anchor che havesse ricercati tutti i tratti della spada. | |
ROD: The conte di Mega marveled at it; still others would be able to marvel well thereat, he being a knight the peer of any other of valor. |
[52r.4] ROD. Maravigliandosene il Conte di Mega, se ne potevano ben maravigliare anchor gli altri, sendo egli Cavalliero al pari d'ogni altro valoroso. | ||
CON: And more still I say to you, that I wish to do it again; I never knew how to find the path to the way to do it one more time; nevertheless much have I wearied myself, much have I thought thereupon, so that I indeed discovered the way of doing it twice successively, but now the cut is not flat. |
[79r.2] et diro vui anchora, ch'io volsi rifarli nè seppi mai ritrovarli modo, nè strada per farli un'altra volta; niente di manco tanto m'affaticai, e tanto vi pensai sopra, che ritrovai pur modo di farne due successivamente, ma di piatto, non gia di taglio. |
[52r.5] CON. Et piu diro vui anchora, ch'io volsi rifarli, ne seppi mai ritrovarli strada ne modo per [52v.1] farli un' altra volta: niente di meno tanto m'affaticai, tanto vi pensai sopra, che ritrovai pure modo di farne due successivamente, ma di piatto non già di taglio. | |
ROD: I would do a hundred of them, not two, in that way; the difficulty is to do them edge on; but now it is time that we begin to practice, before the hour grows later: take up your sword, conte. |
[79r.3] ROD. Io ne farei cento, non che due à quella guisa, o bel tratto, ma già è tempo, che cominciamo ad essercitarsi avanti, che piu tardi l'hora perche cavalcaremo poi un poco col Conte Ugo à riveder Bologna. |
[52v.2] ROD. Io ne farei cento, non che due a quella guisa: la difficultà è a farli di taglio: ma già è tempo che cominciamo ad essercitarci, avanti che piu tardi l'hora: pigliate la spada vostra Conte. | |
[79r.4] CON. Perche non cominciamo? |
|||
[79r.5] RO. da me non manca pigliate la spada vostra. |
|||
With practice weapons, it is not possible to acquire valor nor to learn a perfect schermo. CON: How so, my sword? Isn’t it better to take one meant for practice? |
[79r.6] CON. Come la spada mia? pigliamo le spade da giuoco? |
[52v.3] CON. Come la spada mia? non è meglio pigliar quelle da giuoco? | |
[79r.7] RO. Da gioco? mai non giuocai con quelle armi al tempo di mia vita. |
|||
[79r.8] CO. Per qual cagione? |
|||
ROD: Not now, because with those practice weapons it is not possible to acquire valor or prowess of the heart, nor ever to learn a perfect schermo. |
[79r.9] RO: Perche con quelle armi non si può acquistar valore, ò gagliardia di cuore, nè con esse imparar mai uno Schermo perfetto. |
[52v.4] RO. Non già, perche con quelle arme da giuoco non si può acquistare valore ò gagliardia di cuore, ne con esse imparar mai uno Schermo perfetto. | |
CON: I believe the former, but the latter I doubt. What is the reason, Rodomonte, that it is not possible to learn (so you say) a perfect schermo with that sort of weapon? Can’t you deliver the same blows with that, as with one which is edged? |
[79r.10] CO. La prima vi credo, ma dubito intorno la seconda; qual è la causa Rodomonte, che non si possa imparare, come dicete, un Schermo perfetto con quella sorte d'arme? non menate voi i medesimi colpi con quelle, et con queste da filo? |
[52v.5] CON. La prima vi credo, ma dubito intorno alla seconda. Quale è la causa Rodomonte, che non si possa imparare (come dite) uno Schermo perfetto con quella sorte d'arme? non menate voi i medesimi colpi con quelle, che con queste da filo? | |
Why one cannot learn a perfect blow with practice weapons, but only with those which are edged. ROD: I would not say now that you cannot do all those ways of striking, of warding, and of guards, with those weapons, and equally with these, but you will do them imperfectly with those, and most perfectly with these edged ones, because if (for example) you ward a thrust put to you by the enemy, beating aside his sword with a mandritto, so that that thrust did not face your breast, while playing with spade da marra,[4] it will suffice you to beat it only a little, indeed, for you to learn the schermo; but if they were spade da filo, you would drive that mandritto with all of your strength in order to push well aside the enemy’s thrust. Behold that this would be a perfect blow, done with wisdom, and with promptness, unleashed with more length, and thrown with more force, that it would have been with those other arms. How will you fare, conte, if you take perfect arms in your hand, and not stand with all your spirit, and with all your intent judgment? |
[79r.11] ROD. Non dirò già, che tutti quei modi di ferir, di ripa= [79v.1] rare, & di guardie non facciate con queste, et con quelle parimente, mà le farete con quelle imperfette, et perfettissime in queste da filo |
[52v.6] ROD. Non ditò già che tutti quei modi di ferire, di riparare, & di guardie, non facciate con queste armi, & con quelle parimente, ma le farete con quelle imperfette, & perfettissime con queste da filo: | |
[79v.2] CON. La ragione? |
|||
[79v.3] ROD. Dirolla; se voi fate per essempio riparo alla punta mostratavi dal nemico con ribatter la spada sua con un vostro mandritto, accioche quella punta non vi guardi il petto giocando con spada da marra, basteravui solo di ribatterla un poco, pure che impariate lo Schermo; mà se saranno spade da filo, voi spingerete quel mandritto con tutta la forza vostra per cacciar ben fuore la punta del nemico: Ecco che questo sarà colpo perfetto, fatto con senno, e con prontezza spiccato piu da lunge, e spinto con piu forza, che non saria con quelle altre arme. Come farete, Conte, se pigliarete arme perfette in mano, à non vi star con tutto l'animo, e con tutto il giudicio intento? |
[52v.7] perche se voi fate (per essempio) riparo alla punta mostratavi dal nimico, con ribatter la spada sua con un vostro mandritto, accio che quella punta non vi guardi il petto, giocando con spade da marra; vi basterà solo di ribatterla un poco, pure che impariate lo Schermo: ma se saranno spade da filo, voi spingerete quel mandritto con tutta la forza vostra per cacciar ben fuori la punta del nimico. Ecco che questo sarà colpo perfetto, fatto con senno, & con prontezza, spiccato piu da lunge, & spinto con piu forza, che non sarebbe con quelle altre arme. Come farete Conte, se pigliarete arme perfette in mano, a non vi star con tutto l'animo, & con tutto il giuditio intento? | ||
It is necessary that the warrior remain intent on the point of the weapon of his enemy. CON: Yes, but it is a great danger to train with arms that puncture; if I were to make the slightest mistake, I could do enormous harm. Nonetheless we will indeed do as is more pleasing to you, because you will be on guard not to harm me, and I will be certain to parry, and I will pay constant attention to your point in order to know which blow may come forth from your hand, which is necessary in a good warrior. |
[79v.4] CON. Et di che sorte; ma in fatti àme parte un gran pericolo l'essercitarsi con le armi, che pungono, che s'io facessi un picciol fallo, come andrebbe? |
[52v.8] CON. Sì, ma è un gran perico= [53r.1] lo lo essercitarsi con le arme che pungono: che se io facessi un picciol fallo, potrebbe nocer troppo. | |
[79v.5] ROD. Vi guardarete di no farlo. |
|||
[79v.6] CONT. Si potendo |
|||
[79v.7] ROD. Guarderommi io di non offendervi. |
|||
| [79v.8] CON. Et [80r.1] se la spada vi scappasse ò vi fallisse il colpo? | |||
[80r.2] ROD. Non vi dubbitate, che nell'uno, ne l'altro m'avverria |
|||
[80r.3] CONTE. Et se per mio difetto io ei venissi colto? |
|||
[80r.4] ROD. Serà vostro danno in ultimo. |
|||
[80r.5] CON. Vedete dunque. |
|||
[80r.6] ROD. Credete, Conte, che non haverò l' occhio di continuo alla punta vostra per conoscere qual colpo vi debbia uscir di mano? |
[53r.2] Nondimeno facciamo pur come piu vi aggrada, perche voi guardarete di non mi offendere, & io cercherò di riparare, & starò di continuo intento alla punta vostra per conoscere qual colpo vi possa uscir di mano: | ||
[80r.7] CON. Hareste un buon occhio. |
|||
[80r.8] ROD. Ma Conte, questa è una conditione neccessaria al buon guerriero |
[53r.3] il che è necessario al buon guerriero. | ||
[80r.9] CONTE. Deh per vostra fede Rodomonte pigliamo altre spade che le nostre. Qui sono spade da marra, et queste sono buone. |
|||
Proposition of a schermo which is of a single strike, and a single parry, of a single guard, and in a single time. ROD: Well now, I want to teach to you today a schermo I have never seen to be done by others, and of which I was simultaneously my own tutor and student, which is not to be done otherwise than with good swords, and a single strike, and a single parry, and a single guard; and each of these three things together in a single tempo; with which parry you will be able to ward every sort of blow and offense; and this strike is superior to every other sort of strike, and from this guard every other guard proceeds. |
[80r.10] ROD. Hor sù vi voglio insegnare hoggi uno schermo, che non ho visto mai esser fatto da altri, ilquale però non si fa con altro, che con buone spade. |
[53r.4] ROD. Horsù vi voglio insegnare hoggi uno schermo, che non ho veduto mai esser fatto da altri, & io ne sono stato a me stesso precettore, & discepolo, ilquale però non si fa con altro che con buone spade, | |
[80r.11] CON. Che Schermo è questo? |
|||
[80r.12] ROD. E' un ferir solo, un parar solo, et una guardia sola, et ogni cosa di queste tre insieme è un tempo solo, col qual parato vi possete riparare da ogni sorte di ferire, et di offesa, et questo ferire è superiore ad ogni specie di ferire, et da questa guardia ogni altra guardia procede. |
[53r.5] & è un ferir solo, un parar solo, & una guardia sola; & ogni cosa di queste tre insieme è un tempo solo, co'l qual parato vi potete riparare da ogni sorte di ferire, & di offesa: & questo ferire è superiore ad ogni spetie di ferire, & da questa guardia ogni altra guardia procede. | ||
CON: If thus it is, this seems to me the foundation and base of all this art; indeed the sword has among all the arms the grandest privileges. |
[80r.13] CON. Se cosi è, questo mi par fondamen= [80v.1] to, et base di quest'arte tutta; ma ditemi l' havete imparato da voi stesso, ò pure da altri? |
[53r.6] CON. Se cosi è, questo mi par fondamento & base di tutta questa arte: | |
[80v.2] ROD. Io sono il Precottore, et il discepolo. In fatti la spada ha tra tutte l'arme grandissimi privilegi. |
[53r.7] in fatti la spada ha tra tutte l'arme grandissimi privilegii. | ||
[80v.3] CO. Credo, che sia cosi, et ch'ella fosse la prima ritrovata. |
|||
Prerogatives and praises of the sword. ROD: Of its prerogatives I will leave you to judge, conte. Which is that weapon that can withstand the blows of the sword? What things would you be able to do with any other arm, that you could do with the sword; on the contrary, many parries, and protections, and sorts of strikes you will discover in it, which you cannot easily find in any others; from which it is to be recognized that all of the art consists perfectly in the sword; |
[80v.4] ROD. Delle sue prerogative, ne lascio fare il giuditio à voi. Qual è quell'arme, che dalla spada non pigli i colpi suoi? quante cose voi potete fare con ogn' altr'arme, con essa spada far le potete; anzi molti ripari, schermi, et sorte di ferire ritrovarete in essa, lequali non trovarete cosi agevolmente nelle altre tutte. Donde si conosce, che tutta l'arte perfettamente consiste nella spada. |
[53r.8] ROD. Delle sue prerogative ne lascio fare il giuditio a voi, Conte. Quale è quell'arme che dalla spada non pigli i colpi suoi? Quante cose voi potete fare con ogni altr'arme, con essa spada far le potete: anzi molti ripari, e schermi, & sorti di ferire ritrovarete in essa, iquali non trovarete cosi agevolmente nell'altre tutte: donde si conosce che tutta l'arte perfettamente consiste nella spada: | |
Why the Emperors had the unsheathed sword carried before them. from whence springs the practice that Emperors had borne before them an unsheathed sword, as an emblem of justice, by which they administered, as much as saying that there is no other fitter medium or instrument by which justice may punish the wicked, and defend the good, than by the sword, truly copious in every defense, and in every offense, fine, proper, and an ornament to man. King and Prophet David says in his Psalms, “Gird your sword over your thigh, O Baron, and that will be your ornament, and your splendor.”[5] Did God not have in His hand a sword with which to punish the kings, as is to be read in many places in the Holy Scripture? Did the Angel of the Lord not appear with unsheathed sword in hand to Joshua in Jericho? I would say that in sum the sword is the most perfect, the most agile, the most worthy arm that is to be found, and of greater honor and ornament to the knight, and I believe it may be said that it is the beginning and end of all arms, both offensive and defensive. |
[80v.5] Di qui nasce, che gl' Imperatori si fanno portare dinanzi la spada sfoderata, in segno di Giustitia da essi amministrata, quasi dicendo non esser altro piu atto mezo, od instrumento per la Giustitia in punire gli scelerati, e difensare i buoni di essa spada, veramente copiosa d'ogni difesa, et d'ogni offesa, commoda, destra, e di ornamento all'huomo; dice David ne' Salmi; cinge la spada tua sopra la coscia, ò Barone, Et quella [81r.1] sarà l'ornamento tuo, et lo splendor tuo. Esso Iddio, non tiene la spada in mano per punir i rei? come in molti luoghi della sacrascrittura si legge? l'Angelo di Dio non apparve con la spada sfodrata in mano à Iosuè in Ierico? Dirò che la spada in somma sia la piu perfetta, la piu agile, la piu degna arma, che si ritrovi, e di maggior honore, et ornamento al Cavalliero: et credo si possa dire, ch'ella sia, et principio, e fine di tutte le armi tanto offensive, come difensive. |
[53r.9] di qui nasce che gli Imperatori si fanno portare innanzi la spada sfodrata, in segno di Giustitia, da essi amministrata, quasi dicendo non esser'altro piu atto mezo, od instrumento per la Giustitia in punire gli scelerati, & difensare i buoni di essa spada, veramente copiosa d'ogni difesa, & d'ogni offesa, commoda, destra, & di ornamento all'huomo. Dice David Re, & [53v.1] Profeta ne'salmi suoi, cingi la spada tua sopra la coscia, o Barone, & quella sarà l'ornamento tuo, & lo splendor tuo. Esso Iddio non tiene la spada in mano per punire i rei? come in molti luoghi della Sacra scrittura si legge? l'Angelo di Iddio non apparve con la spada sfodrata in mano a Iosue in Ierico? dirò che la spada in somma sia la piu perfetta, la piu agile, la piu degna arme che si ritrovi, & di maggior honore, & ornamento al Cavalliero: & credo si possa dire, ch'ella sia, & principio, & fine di tutte l'arme cosi offensive come difensive. | |
The sword was the first among arms to be discovered. CON: Do you believe that it was the first discovered? |
[81r.2] CON. Credete, che fosse la prima? |
[53v.2] CON. Credete che fosse la prima ritrovata? | |
Inventor of the sword. ROD: It was certainly the first, and never since abandoned by man; I believe that it had its origin from the first blacksmith, Tubal Cain, son of Lamech by his wife Zilla; will you not observe how many times the sword is named in the Holy Scripture? The sword is the most ancient, conte, and most modern. |
[81r.3] RO. Fu la prima certissimamente, ne mai piu è stata dall' huomo abbandonata. |
[53v.3] RO. Fu la prima certissimamente, ne mai piu è stata dall'huomo abandonata: | |
[81r.4] CON. A'che tempo hebbe origine? |
|||
[81r.5] RO. Credo dal primo Fabbro Tubal Cain, figlivolo di Lamech della moglie Zilla, non vedete quanto nominata sia essa spada nella sacrascrittura? Antichissima fu la spada, Conte, et modernissima. |
[53v.4] credo che hebbe origine dal primo fabro Tubal Cain, figlivolo di Lamech della moglie Zilla; non vedete quanto nominata sia essa spada nella Sacra scrittura? Antichissima su la spada Conte, & modernissima. | ||
Judgment of the ancient single-edged sword. CON: I liked well that ancient sword, to which was given a dull edge[6] on one side, so that it was stronger and safer: you could push the single-edged sword with your left hand also, to deliver the blow more firmly, and if the enemy were to beat it back toward your face, in order to offend you, at least it would not cut your face; if we say, Rodomonte, that it is both to offend and defend, then it may better perform these two tasks if it is of that form. |
[81r.6] CON. Mi piaceano quelle spade antiche assai, à cui davano la costa da un lato accioche piu ferma, e piu sicura fosse. voi potete la spada d'un sol filo spinger con la sinistra mano anchora, per far il colpo piu gagliardo. Et s'avenisse, che'l nimico ve la ri= [81v.1] butasse verso la faccia, se v'offendesse, almeno non vi taglierebbe il viso: si che diciamo, Rodomonte, che questa è per offendere, et per difendere; adunque meglio fà tutte due l'opere in quella forma. |
[53v.5] CON. Mi piacevano quelle spade antiche assai, a cui davano la costa da un lato, accioche piu ferma, & piu sicura fosse: voi potete la spada d'un sol filo spinger con la sinistra mano anchora, per far il colpo piu gagliardo, & s'avenisse che'l nimico ve la ributasse verso la faccia, se v'offendesse; almeno non vi tagliarebbe il viso: si che diciamo Rodomonte che questa è per offendere, & per difendere: adunque meglio fa tutte due l'opere in quella forma. | |
ROD: You do not know, conte, of how much importance the edge of the sword is, and if the enemy then beats back your sword toward your face, it is not a defect of the sword, but of you, that you do not know the art, or that you have too little strength in you; it was indeed safer, but also less able to offend. |
[81v.2] RO. Voi non sapete, conte, di quanta importanza sia il filo, della spada, et s'il nemico poi vi ributta la spada verso la faccia non è difetto della spada ma di voi, che non sapete l'arte, ò che minor forza havete di lui. |
[53v.6] RO. Voi non sapete Conte di quanta importanza sia il filo della spada, & se'l nimico poi vi ributta la spada verso la faccia, non è difetto della spada, ma di voi, che non sapete l'arte, o che minor forza havete di lui: | |
[81v.3] CON. Era pur piu sicura quella. |
[53v.7] era ben piu sicura quella, | ||
[81v.4] ROD. Ma meno anchor offensiva. |
[53v.8] ma meno anchor offensiva. | ||
Judgment of the ancient swords with a dull edge on a side of the half adjacent to the hilt. CON: It was possible to do so in the form of many swords that I have seen, in which the dull edge extends through the entire forte of the sword, which is the half adjacent to the hilt, while the debole of it, which is the half adjacent to the point, has a false and a true edge. |
[81v.5] CON. Si potea farla nella guisa di molte spade, che ho vedute io: nellequali la costa è per tutto il forte della spada, che è dalla meza parte verso l'elzo, et il debole di essa, che è dala meza parte verso la punta havea il falso, et il dritto filo. |
[53v.9] CON. Si potea farla nella guisa di molte spade, che ho vedute io: nelle quali la costa è per tutto il forte della spada, che è dalla meza parte verso l'elzo, & il debole di essa, che è dalla [54r.1] meza parte verso la punta, havea il falso, & il dritto filo. | |
Antiquity of the sword with two edges from the hilt to the point. ROD: It was certainly possible to do it, but the modern usage has rediscovered the most offensive way to be having the entire length of both sides to be sharp edges; because when one comes to the half sword in combat, the false edge of the forte of the sword is quite opportune; think of it, conte: it is very modern to have two edges from the hilt to the point; I would rule that in the time of David they were of this fashion. He says in the Psalms these words: “The highness of God in their mouths, and a double-edged sword in their hand, to inflict vengeance on the nations”;[7] and I discussed with a Hebrew friend of mine in Mantua, that they are understood in the Hebrew language to be written thus as I have said. |
[81v.6] RO. Si potea fare per certo, ma il moderno uso hà ritrovato, che piu offensiva sia havendo da tutti due i lati il taglio, perche quando si viene à meza spada nella pugna dico che è molto à proposito il falso filo del forte della spada, ne vi pensate Conte, che molto moderno sia l'haver due fili dal elzo sino alla punta; impero che al tempo di David ve n'erano di questa maniera; dice [82r.1] egli ne' salmi queste parole? L'altezza d'Iddio nella gola loro, e spada di due fili nella sua mano per far vendetta nelle genti. Et io ragionando con un Hebreo mio amico in Mantova, intesi, che nella lingua hebrea si scrive cosi, come u' hò detto. |
[54r.2] RO. Si potea fare per certo, ma il moderno uso ha ritrovato che piu offensiva sia, havendo da tutti due i lati il taglio: perche quando si viene a meza spada nella pugna, dico che è molto a proposito il falso filo del forte della spada: ne vi pensate, Conte, che molto moderno sia l'haver due fili dall'elzo sin'alla punta: imperò che al tempo di David ve n' erano di questa maniera. Dice egli ne'Salmi queste parole. L'altezza d'Iddio nella Gola loro & spada di due fili nella sua mano, per far vendetta nelle genti; & io ragionando con un Hebreo mio amico in Mantova, intesi che nella lingua Hebrea si scrive cosi come u' hò detto. | |
CON: I have indeed seen that swords have had dull edges for but few days. |
[82r.2] CON. Hò pur vedut'io pochi giorni sono alcune spade con la costa. |
[54r.3] CON. Ho pur veduto io pochi giorni sono alcune spade con la costa. | |
ROD: It is not a long time that those of that style were being used for the most part; also the rediscovery of this sort in these times was but recent; it is the manner in our days that little do we spy of the dull edge. |
[82r.3] ROD. Non è gran tempo, che s'usavano à quel modo per la piu parte, pur se ne trovavano ancora in quei tempi di questa sorte, ma poche; si come adesso à giorni nostri poche ne veggiamo con la costa. |
[54r.4] RO. Non è gran tempo che s'usavano a quel modo per la piu parte: pur se ne ritrovano anchor in quei tempi di questa sorte, ma poche; si come a'giorni nostri poche ne veggiamo con la costa. | |
CON: Were the ancients using, perhaps, hilts with grips like we use? |
[82r.4] CO. Usavan forse gli antichi di far quegli elzi con quelle impugnature, come usiam noi? |
[54r.5] CON. Usavan forse gli antichi di far quegli elzi, con quelle impugnature come usiam noi? | |
Ancient and modern styles of using the hilts. ROD: They certainly used them, except that to them have been joined all the garnishment that you see from pommel to cross, and provide marvelous defense to the hand; some improvement is constantly discovered by modern men. |
[82r.5] RO. L' usavano per certo, eccetto, che u'è stato aggiunto tutto quel guarnimento, che vedete dal Pomo alla Croce, è fa mirabil difesa alla mano; sempre si ritrova da i moderni qualche miglioramento. |
[54r.6] RO. L'usavano per certo, eccetto che u'è stato aggiunto tutto quel guarnimento che vedete dal Pomo alla croce, & fa mirabil difesa alla mano: sempre si ritrova da'moderni qualche miglioramento. | |
CON: Why is the sword carried at the left side? |
[82r.6] CO. Perche si porta la spada dal lato stanco? |
[54r.7] CON. Perche si porta la spada dal lato stanco? | |
Why the sword is carried at the left side. ROD: I don’t know in what other place you would be able to carry it from which you could draw it with less trouble, and in which you would be more prepared if you had need. It does not impede the hands; in that place you are able to promptly place your right hand in order to draw it out; and finally I do not find any site more convenient, and commodious, and that leaves you free and loose of the entire body, than the left side. |
[82r.7] RO. Non sò in qual luogo poteste voi portarla, che vi desse minor noia, e che piu apparecchiata l'haveste al bisogno vostro. Ivi non u'impedisce alcuna delle mani in quel luogo tosto potete porre la destra mano per trarla fuore, e finalmente non trovo sito piu conveniente, et [82v.1] commodo, et che più vi lasci libero, e sciolto della persona tutta, che'l manco lato. |
[54r.8] RO. Non sò in qual luogo poteste voi portarla che vi recasse minor noia, & che più apparecchiata l'haveste al bisogno vostro. Ivi non u'impedisce alcuna delle mani: in quel luogo tosto potete porre la destra mano per trarla fuori, & finalmente non trovo sito piu conveniente, & commodo, & che vi lasci libero, & sciolto della persona tutta che'l manco lato. | |
CON: I have understood some to say that one carries it on that side out of respect that the left side, where the heart lies, is more worthy, and has greater need of defense. |
[82v.2] CO. Hò d'alcuni inteso dire, che si porta da quel lato per rispetto, che la parte sinistra (dove giace il cuore) è piu degna, et piu ha bisogno di difesa. |
[54r.9] CON. Hò da alcuni inteso dire che si porta da quel lato per rispetto, che la parte sinistra, dove giace il cuore; è piu degna, & piu ha bisogno di [54v.1] difesa. | |
Position of the heart in the human body. ROD: This is not a good reason, conte, in my opinion. Firstly, I have seen in anatomy, that the heart does not rest on the left side more so than on the right, but rather in the center of the chest; it is indeed true that the tip leans a little to the left side; but if this were the true reason then left-handed people would also gird it on that side; but that defense of the left side is the reason to carry it on that side? The real reason I believe to be that which I have said, conte, and left-handed people are an indication thereof, that in order to accommodate themselves to draw it forth from their right hand side, they do gird it on their right. |
[82v.3] RO. Questa non è buona ragione, Conte, secondo il mio parere: primieramente non credo, anzi l'ho pur veduto, che'l cuor stia dalla banda sinistra piu che dalla destra; ma stassi nel mezo del petto, è ben vero che la punta si volta un poco verso il lato manco; ma se questa fosse la ragion vera anchora gli huomini mancini se la cingerebbono da quel lato, e poi, che difesa è quella alle parti sinistre per portarla da quel lato destro del fodro? La vera causa è quella, che vi ho detto io, Conte, et ne fanno segno essi mancini, che per farsela piu commoda, è destra al tirarla fuore, la cingono dal diritto lato. |
[54v.2] ROD. Questa non è buona ragione (Conte) secondo il mio parere. Primieramente io ho veduto nelle anotomie, che'l cuore non stà dalla banda sinistra piu che dalla destra: ma stassi nel mezo del petto: è ben vero che la punta si volta un poco verso il lato manco: poi se questa fosse la ragion vera, anchora gli huomini mancini, se la cingerebbon da quel lato: ma che difesa è quella alle parti sinistre per portarla da quel lato? la vera causa credo esser quella che vi ho detto io (Conte) & ne fanno segno essi mancini, che per farsela piu commoda, & destra al trarla fuori, la cingono dal dritto lato. | |
CON: I well believe this to be the actual reason. |
[82v.4] CO. Credo bene, che questa sia la vera cagione. |
[54v.3] CON. Credo bene che questa sia la vera cagione. | |
ROD: You would be well resolved, my conte, to pass this little time in discussions of some small use to us. |
[82v.5] RO. Voi vi siete deliberato di passar questo poco di tempo in cianze; hor prendete anco voi la vostra spada. |
[54v.4] ROD. Voi vi siete deliberato, Conte mio, di passar questo poco di tempo in ragionamenti a noi poco utili. | |
CON: You speak the truth; it is better to turn to actions, because even if these discussions are indeed useful, they may nonetheless be conducted at other times; now wield your sword fancily a bit, please, Rodomonte. |
[82v.6] CO. Ecco, che son contento, et la piglio, hor maneggiate un poco di capriccio, di gratia Rodomonte. |
[54v.5] CON. Dite vero, che è meglio venire a'fatti, perche se bene utili fono questi ragionamenti; si ponno nondimeno fare in altro tempo, hor maneggiate la vostra spada un poco di capriccio di gratia Rodomonte. | |
ROD: Here you are; I do so willingly. |
[54v.6] ROD. Ecco ch'io il faccio volentieri. | ||
On the fancy handling of the sword. CON: Lovely! But how do you accomplish the settling of the sword in your hand after so much, and so many flourishes? |
[83r.2] CO. O' bella; ma come fate voi à rassettarvi quella spada in mano dopo tanti, e tanti avuolgimenti? |
[54v.7] CON. O bella: ma come fate a rassettarvi quella spada in mano dopo tanti, & tanti avuolgimenti? | |
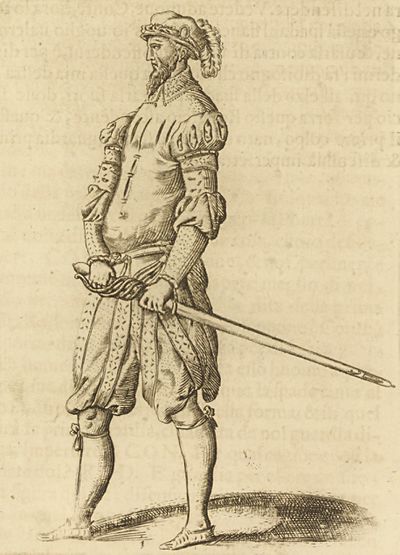
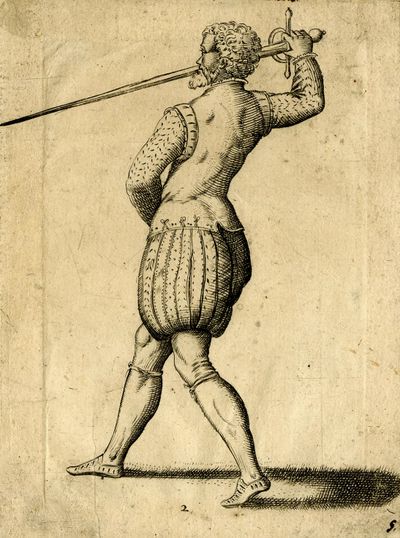
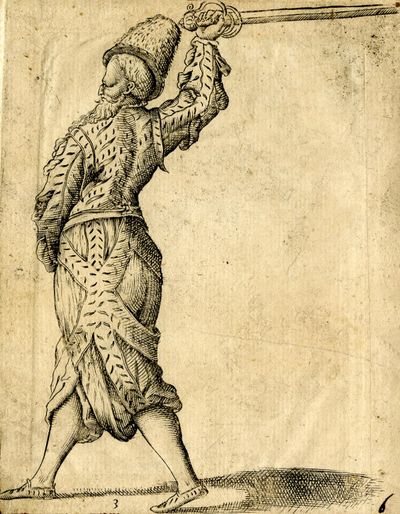
ROD: I cannot describe it to you, conte, but open your eyes well, and pay diligent attention to my wrist, and foremost to the dexterity of the manner of resettling it. Do you see how I do it? Similar actions are to be demonstrated, and to be learned, more and better in proof, and with the sense of sight, than with words; and whoever wanted to express them in words would be in need of that which I know well-- all the muscles of the hand, and the fingers; and I will tell you, that you need to do such and such motion, with this and that muscle, and relax the hand thus, and grip it thus; and he would serve in the role of a good doctor, and a professor of anatomy; because another would not understand it; do these two successive mandritti tondi of yours a bit, conte. |
[83r.3] ROD. Non ve lo posso descrivere, Conte, ma voi aprite ben gli occhi, & ponete diligente cura à i nodi della mano, et alla destrezza del rassettarsela, come vedete, che prima faccio io. |
[54v.8] ROD. Non ve lo posso descrivere, Conte: ma aprite ben gli occhi, & ponete diligente cura a' nodi della mano, & alla destrezza del rassettarsela come prima. Vedete come faccio io? | |
[83r.4] CO. Non veggio nulla; fate di gratia un poco piu adagio. |
|||
[83r.5] RO. Ecco; vedete? |
|||
[83r.6] CO. Bisognarebbe me lo diceste. |
|||
[83r.7] ROD. Non ve lo posso dir con parole. |
[54v.9] similiatti si dimostrano, & s'imparano piu & meglio in prova, & co'l senso del vedere, che con le parole, & a chi volesse esprimerli con parole, | ||
[83r.8] CO.Perche? |
|||
[83r.9] ROD. Saria di bisogno, ch' io sapessi bene quei musculi tutti della mano, e delle dita, e ch'io vi dicessi, bisogna fare il tale, e tal moto con questo, e quel musculo, e snodar la mano cosi, & cosi piegarla: in fatti sarebbe ufficio da un buon Medico, o simili, perche un altro non la capirebbe. |
[54v.10] sarebbe di bisogno, ch'io sapessi bene quei musculi tutti della mano, & delle dita, & ch'io vi dicessi, bisogna fare il tale, & tal moto con questo, & quel musculo, e snodar la mano cosi, & cosi piegarla: & sarebbe uffitio da un buon medico, & professore d'anotomia: perche un'altro [55r.1] non la capirebbe: | ||
[83r.10] CO. In fatti non mi vi posso rassetarre, attendiamo pure ad altro. |
|||
[83r.11] ROD. Fate un poco quei vostri due mandritti tondi insieme. |
[55r.2] fate un poco voi, Conte, quei vostri due mandritti tondi insieme. | ||
CON: Here they are. |
[83r.12] CO Eccoli. |
[55r.3] CON. Eccoli. | |
With the sense of hearing one can recognize that a blow goes flat, although otherwise it is not possible to recognize it. ROD: From the whistle of the sword I hear that they went flat; if they are not good the ear is quick in discerning by the speed of the stroke; don’t you hear the big percussion, and the big reverberation you make in the air, taking a great abundance of it with the flat of the sword? You hear a little less loud, but sharper, whistle, when you do it with the true edge. |
[83r.13] RO. Al fischio della spada sento, che vanno di di piatto, se bene non è si pronto l'occhio in discernergli per la velocità del tratto. |
Co'l senso dell'udito si puo conoscere ch'un colpo sia di piatto, anchor che non si possa conoscerlo. [55r.4] ROD. Al fischio della spada sento che vanno di piatto, se ben non è si pronto l'occhio in discernerli per la velocità del tratto: | |
[83r.14] CO. Et come al fischio? |
|||
|
[83r.15] ROD. Al fischio si; non sentite [83v.1] voi, che gran percossa, e che gran riverberatione fate nell' aria pigliandone gran copia col piatto della spada? sentite un poco voi questo men sonoro, ma piu acuto fischio fatto dal fil dritto. |
[55r.5] non sentite voi che gran percossa, & che gran riverberatione fate nell'aria, pigliandone gran copia co'l piatto della spada? sentite un poco voi questo men sonoro, ma piu acuto fischio, fatto dal fil dritto. | ||
CON: You have great judgment, Rodomonte. |
[83v.2] CO. Havete un gran giuditio Rodomonte. |
[55r.6] CON. Havete un gran giuditio Rodomonte. | |
ROD: It is of some use to have somewhat of letters along with this exercise of ours. |
[83v.3] RO. Egli giova assai l'haver qualche lettere insieme con l'essercitio nostro. |
[55r.7] ROD. Egli giova assai l'haver qualche lettere insieme con l'essercitio nostro. | |
CON: How many strikes do you make? |
[83v.4] CO. Quante spetie di ferire fate voi? |
[55r.8] CON. Quante spetie di ferire fate voi? | |
Three types of strikes: mandritto, rovescio, and punta. ROD: I make three of them: mandritto, rovescio, and punta. |
[83v.5] RO. Ne faccio tre. |
Tre spetie di ferire mandritto, rovescio, e punta. [55r.9] ROD. Ne faccio tre, | |
[83v.6] CO. Et quali? |
|||
[83v.7] RO. Mandritto, rovescio, e punta. |
[55r.10] mandritto, rovescio, & punta. | ||
CON: Isn’t there a falso? |
[83v.8] CO. Non vi è il falso? |
[55r.11] CON. Non v'è il falso? | |
ROD: There is, and it is called “falso” only through being of little moment. |
[83v.9] RO. Si; e s'addimanda falso, solo per esser di poco momento. |
[55r.12] ROD. Vi è, & si domanda falso, solo per esser di poco momento. | |
CON: Do all three of them a bit, please, Rodomonte. |
[83v.10] CO. Fateli un poco tutti tre digratia Rodomonte mio. |
[55r.13] CON. Fateli un poco tutti tre di gratia, Rodomonte mio. | |
ROD: Watch: this is a mandritto, this other is a rovescio, and this is a punta. |
[83v.11] ROD. Ecco: questo è il mandritto; quest'altro è rovescio, et questa è punta. |
[55r.14] ROD. Ecco: questo è mandritto, quest'altro è rovescio, & questa è punta. | |
CON: Where do you leave the fendenti dritti and rovesci, the montante, the mandritto and rovescio sgualembrato, the falso manco and dritto? Where do you leave the stoccata and the imbroccata? You have also not done the mandritto tondo and the rovescio tondo. |
[83v.12] CO. Dove lasciate i fendenti dritti, e rovesci, il montante, il mandritto, et il rovescio sgualembrato, il falso manco, et diritto? Dove lasciate la stoccata, e l'imbroccata; altro non havete fatto, che il mandritto tondo, et il rovescio tondo. |
[55r.15] CON. Dove lasciate i fendenti dritti, & rovesci, il montante, il mandritto, & il rovescio sgualembrato, il falso manco, & dritto? dove lasciate la stoccata, & l'imbroccata? altro non havete fatto che'l mandritto tondo, & il rovescio tondo. | |
Which is the true and the false edge. ROD: You know well what is the true and the false edge, that having the double-edged sword by your hip, that edge which is facing more toward the ground is called the true edge, and that which is toward your upper body, facing the sky, is called the false; |
[83v.13] ROD. Voi sapete bene, che cosa è dritto filo, e falso filo, non è egli il vero? |
Qual sia dritto, & falso filo. [55r.16] ROD. Voi sapete bene che cosa è dritto filo, & falso filo, | |
|
[83v.14] CO. Tenendo la spada di due tagli al fianco; quel taglio, che più guarda verso terra, si chiama dritto filo, e quello che verso le parti alte del corpo riguarda verso l'aria, chia= [84r.1] masi falso. |
[55r.17] che tenendo la spada di due tagli al fianco, quel taglio che piu guarda verso terra si chiama dritto filo, & quello che verso le parti alte del corpo, riguarda verso l'aria, chiamasi falso: | ||
Why they are called the true and the false edge. and the reason is this: that throwing a mandritto, or a rovescio, the sword always falls naturally with that edge. I say therefore that there are no other types of strikes than these said three, that can not be classified as one of them; because all those blows that initiate from the right side of the body, |
[84r.2] RO. Benissimo, et la ragion è questa, che tirando un mandritto, ò un rovescio la spada sempre cala naturalmente con quel taglio; dico adunque, che altra specie di ferire diverso da questò tre detti non vi è, che sotto qualch'una di esse non si contenga: |
Perche si chiami dritto, & falso filo. [55r.18] & la ragion è questa, che tirando un mandritto, o un rovescio; la spada sempre cala naturalmente con quel taglio. Dico dunque che altra spetie di ferire diverso da questi tre detti, non vi è, che sotto qualch'una di esse non si contenga: | |
Which are called mandritti. both with the right forward and with the left, are all to be called mandritti, having their origin from the right side, whether from top to bottom, or bottom to top; and these blows have their endings on the left side. See you, conte, that the tondo mandritto, as well as the sgualembrato, together with the falso dritto, should be included under the name of “dritto”; |
[84r.3] perche tutti quei colpi, che nasceranno dalle destre parti della persona tanto co'l pie destro innanzi, quanto con sinistro tutti si addimanderanno mandritti havendo il principio loro dalle diritte parti, cosi da alto al basso, come da basso ad alto, et havranno il lor fine questi tai colpi nelle sinistre parti. Eccovi Conte, che tanto il tondo mandritto quanto lo sgualembrato, et il falso dritto insieme sotto nome di dritto saranno rinchiusi; |
Quali si dimandino mandritti. [55r.19] perche tutti quei colpi che nasceranno dalle parti destre della persona, tanto co'l pie destro innanzi, quanto co'l [55v.1] sinistro, tutti si domanderanno mandritti, havendo il principio loro dalle dritte parti, cosi da alto a basso; come da basso ad alto; & havranno il lor fine questi tai colpi nelle sinistre parti. Eccovi Conte, che tanto il tondo mandritto, quanto lo sgualembrato, & il falso dritto insieme, sotto nome di dritto, saranno rinchiusi, | |
Which are rovesci. and all those blows that originate from the left side of the body and terminate on the right side, both from high to low as well as from low to high, should be called “rovesci”. Under the rovescio therefore are classified the rovescio tondo, the sgualembrato, and the falso manco; and it is called “rovescio” because it springs from the corner opposite from the dritto. |
[84r.4] e tutti quei colpi, che haveranno origine dalla parte sinistra della vita, e finiranno nelle destre parti tanto da alto à basso, quanto da basso ad alto, chiamerannosi rovesci; sotto il rovescio adunque si contiene il rovescio tondo, lo sgualembrato, et il falso manco, et dicesi rovescio, perche egli è nato dal canto rovescio del dritto. |
Quali siano rovesci. [55v.2] & tutti quei colpi che havranno origine dalla parte sinistra della vita, & finiranno nelle destre parti, tanto da alto à basso, quanto da basso ad alto, chiamerannosi rovesci. Sotto il rovescio dunque si contiene il rovescio tondo, lo sgualembrato, & il falso manco; & dicesi rovescio, perche egli è nato dal canto rovescio del dritto. | |
It appears that the fendente and the montante should differ from the rovescio. CON: Where do you place the fendenti dritti and rovesci, and the montante? |
[84r.5] CO. Dove riporrete voi i fendenti dritti, et rovesci, et il montante? |
Pare che
siano diversi
il
fendente,
& il montante,
dal
rovescio. [55v.3] CON. Dove riporrete voi i fendenti dritti, & rovesci, & il montante? | |
ROD: I do not differentiate them from mandritti and rovesci. |
[84r.6] ROD. Non gli faccio differenti da i mandritti, et rovesci. |
[55v.4] RO. Non li faccio differenti da' mandritti, & rovesci. | |
CON: How not? Tell me: are the mandritti not begun on the right side, and the rovesci on the left? And the fendenti from high to low with the true edge, or alternately from low to high? |
[84r.7] CO. [84v.1] Come nò; ditemi i mandritti non nascono dalle parti destre, et i rovesci dalle manche, et essi fendenti da alto à basso per dritto filo, overo da basso ad alto? |
[55v.5] CON. Come no? Ditemi: i mandritti non nascono dalle parti destre, & i rovesci dalle sinistre? & essi fendenti da alto a basso per dritto filo, ò vero da basso ad alto? | |
Three types of strikes derived from three dimensions of continuous quantity. ROD: You maintain that I do not know that obvious argument, conte, for although the fendenti descend or ascend through a straight line, it appears possible to denominate them as being more from the right than the left side; and in addition, there is this more forceful argument: that there are three dimensions: height, width, and depth; it appears that the mandritti and rovesci terminate in width; the thrust of the point, and its withdrawal, terminate in depth; it is accordingly just that the fendenti, and those that you call montanti, terminate in height; and that as these differences of position are varied, thus are these blows also varied; |
[84v.2] RO. Havete non so che d'apparente ragione, Conte, conciosia che per moto retto discendano i fendenti, overo ascendano, ne par, che si possino denominare piu dalle destre, che dalle sinistre parti; et in oltre vi è poi questa piu efficace ragione, che facendosi tre misure, longhezza, larghezza, e spessezza, per dir cosi, par, che i mandritti, et rovesci siano termini della larghezza; il cacciar della Punta, et il tirarla, termini della spessezza: giusta cosa adunque sarà, che i fendenti, et questi vostri chiamati montanti fossero termini della longhezza, e che come le differenze di positione sono varie, cosi fossero anco questi colpi vari, |
Tre specie di ferire tolte dalle tre misure della quantità continua. [55v.6] RO. Havete non sò che d'apparente ragione (Conte) conciosia che per moto retto discendano i fendenti ò vero ascendano; ne par che si possano denominare piu dalle destre, che dalle sinistre parti; & in oltre vi è poi questa piu efficace ragione, che facendosi tre misure, lunghezza, larghezza; & profondità, par che i mandritti, & rovesci, siano termini della larghezza, il cacciar della punta, & il tirarla, termini della profondità: giusta cosa dunque sarà che i fendenti, & questi vostri chiamati montanti, siano termini della lunghezza, & che come le differenze di positione, sono varie, cosi fossero anco questi colpi vari: | |
Regarding nature there may be four kinds of strikes. whence, my conte, regarding nature there may be four types of blows: mandritto, rovescio, fendente, and punta; but we are not considering blows other than those of the sword worn at the hip; we discover therein but those three. |
[84v.3] la onde, Conte mio generoso, in quanto alla natura sariano forse quattro spetie di ferire, Mandritto, rovescio, fendente, et Punta; ma non considerando noi i colpi da altro, che dalla spada al fianco non ritroviamo altri, che quelli tre. |
In quanto alla natura sariano quattro spetie di ferire. [55v.7] la onde (Conte mio) in quanto alla natura sarebbono forse quattro spetie di ferire, Mandritto, Rovescio, Fendente, & Punta: ma non considerando noi i colpi da altro, che dalla spada al fianco; non ritroviamo altri, che quelli tre. | |
CON: How? |
[84v.4] CO. Come? |
[55v.8] CON. Come? | |
There are only three kinds of strikes, considering those had by the sword at the hip. ROD: I will explain it: if you find for yourself your sword at your hip, laying hand to sword teaches you the mandritto, moving your hand from your right, located on the grip of the sword, toward your left side; unsheathing the sword teaches you the rovescio, drawing it from the left to the right side. Seeing that you have fury, make it to be that the point of your sword is aimed at the breast or the face of your enemy; whereupon from putting your hand to your sword, and drawing it, and setting yourself in place against your enemy, you derive these three natural blows; from here you cannot, conte, derive the high to low fendente, or the low to high. |
[84v.5] ROD. Dirollo; se vi ritrovarete la spada [85r.1] al fianco, il metter mano alla spada v'insegna il mandritto movendo la mano dal suo destro sito all'impugnadura della spada nello stanco lato; lo sfoderar della spada v'insegna il rovescio, tirandola dallo stanco al dritto lato; tratta che l'havete fuore, ritrouarete la punta della spada vostra, che riguarda il petto ò la faccia del nimico; dove dal metter mano alla spada, e trarla fuore e rassettarvi verso il nemico voi cavate questi tre colpi naturali; di qui non potete, conte, cavare il fendente d'alto à basso, ò da basso ad alto, |
Tre sono solamente le spetie del ferire, considerando le dall' haver la spada al fianco. [55v.9] RO. [56r.1] Dirollo: se vi ritrovarete la spada al fianco; il metter mano alla spada vi insegna il mandritto, movendo la mano dal suo destro sito all'impugnatura della spada nello stanco lato: lo sfodrar della spada v'insegna il rovescio, tirandola dallo stanco al dritto lato. Tratta che l'havete fuori, ritrouarete la punta della spada vostra, che risguarda il petto, ò la faccia del nimico: dove dal metter mano alla spada, & trarla fuori, & rassettarvi verso il nimico; voi cavate questi tre colpi naturali: di qui non potete (Conte) cavare il fendente d'alto a basso, ò da basso ad alto. | |
Which is punta dritta, and which rovescia. Concerning the third strike, called “punta”, if the punta issues from the right side, it will be called punta rovescia,[8] and if it issues then from high to low, or from low to high, and thus whether its ending is on the left side or the right, all will be under the name of “punta”; it appears to me that having demonstrated to you in full through such reasons, there are only three main types of blows in our art; yet placing the mandritto fendente under the mandritto, and the fendente rovescio under the rovescio, gives force that each blow originates from the right or from the left side. |
[85r.2] quanto al terzo ferir chiamato punta, se nascerà la punta dalle parti diritte chiamerassi punta dritta, se dalle stanche chiamerasse punta rovescia, et nasca poi d'alto à basso, ò da basso ad alto, et cosi sia il suo fine ò alle stanche parti, o alle diritte tutte saranno sotto il nome di punta; si che parmi d'havervi dimostrato à pieno per qual cagione solo tre spetie principali sieno i colpi dell'arte nostra, ponendo però il mandritto fendente sotto il mandritto, et il fendente rovescio sotto il rovescio, sendo forza ch'ogni colpo nasca dal dritto ò dal stanco lato. |
Qual sia puta dritta, & qual rovescia. [56r.2] Quanto al terzo ferire, chiamato punta, se nascerà la punta dalle parti dritte, chiamerassi punta rovescia: & nasca poi da alto à basso, ò da basso ad alto, & cosi sia il suo fine, ò alle stanche parti, ò alle diritte; tutte saranno sotto il nome di punta: si che parmi d'havervi dimostrato a pieno per qual cagione, solo tre spetie principali siano i colpi dell'arte nostra; ponendo però il mandritto fendente sotto il mandritto, & il fendente rovescio sotto il rovescio, sendo forza ch'ogni colpo nasca dal dritto, ò dallo stanco lato. | |
CON: I prefer that argument of yours, according to which the fendenti naturally form another major and distinct type. |
[85r.3] CON. Più [85v.1] mi piacerebbe quella vostra ragione per laquale naturalmente fate essi fendenti un'altra principal spetie, e diversa. |
[56r.3] CON. Più mi piacerebbe quella vostra ragione, per la quale naturalmente fate essi fendenti un'altra principale spetie, & diversa. | |
Whosoever would derive the types of blows from the dimensions and ends thereof, sets there to be three or six in number. ROD: Returning to that argument, either there would be three types or six; because if you would consider only the three dimensions, there would be three: dritto, fendente, and punta; but if you consider the six ends of the three dimensions of space, there would be six: mandritto and rovescio, fendente descendente and fendente ascendente, and thrusting the punta and withdrawing it. |
[85v.2] ROD. Quanto à quella ragione anchora, ò che sariano tre le spetie, ò sei; perche se consideraste solo le tre dimensioni, sariano tre, dritto, fendente, et punta; ma se consideraste i sei fini di esse tre dimensioni, ò spacii sariano sei, mandritto, et rovescio, fendente, descendente, et fendente ascendente cacciar di punta, e ritrarla. |
Chi vol prendere le spetie del ferire dalle dimensioni, & termini della quantità ponno essere treet sei. [56r.4] ROD. Quanto à quella ragione anchora, ò che sarebbono tre le spetie, o sei: perche se consideraste solo le tre dimensioni, sarebbono tre, dritto, fendente, & punta: ma se consideraste i sei fini di esse tre dimensioni ò spatii, sarebbono sei, mandritto, & rovescio, fendente descendente, & fendente ascendente, cacciar di punta, & ritrarla. | |
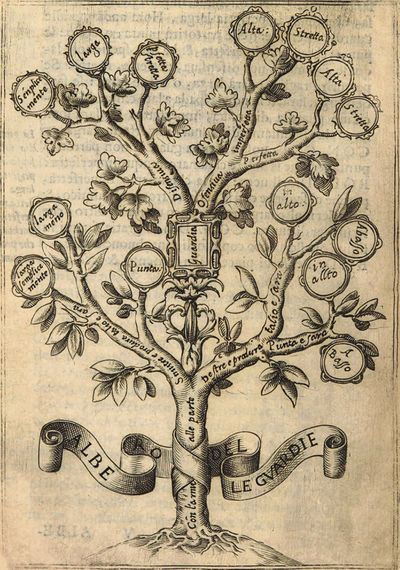
CON: No, no, let us follow the common way: you know what I want from you, Rodomonte: that you make me something like a tree of all these general and particular blows, and make of them an orderly division. |
[85v.3] CO. Nò nò, seguitiamo pur la via commune; sapete che cosa vorrei,sapete che cosa vorrei da voi Rodomonte? |
[56r.5] CON. Nò nò, seguitiam pur la via commune: sapete che cosa vorrei da voi Rodomonte; | |
[85v.4] RO. Che? |
|||
[85v.5] CO. Vorrei, che mi faceste come un Albero di tutti questi generali, e particolari colpí, e farne un partimento regolato. |
[56r.6] che voi mi faceste come un'albero di tutti questi generali, & particolari colpí, & farne [56v.1] un partimento regolato. | ||
|
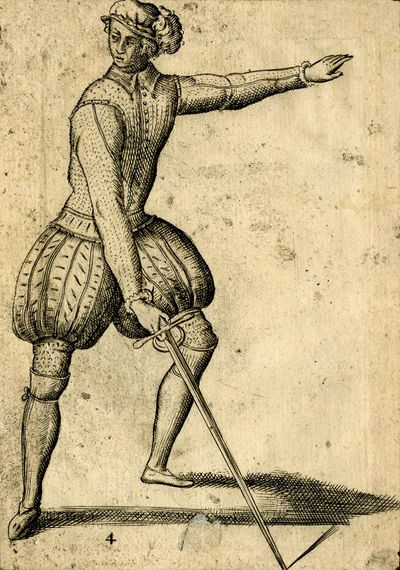
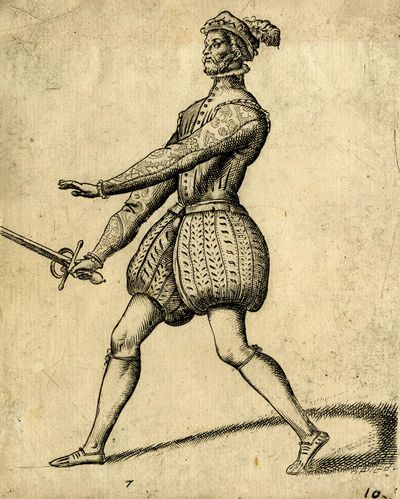
Tree of Principal Blows [87r] ALBERO DEI COLPI PRINCIPALI. [57v] ALBERO DE I COLPI PRINCIPALI |
Division of the family of strikes into types according to their differences. I am happy to do this welcome thing for you; accordingly I tell you that the first family will be the strike. The strike can be of two sorts, either the cut or the thrust. The cut is either with the true edge of the sword or with the false edge. |
[85v.6] ROD. Per farvi cosa grata son contento; onde vi dico, che il primo genere sarà esso ferire. il ferire può esser di due sorti, ò di taglio, ò di Punta; il taglio ò con il dritto fil di essa spada, ò con il falso filo; |
Divisione del genere del ferire nelle sue spetie per le differenze. [56v.2] ROD. Per farvi cosa grata; son contento: onde vi dico, che'l primo genere sarà esso ferire. Il ferire puo essere di due sorti, o di taglio, o di punta. Il taglio, o co'l diritto filo d'essa spada, o co'l falso filo. |
The blows with the true edge are of two types, mandritto and rovescio; the mandritto can be tondo, fendente, and sgualembrato, depending on how the edge falls; if simply from high to low, it will be called “fendente discendente dritto”; if it rises from low to high, it will be called “fendente ascendente dritto”; if the true edge cut goes from the right to the left side, it will be called “mandritto tondo”; if it should go sgualembro, that is, that it begins high and ends low, and simultaneously from the right to the left side, they will call it “mandritto sgualembrato”; if, on the other hand, it goes from low to high, it will be a “sgualembrato ascendente”, which, however, is composed of the tondo and of the fendente. |
[85v.7] il ferire con dritto filo ha sotto di se due specie, mandritto, et rovescio; il mandritto può esser tondo, fendente, et sgualembrato, secondo, che cade il filo, se d'alto à basso semplicemente si chiamerà fendente discendente dritto; se montarà da basso ad alto chiamerassi fendente asce= [86r.1] dente dritto; s'el taglio pel dritto andarà dal destro al sinistro lato chiamerassi mandritto tondo: se caminerà di sgualembro, cio è, che cominci d'alto, e finisca à basso, et insieme dal destro al sinistro lato, lo chiamano mandritto sgualembrato, se pel contrario, da basso ad alto sia sgualembrato dritto ascendente, il quale pero è composto del tondo, e del fendente |
Spetie del ferire co'l dritto filo. [56v.3] Il ferire con dritto filo ha sotto di se due spetie, mandritto, & rovescio: il mandritto puo esser tondo, fendente, & sgualembrato, secondo che cade il filo: se d'alto a basso semplicemente, si chiamerà fendente discendente dritto: se montarà da basso ad alto; chiamerassi fendente ascendente dritto: se il taglio per lo dritto andarà dal destro al sinistro lato; chiamerassi mandritto tondo: se caminerà di sgualembro, cioè che cominci d'alto, & finisca a basso, & insieme dal destro al sinistro lato; lo chiameranno mandritto sgualembrato: se per lo contrario da basso ad alto; sarà sgualembrato ascendente: ilquale però è composto del tondo, & del fendente. | |
There are as many types of strikes with the true edge as there are with the false. These are the types of the mandritto. The rovescio has as many other types, and not more; and if one would strike with the false edge, there are born therefrom as many kinds of strikes as with the true edge, except that you need to add the designation of “falso” to all the particular names, saying “falso mandritto”, “falso rovescio”, “falso mandritto tondo”, “falso mandritto sgualembrato”, “falso fendente”, and thus with all the others from side to side, adding to each this designation of “falso”. |
[86r.2] queste; sono specie del mandritto. Il rovescio ha altre tante specie, e non piu. Et se si ferirà col falso filo ne nasceranno altretante specie di ferire, quanto col dritto filo, eccetto che vi si aggiongerà questo nome di falso à tutti. I particolari nomi dicendo, falso mandritto, falso rovescio, falso mandritto tondo, falso mandritto sgualembrato, falso fendente, e cosi di tutti gli altri à parte à parte giungendovi questo nome di falso. |
Quante sono le spetie del ferire co'l dritto filo tante sono quelle del ferire co'l falso. [56v.4] Queste sono le spetie del mandritto. Il rovescio ha altre tante spetie, & non piu: Et se si ferirà co'l falso filo; ne nasceranno altre tante spetie di ferire, quante co'l dritto filo, eccetto che vi si aggiungerà questo nome di falso a tutti i particolari nomi, dicendo, falso mandritto, falso rovescio, falso mandritto tondo, falso mandritto sgualembrato, falso fendente, & cosi di tutti gli altri a parte a parte, aggiungendovi questo nome di falso. | |
Types of strikes with the point. If one would strike with the point, either it will begin from the right side, and will be called “punta diritta”, or from the left side, and will be called “punta rovescia”;[9] the punta diritta either drops from high to low, and will be called “punta diritta discendente”, or goes from low to high, and will be called “punta diritta ascendente”, or alternately “stoccata”, terminating then on either the right side or the left; or it will go straight ahead, and is called “punta ferma diritta”; of the punta rovescia, there are as many others that can be spoken of. However, if you mix together these types, there are born thereof other imperfect blows, made up of these, such as mezi mandritti, tramazzoni, false feints, jabs, and plenty of other blows, reducible nonetheless to this Tree, which I now present to you for your gratification. |
[86r.3] Se si ferirà con la punta, ò nascerà dalle parti diritte e chiamerassi punta diritta, ò dalle parti stanche, e chiamerassi punta rovescia: la punta diritta ò cala d'alto à basso e chiamerassi punta diritta discendente, ò da basso ad alto e chiamerassi punta dritta ascendente, overo stoccata, finisca poi dal destro lato ò dallo stanco, ò che va drittamente, e chiamasi [86v.1] punta ferma diritta; della punta rovescia, altre tanto si puo dire. Ma di queste specie poi mischiate insieme ne nascono altri imperfetti colpi composti di questi, come mezi mandritti, tramazzoni, falsi finti, puntati, et altri assai colpi riducibili pero à questo albero ch'io per compiacervi hora vi descrivo. |
Spetie lel ferire con punta. [56v.5] Se si ferirà con la punta, o nascerà dalle parti diritte, & chiamerassi punta diritta, o dalle parti stanche, & chiamerassi punta rovescia: la punta diritta, o cala da alto a basso, & chiamerassi punta diritta discendente, o da basso ad alto, & chiamerassi punta diritta ascendente, overo stoccata, finisca poi dal destro lato, o dallo stanco: o che và dirittamente, & chiamasi punta ferma diritta: della punta ro= [57r] vescia, altro tanto si può dire. Ma di queste spetie poi mischiate insieme ne nascono altri imperfetti colpi, composti di questi, come mezi mandritti; tramazzoni, falsi finti, puntati, & altri assai colpi, riducibili però à questo Albero, ch'io per compiacervi hora vi descrivo. | |
Objection as to whether there should be only two principal strikes: cut and thrust. CON: According to this profound distinction of yours, it appears to me that this first division of the three types, namely, mandritto, rovescio, and punta, is not convenient; because the mandritto and rovescio are two prime types derived from the straight edge; and the thrust, which you have divided, contrasts the cut, so that it appears that there are only two principals: thrust, and cut. |
[86v.2] CO. Secondo questa vostra profonda distintione mi pare che quella prima delle tre specie, cioè mandritto rovescio, e punta non sia conveniente: perche il mandritto, e rovescio sono due specie prime del diritto filo: et la punta c'havete divisa voi contra il taglio, talche pare, che siano solamente due principii, Punta, e taglio. |
Dubitatione
che siano
solamente
due principii
di ferire
taglio,
&
punta. [58r.1] CON. Secondo questa vostra profonda distintione; mi pare che quella prima delle tre spetie, cioè mandritto, rovescio, & punta, non sia conveniente: perche il mandritto, & rovescio sono due spetie prime del diritto filo, & la punta che havete divisa voi, contra il taglio; tal che pare che siano solamente due principii; Punta & taglio. | |
Refutation of the objection. ROD: This is a most lovely objection, to which I respond, that I made those three types (mandritto, rovescio, and punta) the principal ones, making such divisions from putting the hand to the sword (as I told you), and not according to the nature of the blows, or of the sword, or of the location, or dimensions. |
[86v.3] ROD. Questa è una bellissima dubitatione alla quale rispondo, che feci quelle tre specie, mandritto, rovescio, et punta principali facendo tal divisione dal metter mano alla spada (come vi dissi) ma non secondo la natura de i colpi, e della spada, e del sito, e delle dimensioni. |
Solutione della dubitatione. [58r.2] ROD. Questa è una bellissima dubitatione, alla quale rispondo, che feci quelle tre spetie, mandritto, rovescio, & punta, principali, facendo tal divisione dal metter mano alla spada (come vi dissi) ma non secondo la natura de'colpi, & della spada, & del sito, & delle dimensioni. | |
[86v.4] CON. Puo esser questo, che siate tanto valente Signor Rodomonte? |
|||
[86v.5] ROD. Sono tale come mi vedete alli piaceri vostri, Conte gentile. |
|||
CON: Tell me a bit, which of these three types of blows of yours holds the first place? |
[86v.6] CO. Vi ringratio Signor ma ditemi un poco qual [87v.1] è di quelle vostre tre spetie di ferire, che tenga il primo luogo? |
||
Ranking of nobility among the types of strikes. ROD: I believe that the first would be the punta, and after that the rovescio, and then the mandritto. |
[87v.2] ROD. Credo che prima sia la punta. |
Ordine in nobiltà tra le spetie di ferire. [58r.4] ROD. Credo che prima sia la punta, | |
[87v.3] CO. et dopo essa? |
[58r.5] & dopo essa | ||
[87v.4] ROD. il rovescio |
[58r.6] il rovescio, | ||
[87v.5] CO. Et poi il mandritto. |
[58r.7] & poi il mandritto. | ||
[87v.6] RO. Cosi è. |
|||
CON: And I maintain the exact opposite. Because it seems to me that the mandritto is more noble, more natural, and more proper, and after that its opposite, the rovescio, and finally the punta; and for what reason do you assign your order? |
[87v.7] CO. Per mia fe ch'io tenea tutto il contrario. |
[58r.8] CON. Et io tenea tutto il contrario. | |
[87v.8] RO. Per qual cagione? |
|||
[87v.9] CON. Che sò io; parmi che il mandritto sia piu nobile, piu naturale, e piu destro, e dopo esso il suo contrario rovescio; ultimatamente essa punta. Et voi che ragione assignate all'ordine vostro? |
[58r.7] Perche parmi che'l mandritto sia piu nobile, piu naturale, & piu destro, & dopo esso il suo contrario rovescio, ultimamente, essa punta: & voi che ragione assegnate all'ordine vostro? | ||
Praise of the strike of the punta and how it takes precedence over the others. ROD: I will tell you; we must say without fail that among the offensive blows, those which have more offense are of greater perfection, and to them must be the first place. And because the thrust is of the greatest offense, and more fatal, doing damage and detriment in the depth of the body (a place more perilous, and less apt to be healed or tended) because of this we say that the punta deserves the first place; of which relates Vegetius that the Romans, when training their youths in arms, wanted them to strike more with the point than the edge, and thus doing, were more times victorious; but throwing with the edge, they remained cheated of victory on many occasions; the point therefore offers to the enemy greater terror, since that stroke is more fatal, and also offends more easily, and requires less force to drive it forward, than to throw a blow with the edge. |
[87v.10] RO. La diro. Noi dovemo senza fallo dire, che tra i colpi offendenti quelli che piu hanno dell'offensivo sono di maggiore perfettione, et che ad essi devesi il primo luogo; Et per che la punta è di maggior offesa, & piu mortale facendo danno, e detrimento nel profondo del corpo (luogo piu pericoloso, et meno atto da essere sanato ò curato. La punta adunque merita il primo luogo: la onde narra Vegetio, che i Romani essercitando la lor gioventù nelle Armi volevano, che più di punta, che di taglio ferissero, et cosi facendo il piu delle volte vinsero; ma menando di taglio spesse volte restarono gabbati; la punta adunque porge al nemico maggior terrore come ferita piu [88r.1] mortale; et è ancora piu facile all'offendente, et minor forza vi bisogna à spingerla, che à tirar un colpo di taglio. |
Lode del ferire di punta & come egli preceda à gli altri. [58r.10] ROD. Ve la dirò, noi dovemo senza fallo dire che tra i colpi offendenti, quelli che piu hanno dell'offensivo, sono di maggior perfettione, & che ad essi devesi il primo luogo. Et perche la punta è di maggior offesa, & piu mortale, facendo danno, & detrimento nel profondo del corpo (luogo piu pericoloso, & meno atto da esser sanato, o curato) per questo diciamo che la punta merita il primo luogo: la onde narra Vegetio: che i Romani essercitando la lor gioventù nelle armi; volevano che piu di punta, che di taglio ferissero, & cosi facendo il piu delle volte vinsero: ma tirando di taglio spesse volte restarono ingannati: la punta dunque porge al nimico maggior terrore, come ferita piu mortale; & è anchora piu facile all'offendente, & mi= [58v.1] nor forza vi bisogna a spingerla, che a tirar un colpo di taglio. | |
CON: Why then do you deem the rovescio more worthy than the mandritto? |
[88r.2] CO. Di questa certo vi cedo, ma perche fate piu degno il rovescio del mandritto? |
[58v.2] CON. Perche poi fate piu degno il rovescio del mandritto? | |
Why the rovescio is more worthy than the mandritto. ROD: For the same reason, for being of greater offense; you see, this mandritto that I deliver to you, offends you in principle, but goes falling every time, and taking less distance from the body. Behold, how my arm goes falling just now; but, I ask of you, regard this rovescio a bit, how on the contrary it goes on an entirely rising path; don’t you see how much the arm and the shoulder lengthen themselves just now, completely elevating themselves, continuously augmenting the strike, and doing greater effect? |
[88r.3] RO. Per l'istessa cagione, per esser di maggior offesa. |
Perche il rovescio sia piu degno del mandritto. [58v.3] ROD. Per l'istessa cagione, per esser di maggior offesa: | |
[88r.4] CO. Et come? |
|||
[88r.5] ROD. Come ah; vedete questo mandritto ch'io vi meno, v'offende nel principio poi và calando tutta volta, e pigliando spatio minore del corpo, ecco come và calando il mio braccio adesso, vedete, vedete? |
[58v.4] vedete, questo mandritto ch'io vi meno, v'offende nel principio, poi va calando tutta volta, & pigliando spatio minore del corpo. Ecco, come va calando il mio braccio adesso: | ||
[88r.6] CO. Si veggio. |
|||
[88r.7] ROD. Ma riguardate vi priego un poco à questo rovescio, che pel contrario và tutta via crescendo. |
[58v.5] ma riguardate, vi priego, un poco a questo rovescio, che per lo contrario va tutta via crescendo: | ||
[88r.8] CON. Fatevi in la ò Rodomonte. |
|||
[88r.9] ROD. Non dubitate; non vedete quanto si allonga adesso il braccio, e la spalla, tutto inalzandosi accrescendo di continuo la ferita, e facendo maggior effetto. |
[58v.6] non vedete quanto si allunga adesso il braccio, & la spalla, tutto inalzandosi, accrescendo di continuo la ferita, & facendo maggior effetto? | ||
CON: I see it. |
[88r.10] CO. Lo veggio. |
[58v.7] CON. Lo veggio. | |
ROD: In the mandritto, as you throw the right arm straight, the sword goes falling, and returning to you, and covers less ground in order to offend your adversary; but the rovescio does just the opposite. Look how it goes continuously, taking greater distance, and augmenting, how it prepares itself for the enemy; if therefore the rovescio covers greater ground in order to offend the enemy than does the mandritto, and if the blow that does thus must deserve precedence, then rationally the rovescio will precede the mandritto. But I give to you another reason: the rovescio commences from the right side of the enemy, which is more noble; and that blow is more offensive that offends the nobler parts; hence the rovescio would be more noble. |
[88r.11] RO. Nel mandritto, tirando il braccio destro verso voi và calando, e torna à voi la spada, et minor campo piglia per offendere l'avversario, mà il rovescio fà tutto l'opposito. Ecco, come di continuo và pigliando spatio maggiore, et crescendo, et come meglio accingesi all'inimico. Ma vi dò un'altra ragione, il rovescio comin= [88v.1] cia dalle parti destre del nemico, che sono piu nobili, et però è colpo piu offensivo, sendo le parti diritte piu nobili. |
[58v.8] ROD. Nel mandritto, tirando il braccio destro verso voi, va calando, & tornando a voi la spada, & minor campo piglia per offendere l'avversario: ma il rovescio fa tutto l'opposito. Ecco come di continuo va pigliando spatio maggiore, & crescendo, & come meglio accingesi al nimico: se dunque il rovescio piglia maggior campo per offendere il nimico che non fa il mandritto, & se il colpo che ciò fa; deve precedere; ragionevolmente il rovescio precederà il mandritto. Ma vi dò un'altra ragione; il rovescio comincia dalle parti destre del nimico, che sono piu nobili: & quel colpo è piu offensivo, che offende le parti piu nobili: dunque il rovescio sarà piu offensivo. | |
CON: Didn’t you say to me, that a man’s heart lies in the middle, and is inclined toward the left side? How then are wounds in the left side not more fatal than in the right? |
[88v.2] CO. Non mi diceste voi, che'l cuore dell'huomo sta nel mezo, e si piega al lato manco? Come non saranno adunque piu mortali le piaghe nelle parti sinistre, che nelle destre? |
[58v.9] CON. Non mi diceste voi, che il cuor dell'huomo stà nel mezo, & si piega al lato manco? come non saranno dunque piu mortali le piaghe nelle parti sinistre, che nelle destre? | |
ROD: I did tell you that the tip of the heart is inclined a little toward the left side, but do I not now assign the reason, saying that the right side is more noble, and of greater vivacity, and those offenses deprive it of vivacity and vigor? |
[88v.3] RO. Vi dissi, che la punta del cuore si piega un poco al lato manco, ma hora non v'assegno la ragione dicendo, che son piu nobili le dritte, e di maggior vivacità, et quelle offese, si perde la vivacità, et il vigore? |
[58v.10] ROD. Vi dissi, che la punta del cuore si piega un poco al lato manco, ma hora non v'assegno la ragione, dicendo che son piu nobili le diritte, & di maggior vivacità, & quelle offese, si perde la vivacità & il vigore? | |
CON: I understand you, but in fact I concede begrudgingly that the rovescio should be placed before the mandritto, and be of greater valor; it appears to me, rather, that the mandritto must have preceded the rovescio, because nature seems to offer it. |
[88v.4] CO. V'intendo, ma in fatti vi concedo mal volontieri, che il rovescio primo sia dil mandritto e di maggior valore; parmi pur che'l mandritto dovesse precedere il rovescio, perche la natura par che'l porga. |
[58v.11] CON. V'intendo, ma in fatti vi concedo mal volen= [59r.1] tieri, che'l rovescio prima sia del mandritto, & di maggior valore: parmi pure, che'l mandritto dovesse precedere il rovescio; perche la natura pare che lo porga. | |
The mandritto is superior to the rovescio naturally. ROD: I, too, know well that naturally the mandritto is superior, and more worthy than the sinister; the philosophers prove it, they place rather the East of the World, more noble than the West (being the right part), where they wish, as the Eastern heavenly influences have more strength than the Western; of the animals as well, the right sides are always more lively, and vigorous, and noble; but in the case of arms, the rovescio (as I told you) increases more, goes with greater vigor, offers more terror to the enemy, offends the nobler parts, and finally is more offensive. |
[88v.5] ROD. O'che voi, Conte, volete cedere alla ragione ò nò. So bene anch'io, che naturalmente il mandritto è primo, e piu degno del sinistro, lo provano i Philosofi, anzi che pongono l'Oriente del Mondo piu nobile dell'Occidente, sendo la parte destra dove vogliono, che habbiano piu vigore gl'influssi celesti Orientali de gli Occidentali: ne gli animali anchora le parti diritte sono sempre piu [89r.1] vive di piu vigore, e piu nobili: ma nel caso dell'arme il rovescio (come vi dico) cresce piu, va con maggior vigore, porge piu terrore al nimico, e finalmente è piu offensivo. |
Il mandritto è primo del rovescio naturalmente. [59r.2] ROD. Sò bene anch'io, che naturalmente il mandritto è primo, & piu degno del sinistro: lo provano i Filosofi, anzi che pongono l'Oriente del Mondo, piu nobile dell'Occidente (sendo la parte destra) dove vogliono, che habbiano piu vigore gl'influssi celesti Orientali, de gli Occidentali: ne gli animali anchora, le parti dritte, sono sempre piu vive, di piu vigore, & piu nobili: ma nel caso dell'arme il rovescio (come vi dico) cresce piu, va con maggiore vigore, porge piu terrore al nimico, offende le parti piu nobili, & finalmente è piu offensivo. | |
CON: It appears also that the mandritto goes to discover first the left side of the adversary, which is more mortal, and wounds it; and it seems to me also that it is propelled with greater force than is the rovescio, going through a more natural path, and in accord with the natural mode of the arm, and it is for many other additional reasons, Rodomonte, that I do not thus readily subscribe to this opinion of yours. |
[89r.2] CON. Pare anchora che'l mandritto vada à ritrovare prima le parti sinistre dell'avversario, che son piu mortali, e quelle ferisca, et parmi anco che sia sospinto da maggior forza che'l rovescio andando per piu natural sentiero, et secondo il moto naturale del braccio, et per molte altre ragioni anchora, si che non approvo cosi facilmente Rodomonte questa vostra openione. |
[59r.3] CON. Pare anchora che'l mandritto vada a ritrovare prima le parti sinistre dell'avversario, che son piu mortali, & quelle ferisca: & parmi anco che sia sospinto da maggior forza, che'l rovescio, andando per piu natural sentiero, & secondo il moto naturale del braccio, & per molte altre ragioni anchora, si che non approvo cosi facilmente (Rodomonte) questa vostra opinione. | |
Distinction that the mandritto may be more, and less noble than the rovescio. ROD: To the end that it will be conveyed to you, conte, I will say to you, making another distinction, that you can consider the blow in two ways: from the perspective of he who gives it, and from the perspective of he who receives it. If you consider from the perspective of the agent, the mandritto proceeds more naturally from the right side, and for this reason it will be nobler; if you consider it from the perspective of he who receives it, to him it will offend the more mortal parts, and thus you can call it your more worthy way; but we do not deal with this difficulty, and proceed otherwise I pray you; indeed I will also give you this reason, which I had not previously remembered: the rovescio, moreso than the offensive mandritto, offends the enemy in the right side, whereby it aids and defends one, and for this reason: it comes to pass that the mandritto offends the more mortal and weaker parts; it can be said to be more offensive; tell me, if with a rovescio you sever your enemy’s right arm, then what a defense it would be? |
[89r.3] RO. Alla fine sarà rimessa in voi Conte, et vi dirò facendo un altra distintione, che potete considerare il colpo in due modi. da chi lo fa, e da chi lo riceve. Se lo considerarete dall'agente, il mandritto procede piu naturalmente dal destro lato e per questa cagione sarà piu nobile. Se lo considerate in chi lo riceve gli offenderà le parti piu mortali e cosi lo potete chiamare à vostro modo piu degno, ma non facciamo in questo difficulta, et procediamo oltre di gratia: pur vi do questa ragione anchora, laquale non mi ramencavo, il rovescio offende piu del mandritto of= [89v.1] fensivo il nimico nelle parti destre con le quali esso s'aiuta, e si difende, et per questa ragione (avenga che il mandritto offenda le parti piu mortali, e piu deboli) si può dire piu offensivo. Ditemi se con un rovescio troncaste il braccio diritto del nimico, che difesa sarebbe egli poi? |
Distintione
che il
mandritto
sia piu,
& meno
nobile
del rovescio. [59r.4] RODO. Alla fine sarà rimessa in voi (Conte) & vi dirò, facendo un'altra distintione, che potete considerare il colpo in due modi: da chi lo fa, & da chi lo riceve. Se lo considerarete dall'agente, il mandritto procede piu naturalmente dal destro lato, & per questa cagione sarà piu nobile: se lo considerate in chi lo riceve, gli offenderà le parti piu mortali, & cosi lo potete chiamare à modo vostro piu degno: ma non facciamo in questo difficultà, & procediamo oltre digratia: pure vi dò questa ragione anchora, laquale non mi rammentava, il rovescio offende piu del mandritto offensivo il nimico nelle parti destre, con le [59v.1] quali esso s'aiuta, & si difende; & per questa ragione, avenga che'l mandritto offenda le parti piu mortali, & piu deboli; si può dir piu offensivo: ditemi, se con un rovescio troncaste il braccio dritto del nimico, che difesa sarebbe egli poi? | |
CON: I do not want to disagree with you anymore, Rodomonte; you indeed fashion your schermo with full valor and art. |
[89v.2] CON. Non la voglio piu contrastare Rodomonte con voi, fate pur quel vostro Schermo pieno di valore, et d'arte. |
[59v.2] CON. Non la voglio piu contrastare (Rodomonte) con voi; fate pur quel vostro schermo pien di valore, & d'arte. | |
ROD: Open well your ears, and watch how I do: place yourself, conte, in whatever guard you wish. |
[89v.3] RO. Aprite ben gli occhi, et vedete come faccio, ponetevi Conte sopra qual guardia volete. |
[59v.3] ROD. Aprite ben gli occhi, & vedete come faccio: ponetevi (Conte) sopra qual guardia voi volete. | |
CON: Look, I place myself in cinghiara porta di ferro. |
[89v.4] CON. Eccomi, che mi rassetto in cinghiara porta di ferro. |
[59v.4] CON. Eccomi che mi rassetto in cinghiara porta di ferro. | |
Only seven guards are necessary for this proposition. ROD: Oh, by your faith, conte, don’t give me these bizarre names of guards of yours, please abandon calling them your code lunghe distese, your falconi, porte de ferro larghe, o strette, and such strange fantasies, because as we make three main types of strikes, thus we discover only three main offensive guards, and three defensive ones, and one general one. |
[89v.5] RO. Deh per vostra se Conte non nominate questi vostri nomi bizarri di guardie lasciate di gratia di dire queste vostre code longhe distese, questi vostri falconi porte di ferro larghe ò strette e tante strane fantasie perche come facciamo tre principali specie di ferire cosi ritrovo solo tre principali guardie offensive, e tre difensive et una generale. |
Sette sono solamente le guardie necessarie a questo propofito. [59v.5] ROD. Deh per vostra se (Conte) non nominate questi vostri nomi bizarri di guardie, lasciate di gratia il dire queste vostre code lunghe distese, questi vostri falconi, porte di ferro, larghe, o strette, & tante strane fantasie, perche come facciamo tre principali spetie di ferire, cosi ritrovo solo tre principali guardie offensive, & tre difensive, & una generale. | |
CON: And how are they called? |
[89v.6] CO. Et come si chiameranno? |
[59v.6] CON. Et come si chiameranno? | |
Novel names imposed on the seven guards. ROD: The first is called “guardia difensiva, imperfetta”; |
[89v.7] RO La prima chiamerassi guardia difensiva imperfetta, la seconda guardia alta perfetta offensiva, la terza guardia alta imperfetta offensiva, la quarta guardia larga imperfetta difensiva, la quinta guardia stretta perfetta difensiva; La Sesta guardia larga [90r.1] imperfetta offensiva; La Settima guardia stretta offensiva perfetta. |
Nomi imposti novellamente alle sette guardie. [59v.7] ROD. La prima chiamerassi Guardia difensiva imperfetta: la seconda, guardia alta perfetta offensiva: la terza guardia alta imperfetta offensiva: la quarta guardia larga imperfetta difensiva: la quinta guardia stretta perfetta difensiva: la sesta guardia larga imperfetta offensiva: la settima guardia stretta offensiva perfetta. | |
CON: I don’t understand you, you seem to me to use some terms, and some names that are so outlandish, that I don’t believe they are of the art. |
[90r.2] CO. Maledetto sia pure quel poco ch'io me ne intenda; mi parete usare certi termini, e certi nomi tanto stravaganti, ch'io non credo siano nell'Calendario. |
[59v.8] CON. Io non v'intendo, mi parete usare certi termini, & certi nomi tanto stravaganti, ch'io non credo siano nell'arte. | |
ROD: This too I knew, conte, but did I not say to you, that for fighting between man and man, that this, my new imagination, and this, my schermo, would suffice you, in order to offend the enemy, as well as to defend yourself from him? |
[90r.3] RO. Questo sapevo anch'io, Conte, ma non vi dissi, che per combattere da huomo à huomo vi basteria questa mia nuova imaginatione, et questo mio schermo si per offender il nimico, come per difendersi da lui? |
[59v.9] RODO. Questo sapeva anch'io (Conte) ma non vi dissi, che per combattere da huomo a huomo, vi basterebbe questa mia nuova imaginatione, & questo mio schermo, si per offender'il nimico, come per difendervi da lui? | |
CON: You certainly did say it, but it will be necessary, Rodomonte, since you change the names used by so many Masters of Arms, first to begin to teach the significance of the terms. What do you mean by “guard”? Do you want perhaps to mean that which is meant by others? |
[90r.4] CO. Lo diceste per certo, ma sarà di bisogno Rodomonte, poi che mutate i nomi usati da questi tanti maestri d'Arme di cominciare ad imparare prima la significatione de i termini. Che cosa intendete per guardia? Volete intender forse quello, che intendono gli altri? |
[59v.10] CON. Lo diceste per certo: ma sarà di bisogno Rodomonte, poi che mutate i nomi usati da questi tanti Maestri d'Arme, di cominciar ad imparare prima la significa- [60r.1] tione de'termini. Che cosa intendete per guardia? volete intendere forse quello ch'intendono gli altri? | |
What a guard may be. ROD: Know you well, that lying calm and settled in some form with arms, either in order to offend or defend, that settlement, and that position, and that composition of the body in that guise, in that form, I call “guard”. |
[90r.5] RO. Ben sapete, lo star quieto, et agiato in qualche forma conn l'arme, ò per offendere, ò per difendere quello agiamento, e quel sito, e quella compositione di corpo in quella guisa, et in quella forma, chiamo io guardia. |
Che cosa sia guardia. [60r.2] ROD. Ben sapete; lo star quieto, & agiato in qualche forma con l'arme, o per offendere, o per difendere, quello agiamento, & quel sito, & quella compositione di corpo in quella guisa, in quella forma, chiamo io guardia. | |
CON: Can you not settle yourself with your right foot and with your right side advanced, more exposed to the enemy, and thus with the left foot and with the left side? And can you not form all those guards named by our Masters, and by the common school, and “guardia da entrare”, and “guardia di testa”, and “guardia stretta”, and “guardia larga”, and “becca cesa”, and all the others? |
[90r.6] CO. Sia lodato il cielo, non vi potete rassetar col pie destro, et con le parti vostre destre innanzi piu scoperte al nimico? |
[60r.3] CON. Non vi potete rassettar co'l pie destro, & con le parti vostre destre innanzi piu scoperte al nimico, | |
[90r.7] RO. Posso. |
|||
[90r.8] CO. Et cosi col pie sinistro, e con le parti sinistre? |
[60r.4] & cosi co'l pie sinistro, & con le parti sinistre? | ||
[90v.2] CO. Non possete voi dunque formare tutte quelle guardie nominate da i Maestri nostri, e dalla commune Schuola? et guardia da entrare, e guardia di testa, e guardia stretta, e guardia larga, e beccacesa, et le altre tutte? |
[60r.5] & non possete formar tutte quelle guardie nominate da' Maestri nostri, & dalla commune scuola; & guardia da entrare, & guardia di testa, & guardia stretta, & guardia larga, & becca cesa, & l'altre tutte? | ||
There can be nearly an infinity of guards. ROD: I can; rather there are an infinity of guards, conte, as there can be an infinity of settlements and positions; and it is true that each increment of space that you move the sword from high to low, or from low to high, from the forward to the rear, and the contrary, and from the right side to the left, and the contrary, and each little bit that you retire your foot from place to place, and in sum every infinitesimal movement forms diverse guards, which movements are without number or end. These Masters have, rather, placed names to those more necessary in order to have a way to be able to teach to their disciples with more facility, and having taken such names from some similarity or effect, from which whomever has well considered the semblances of the animals perhaps may have been able more appropriately to say “guard of the Unicorn”, “guard of the Lion”, and other such; but I, who am not a Master of a school, to you, who are not now my disciple, do not intend to give you to understand today all our exercises entirely for practice, but I will select only a schermo (as I said) with which, coming to blows with your enemy, or assaulted by him, or assaulting him, you can perfectly and preparedly strike him mortal wounds, and make a most secure defense from his; |
[90v.3] RO. Infinite sariano le guardie, Conte, si come infiniti possono essere gli agiamenti, et i siti, e che sia vero ogni poco di spaciò, che movete la spada d'alto à basso ò da basso ad alto, dallo innanzi all'di dietro, e pel contrariò dal diritto lato al manco, e per contrario, et ogni poco che ritirate il pie da luoco à luoco, et in somma ogni picciolissimo movimento vi forma guardia diversa, i quai movimenti possono esser senza numero, et fine. Hanno però questi mastri posto nome alle piu necessarie per haver modo di poter insegnare à i discepoli con piu facilità, et hanno pigliato tai nomi da qualche similitudine od effetto; onde chi bene havesse naturalmente considerato à somiglianza de gli animali havrebbe forse possuto piu propriamente dir guardia di Liocorno, guardia di Leone, et altri simili; ma io Conte valoroso, che non sono Maestro di Schuola, e voi [91r.1] non sete già mio discepolo, non intendo darvi ad intendere hoggi tutto l'essercitio nostro intieramente per gioco, ma scieglierò solo un schermo (come vi dissi) col quale venendo voi alle mani col vostro nemico, ò assaltato da lui, ò assaltando egli possiate perfettamente, et acconciamente ferirlo di piaga mortale, e dalle sue fare sicurissima difesa. |
Ponno essere le guardie quasi infinite. [60r.6] ROD. Posso; anzi infinite sarebbono le guardie (Conte) si come infiniti possono essere gli agiamenti, & i siti: & che sia vero, ogni poco di spatio che movete la spada d'alto a basso, o da basso ad alto, dallo innanzi al di dietro, & per contrario, & dal diritto lato al manco, & per contrario; & ogni poco che ritirate il pie da luogo a luogo, & in somma ogni piccolissimo movimento vi forma guardia diversa: i quali movimenti possono essere senza numero & fine. Hanno però questi Maestri posto nome alle piu necessarie per haver modo di poter insegnare a' Discepoli con piu facilità, & hanno pigliato tali nomi da qualche similitudine, od effetto: onde chi bene havesse naturalmente considerato la somiglianza de gli animali; havrebbe forse potuto piu propriamente dire guardia di Leocorno, guardia di Leone, & altri simili: ma io che non sono Maestro di scuola, a voi, che non siete già mio discepolo; non intendo dare ad intendere hoggi tutto l'essercitio nostro intieramente per gioco: ma sceglierò solo un schermo (com'io dissi) co'l quale venendo [60v.1] voi alle mani co'l vostro nimico, o assaltato da lui, o voi assaltando lui; possiate perfettamente, & acconciamente ferirlo di piaga mortale, & dalle sue far sicurissima difesa: | |
The names of the seven guards are taken both from their form and from their purpose. hence I set only seven guards, and these in order to name them conveniently are placed according to the form and the purpose of the guard; I designate offensive or difensive, according to the purpose; larghe, strette, or alte, according to the form; perfette or imperfette according to their perfection or imperfection. And if I wanted to show you today the entire art and the entirety of the mastery of arms, stating what are tempo, and mezo tempo, and contratempo; what are guards and how many there are, and how to form them all; how many ways of striking there are, and all the blows, which ones offending and which defending; with how many kinds of arms one can combat, and the protections and advantages that are in each one of them, when one is on foot and on horseback; how many prese there are, and how to form them; and in sum all the military exercises, not only would I not know how to do so easily, but moreover I could not do it in the space of a year. |
[91r.2] La onde pongo solo sette guardie, e quelle per nomi convenienti pigliati dalla forma e dal fine di essa guardia chiamo offensive, ò difensive secondo il fine, larghe, strette, od alte, secondo la forma, perfette od' imperfette, secondo la perfettione, o imperfettione sua. Et s'io volessi mostrarvi hoggi l'arte tutta, e tutto il magistero delle arme dichiarandovi, che cosa sia tempo, et mezo tempo, che sia guardia, et quante sieno, e formarle tutte, quanti sieno i modi di ferire, et i colpi tutti, quali offendono, et quali difendano, con quante sorte d'armi si può combattere, e li schermi che sono in ciascuna di esse, si à piedi, come à Cavallo, quanto sieno le prese, e tutte formarle, et in somma tutto l'essercitio Militare, oltra ch'io facilmente non lo saprei, non lo potrei fare [91v.1] anchora in ispacio d'un anno; hor guardate se in meza hora gia passata si potesse. |
I nomi
delle sette
guardie
sono tolti
altri dalla
forma,
& altri
dal fine loro. [60v.2] la onde pongo solo sette guardie, & quelle per nomi convenienti pigliati dalla forma, & dal fine di essa guardia; chiamo offensive, o difensive, secondo il fine, larghe, strette, o alte, secondo la forma; perfette o imperfette, secondo la perfettione, o imperfettion sua. Et s'io volessi mostrarvi hoggi l'arte tutta, & tutto il magistero delle arme, dichiarandovi che cosa sia tempo, & mezo tempo, & contratempo; che sia guardia, & quante siano, & formarle tutte; quanti siano i modi di ferire, & i colpi tutti; quali offendono & quali difendono; con quante sorti d'arme si puo combattere, & gli schermi, & gli avantaggi che sono in ciascuna di esse, si a piedi come a cavallo; quante siano le prese, & tutte formarle; & in somma tutto l'essercitio militare, oltra ch'io facilmente non lo saprei, non lo potrei far anchora in ispatio d'un'anno. | |
CON: At least tell me now what advantage is, and what tempo is. |
[60v.3] CON. Almeno ditemi per hora che cosa è avantaggio, & che cosa è tempo. | ||
ROD: You have to know, conte, the advantage now can be considered to be in settling yourself in guard, in the striking, and in the stepping. Accordingly it may be said that you settle yourself in guard with advantage when the point of your enemy’s sword is outside your body and not aimed at you, and when the point of your sword is aimed at the body of your enemy in order to offend him, so that you may, in such fashion, easily offend him, and it will be difficult for him to defend himself from you; consequently you will be able to strike him in little time, and in order to defend himself, he will require more time; and conversely, he will find it difficult to offend you, and you will be able to easily defend yourself from him for the selfsame reason, he having need of much, and you of little time. |
Che cosa sia il por si in guardia con avantaggio. [60v.4] ROD. Voi havete a saper Conte, che l'avantaggio per hora si puo considerare nel rassettarsi in guardia, nel ferire, & nel passeggiare. Allhora si dice che voi vi rassettate in guardia con avantaggio, quando la punta della spada del nimico è fuori della vita vostra & non vi guarda, & quando la punta della spada vostra guarda la vita del nimico per offenderlo: percioche voi in tal maniera potrete facilmente offender lui, & esso difficilmente potrà da voi difendersi; poi che in poco tempo potrete voi ferirlo, & a lui per difendersi, bisognarà piu tempo; & per lo contrario potrà egli difficilmente offender voi: & voi potrete facilmente da lui difendervi per la medesima cagione, ha- [61r.1] vendo egli bisogno di molto, & voi di poco tempo. | ||
CON: This (I believe) one could quite well do, if the enemy were not intent upon this exercise. But if he shrewdly did not allow me to place myself in guard with advantage, what would I have to do? |
[61r.2] CON. Questo (credo io) si potrebbe benissimo fare, quando il nimico non fosse intendente di questo esercitio. Ma se egli accorto non mi lasciasse porre in guardia con avantaggio, che cosa dovrei io fare? | ||
Advisement should the enemy not allow one to place oneself in guard with advantage. ROD: I would like you to step, vaulting at him diagonally, and wearying him continuously, now with a mezo mandritto, and now with a mezo rovescio, and often with a variety of feints, taking heed nonetheless always to keep your body away from the point of his sword, because he could easily give you the time and the occasion to seize the advantage of placing yourself in guard. |
Avertimento
se
il nimico
non lasciasse
porsi in
guardia
con avantaggio. [61r.3] RO. Vorrei, che voi passeggiaste, volteggiandolo per traverso, & attediandolo di continuo, hor con un mezo mandritto, & hor con un mezo rovescio, & spesso con varie finte; avertendo però sempre di levar la persona vostra dalla punta della sua spada, perche potrebbe egli facilmente darvi il tempo & l'occasione, da prendere voi l'avantaggio nel porvi in guardia. | ||
CON: And if he were to weary me with similar feints and half blows, what would I have to do? |
[61r.4] CON. Et s'egli attediasse me con simili finti & mezi colpi, che devrei fare? | ||
That which would have to be done if the enemy wearies one with feints and half-blows. ROD: You would have to retire backwards one or two steps; as a result, he would not be able to strike you, being thus unable to reach you, and you would have to step so that the mind of the adversary would be baited by the proposition that he might accomplish the striking of you, and the way that it were determined; because at all times the variation of your body with the stepping also causes a change in the thought and the plan. But always remain attentive in the stepping to seize the opportunity to place yourself in guard with the advantage of the sword. |
Quello si
debba fare
se il nimico
atte
diasse con
finti &
mezi colpi. [61r.5] ROD. Voi havete a tirarvi indietro uno, o due passi; accioche egli non possa ferirvi, non potendo cosi giungervi; & devete passeggiare, accio che esca di mente all'aversario il proposito che esso havea fatto di ferirvi, & il modo che si era determinato: perche spesse volte il variamento della persona co'l passeggiare fa anco variare il pensiero & il disegno. Ma sempre state avertito nel passeggiare di prendere occasione di porvi in guardia co'l vantaggio della spada. | ||
CON: What, then, is the advantage in the strike? |
[61r.6] CON. Qual'è poi l'avantaggio nel ferire. | ||
What would be advantageous in the strike from its perspective. ROD: Bear in mind to never try to strike unless when you throw the blow you can reach the enemy with a half step, or at most a step. |
Qual sia avantaggio nel ferire dal canto di se stesso. [61r.7] ROD. Havete d'avertire che mai non tentiate di ferire se non quando potete nel colpire giungere il nimico con un mezo passo, o al piu con un passo. | ||
CON: And why is that? Could I not still try although I could reach him in two steps? It seems to me that it still wounds, that it doesn’t have to lose time. |
[61r.8] CON. Et per che questo? Non potrei anco tentare pur che potessi giungerlo in piu passi? a me pare pur che si ferisca, che non si deve perder tempo. | ||
When one strikes, one must not regard his own point, but that of his enemy. ROD: If you always want to attempt to throw blows when you still cannot reach your enemy without more steps, then you will spend too much time in throwing them, and give too much of it to the enemy in order to be able to shun your blow, and simultaneously to strike you, because you would overly disconcert yourself needing to move yourself from that distance between you. But when you can close with a step, and with half of one, you will not disconcert yourself, and you will strike quickly, without giving the enemy time to protect himself. Then you will have to pay attention that when you strike, you do not look to the point of your own sword, but rather to that of your enemy. |
Quando si ferisce non si deve guardare alla punta della sua spada, ma a quella del nimico. [61r.9] ROD. Se sempre voleste tentare di colpire, quando anco non poteste aggiungere il nimico, se non con piu passi; troppo tempo spendereste voi nel colpire, & troppo ne dareste al nimico da potere schifar il colpo, & insieme da ferir voi; per- [61v.1] che vi disconcertareste troppo, bisognando movervi di si lontano. Ma quando potete giungere con un passo, e con mezo; voi non vi sconcertate, & presto ferite, senza dar tempo al nimico di ripararsi. Poi devete avertire, che quando ferite, non guardiate alla punta della spada vostra, ma a quella del nimico. | ||
CON: It seems to me that if I want to strike it is necessary that I look to the place where the enemy is exposed, otherwise I would throw the blow without doing him any harm, and that if I have to look to where I must thrust the point of my sword, it is necessary that I regard it as well. |
[61v.2] CO. A me pare che se voglio ferire bisogna ch'io veggia il luogo, dove il nimico si scopre, che altrimenti colpirei senza sua offesa, & che se debbo vedere ove ho da cacciar la punta della spada mia; bisogna anco che io la guardi. | ||
Advantage in the strike from the perspective of the enemy. ROD: It is indeed necessary to look to where the enemy is exposed, because it is to there that the blow must be thrown; but it is necessary to throw the blow without looking to one’s own sword; and with the speed of eye necessary to a good warrior, one can in the selfsame time see the place where the enemy is exposed, and regard the point of the enemy’s sword. Know you well, then, that greater damage can come to you from being offended than can easily come to you from being on the offense, and therefore it is necessary to pay attention to the sword of your enemy in order to be able to defend, reserving yourself for a better time to offend him. Therefore, conte, from your perspective you have the advantage in the strike when you can hit in one step, or half of one; and from the perspective of your enemy, when he would try some blow without being able to reach you, or being able to reach you in more steps, because he, in disconcertedly attempting his blow, or in the elevation of his sword, will give to you time in which to strike him, and similarly, when he, not having regarded the point of your sword, will give to you occasion to offend him. |
Avantaggio nel ferire dal canto del nimico. [61v.3] RODO. E'ben nccessario guardare ove il nimico si scopre, perche ivi si deve colpire: ma si può colpire senza guardare alla propria spada, & per la velocità dell'occhio necessaria al buon guerriero; si puo in un medesimo tempo vedere il luogo ove il nimico si scopre, & guardare la punta della nimica spada. Poi sapete bene che puo venirvi maggior danno dall'essere offeso, che non può venirvi utile dall' offendere; & per ciò bisogna avertire alla punta della spada del nimico per potervene difendere, riservandovi a miglior tempo l'offender lui. Dunque, Conte, dal canto vostro havrete avantaggio nel ferire, quando potrete colpire in un passo, o in mezo: & dal canto del nimico prenderete l'avantaggio, quando esso vi trarrà qualche colpo senza potervi giungere, o giungendovi in piu passi: perche egli nel suo trarre il colpo sconcertatamente, o nell'alzar la sua spada; vi darà tempo di ferirlo; & similmente quando esso, non havendo risguardo alla punta della spada vostra; vi darà occasione di offenderlo. | ||
CON: This seems true to me; because he cannot already strike me before his sword connects with my body, and that if my sword reaches his body sooner, then he will be wounded sooner. But then, given that you have said to me that the advantage may be in placing oneself in guard, and in striking, tell me in addition what there may be in stepping. |
[61v.4] CON. Questo mi par vero; perche egli non può già ferirmi prima che aggiunga alla vita mia la sua spada; che se piu tosto giungerà la spada mia alla persona sua; piu tosto anco verrà egli ferito. Ma [62r.1] poi che mi hanete detto qual sia l'avantaggio nel porsi in guardia, & nel ferire; ditemi anco qual sia nel passeggiare. | ||
Advantage in the stepping from the perspective of the enemy. ROD: Briefly I tell you that when the enemy, in stepping, lifts his left foot in order to move a step, that he is then a bit discommoded, and then you can strike him with ease, and again change guard without fear, because he is intent on the other; and this is from the perspective of the enemy. |
Auantaggio nel passeggiare dal canto del nimico. [62r.2] ROD. Brevemente vi dico; che, quando il nimico nel passeggiare alza il piede per movere il passo, allhora egli si discommoda alquanto, & allhora voi agiatamente potete ferirlo, & anco mutare guardia senza timore, perche egli è intento ad altro; & questo è quanto dal canto del nimico. | ||
Advantage in the stepping from one’s own perspective. From your perspective, then, when you are stepping, approaching the enemy, and go closing the step, then you have much advantage; for as much closer as you are with your feet, you will have that much more force in your blows, and in your self defense, and otherwise accordingly will you be able to close with your enemy in less time. |
Auantaggio nel passeggiare dal canto di se stesso. [62r.3] Dal canto vostro poi, quando voi passeggiando vi accostarete al nimico, & andarete stringendo il passo, allhora havrete molto avantaggio: per ciò che quanto piu siete stretto co'piedi; tanto piu havete forza nel colpire, & difendervi, & oltre di ciò potete giungere il nimico con minor tempo. | ||
Which is the greater advantage: to go to encounter the enemy or to wait for him. CON: Tell me, Rodomonte, give me advice, how should I go when I want to close the distance with my enemy; which is the greater advantage: to go to encounter him, or to wait for him? |
Qual sia maggior vantaggio andare a trouare il nimico o aspettarlo. [62r.4] CON. Ditemi Rodomonte, voi mi date avertimento, come debba andare quando voglio appressarmi al nimico: Qual'è maggior vantaggio, andare a ritrovarlo, o aspettarlo? | ||
ROD: All the answer to this question is reduced to you being in advantage, and the enemy in disadvantage, because if you go in tempo, such that you are in disadvantage of the sword, and your enemy is in advantage of guard, your going would undoubtedly be worse; but if it were the contrary, it would certainly be better. |
[62r.5] ROD. Tutta la risolutione di questa dimanda si riduce all'essere voi in avantaggio, & il nimico in disavantaggio; perche se andaste in tempo, che voi sete in disavantaggio della spada, & il nimico fosse in vantaggio di guardia; sarebbe senza dubbio peggiore il uostro andare: ma se foste per lo contrario; migliore sarebbe di certo l'aspettare. | ||
CON: I do not doubt this, but I want to learn when one and the other were of advantage, and what would be the case were all else equal. |
[62r.6] CON. Non dubito io di questo; ma io voglio intendere quando l'uno, & l'altro fossero in avantaggio, & che il caso fosse in stato pari. | ||
ROD: One never strikes safely if not during the disadvantage of the enemy; therefore it seems impossible to say that both may have the advantage, and be in equal conditions. Indeed because you ask not of throwing a blow, but of going to encounter the enemy, I would say that it is better to wait; because he who would go discommodes himself, and the moving of his body often moves the spirit as well; and who stands firm does not receive discommodity, neither by change of body nor of spirit; hence it appears that when both the one and the other could have advantage, that the lesser advantage would always be to whom would go to encounter his enemy; and that when the both could be of disadvantage, the lesser disadvantage would always be to that one who waits for the adversary, and so much more so if he who waits knows to maintain himself in guard. |
[62r.7] ROD. Non si ferisce mai sicuramente se non in disavantaggio del nimico; & però pare impossibile dire, che amendue siano in avantaggio, & in stato pari. Pure perche dimandate non del colpire, ma dell'andare a ritrovar l'aversario, io direi, che fosse meglio aspettare: perche chi và, si discommoda, & il moversi co'l corpo fa spess- [62v.1] so anco movere l'animo; & chi sta fermo non riceve discommodità ne mutatione di corpo, ne di animo: onde pare che, quando anco l'uno & l'altro potessero essere in vantaggio, sarebbe sempre minore il vantaggio di chi và a ritrovare il nimico; & che quando amen due potessero essere in disavantaggio, sarebbe sempre minore il disavantaggio di colvi che aspetta l'aversario, & tanto piu se chi aspetta saprà mantenersi in guardia. | ||
Which is better, either to be the first to strike, or to wait for the enemy to strike. CON: If this is true, speaking of going to encounter the enemy, what then do you say of striking? Is it better to wait for the enemy to strike, or for him to be the first to throw a blow? |
Qual sia meglio ò essere il primo à ferire, ò aspettare che il nimico ferisca. [62v.2] CON. Se questo è vero parlandosi dell'andare a ritrovare il nimico, che direte poi del ferire? è meglio aspettare che il nimico ferisca, o essere egli il primo a colpire? | ||
ROD: It is better to wait for the enemy to strike. |
[62v.3] ROD. E meglio aspettare, che il nimico ferisca. | ||
CON: It seems to me rather to be the opposite; because when I will be the first to strike it necessitates the enemy to defend himself, and while he pays attention to his defense, he cannot devote attention to offending me. |
[62v.4] CON. Anzi a me pare il contrario: perche quando io sarò il primo a ferire bisognerà che il nimico si difenda, & mentre che egli attenderà alla difesa, non potrà attendere all'offendere me. | ||
ROD: This reason of yours would be valid if while one defended oneself one was not still able to offend; but such is discovered to be false of many defenses, which are able to be offenses as well, among which we can place our schermo, which is a single parry, a single strike, and a single time. |
[62v.5] ROD. Valerebbe questa ragion vostra, se mentre si difende non si potesse anco offendere: ma ciò è falso ritrovandosi molte difese, che insieme possono essere offese, tra lequali possiam riporre il nostro schermo, ch'è un parar solo, un ferir solo, & un tempo solo. | ||
CON: Why do you say thus to me, that it is better to wait, that the enemy be the first to strike? |
[62v.6] CON. Perche dunque dite, che sia meglio aspettare, che il nimico sia il primo a ferire? | ||
ROD: Because he who strikes first, uncovers himself first, and uncovering himself, cannot in the same time cover himself; hence, when your adversary uncovers himself, you can seize the opportunity to strike him; and if you are shrewd, you may also, passing a step diagonally, hit the enemy in the same time. Besides which, if you uncover yourself much, it is better to do so in guard than while striking; because in guard you can more conveniently recover yourself, but when you throw a blow you are entirely intent on hitting. And then, if you consider well, while the adversary strikes, of course he either somewhat raises, or somewhat lowers his sword, in which time he often removes his sword from your presence, and consequently rests in disadvantage; for which reason you can say that it is advantageous to wait for the enemy to be the first to throw a blow. |
[62v.7] ROD. Perche, chi prima ferisce, prima si scopre, & scoprendosi, non può nel medesimo tempo coprirsi: onde voi quando l'aversario vostro si scopre, potete prendere opportunità di ferirlo, & se foste accorto, potreste anco, passando per traverso un passo colpire nel medesimo tempo del nimico. Oltra che se ben voi vi scopriste anco, meglio è scoprirsi in guardia che ferendo; perche in guardia siete piu commodo a ricoprirvi, & quando colpite siete tutto intento a ferire. Et poi, se considerate bene, mentre l'aversario ferisce, è forza ch'egli alzi alquanto in alto, o al- [63r.1] quanto abbassi la spada, nel qual tempo spesso rimove dalla presenza vostra la spada sua, & per consequente resta in disavantaggio: per lequali ragioni potete dire, ch'è avantaggio l'aspettare che il nimico sia primo a colpire. | ||
CON: I rest very satisfied by such as you have said to me concerning wherein may lie the advantage in placing oneself in guard while striking and stepping; now I wish to know what tempo is, and what is signified to us by saying a “tempo” and a “mezo tempo”. |
[91v.6] CO. Che domin'è questo tempo? e che cosa vogliano significare noi dicendo, un tempo, un mezo tempo? |
[63r.2] CON. Resto molto sodisfatto di quanto mi havete detto circa a che cosa sia il vantaggio nel porsi in guardia nel ferire, & nel passeggiare; | |
ROD: It is a great controversy among the philosophers, in viewing the nature of tempo, and it is difficult to comprehend, and better to inquire about it of Bocadiferro, now that we come to it. |
[91v.7] ROD. E'gran controversia trà Filosofi, in veder la natura del tempo, et è difficile à comprenderlo. |
[63r.3] hora desidero sapere che cosa sia tempo, & che vogliano significar noi dicendo un tempo, & un mezo tempo. | |
[91v.8] CO. Ne'domandaremo poi: ma ecco il Boccadiferro. |
[63r.4] ROD. E' gran controversia tra i Filosofi, in veder la natura del tempo, & è difficile a comprenderlo, | ||
CON: O Dottore, what do you understand about tempo, and what it is? |
[91v.9] O'Dottore, che cosa intendete voi per tempo, e, che cosa è égli? |
[63r.5] & è meglio dimandar ne al Boccadiferro che hora se ne viene. | |
Definition by the philosophers of “tempo”, and its manifestation. BOC: It will be difficult to understand it, Signor conte; the philosophers say that tempo is measured in motion, and in rest, according to earlier and later; and more intelligently, I say to you, that a body which moves itself, moves itself from one place in order to travel to another; the place from whence it departs is one end of that journey, and the motion is the other end; now divide that journey and that path into two equal parts through the middle; the first half toward the end from whence it departs is called the first part; the other half is called the final part; this consideration of the first and second part (that is to say, earlier and later) in the discourse of our spirit, the philosophers call “tempo”, where the numbering of the parts of the successive motion is tempo. |
[91v.10] BOC. Sarrà difficile à capirlo Signor Conte. I philosophi dicono, che'l tempo è misura del moto, e'della quiete, secondo prima, et poi. |
Diffinitio ne filosofi ca del tempo & sua dichiaratione. [63r.6] CON. O Dottore che cosa intendete voi per tempo, & che cosa è égli? | |
[92r.2] BOC. Vi dirò; un corpo si muova muovesi da un luogo per gire in un altro, il luogo donde si parte è un termine di quello spatio, che fa il corpo mobile, il luogo poi dove giunge, et finisce lo spatio, et il moto e'l altro termine; hor dividete quello spatio, e quel camino in due parti eguali per mezo; la prima metà verso il termine d'onde si parte chiamassi prima parte, l'altra metà, si chiama parte ultima, questa tale consideratione di questa prima, e seconda parte, cio è prima, et poi nel discorso dell'anima nostra chiamano essi philosophi tempo dove la dinumeratione delle parti del moto successivo, è tempo. |
[63r.7] BOC. Sarà difficile a capirlo, Signor Conte: i Filosofi dicono che il tempo è misura del moto, & della quiete, secondo prima & poi: | ||
[92r.3] CO. Non la piglierei in cent'anni. |
|||
[92r.4] BOC. Questo aviene, perche non havete i principii. |
|||
CON: For what reason is it not recognized during sleep? |
[92r.5] CO. Perche cagione nel sonno non si conosce? |
[63r.8] & per piu intelligenza, dicovi, che un corpo che si mova, muovesi da un luogo per gire in un'altro, il luogo donde si parte, è un termine di quello spatio, che fa il corpo mobile: il luogo poi dove giunge, & finisce lo spatio, & il moto; è l'altro termine: hor dividete quello spatio, & quel camino in due parti eguali per mezo: la prima metà verso il termine, donde si parte, chiamasi prima parte, l'altra metà si chiama parte ultima: questa tale consideratione di questa prima, & seconda parte (cioè prima & poi) nel discorso dell'anima nostra chiamano essi Filosofi tempo, dove la numeratione delle parti del moto successivo è tempo. | |
[92r.6] BOC. Se non intendete la natura del tempo, ditemi voi, come capirete la cagione? |
|||
[92r.7] CO. Ditela pur, ò capirla ò no. |
|||
Why during sleep tempo is not recognized. BOC: Because when the external senses are bound (sleep being nothing other than a binding of all the external senses) we do not comprehend motion, and consequently tempo is not recognized, which is an occasion inseparable from motion, or to say it better, it is the same motion according to other considerations; whereupon reaching the first instant, the first beginning of the tempo of sleep, to the last instant, the sleep ends, it not being possible to understand the tempo mezo, |
[92r.8] BOC. Perche sono legati i sensi esteriori (altro non è il sonno, che un legame di tutti gli esterni sensi, non comprendiamo il moto e conseguentemente non si conosce il tempo ilquale è accidente [92v.1] inseparabile dal moto ò per dir meglio, e esso istesso moto secondo altra consideratione dove congiungendo il primo instante primo principio del tempo del sonno, all'ultimo instante fine di esso sonno, non si puo comprender il tempo mezo, |
Perche nel sonno non si conosca tempo. [63r.9] CON. Perche cagione nel sonno non si conosce? [63v.1] moto, o per dir meglio, è esso istesso moto secondo altra consideratione: dove congiungendo il primo instante, primo principio del tempo del sonno, all'ultimo instante, fine d'esso sonno, non si può comprender'il tempo mezo, | |
When in dreams it is possible to understand tempo. except when the imagination works and creates dreams, as in respect of that motion; then is understood tempo, and then the understanding grasps tempo to the extent of movement in that dream. |
[92v.2] eccetto però quando l'imaginativa lavora, et fa l'insogno; che per rispetto di quel moto alhora si comprende il tempo, e tanto dura la cognitione del tempo quanto il movimento di quel sogno. |
Quando nel sonno si possa conoscere il tempo. [63v.2] eccetto però quando l'imaginativa lavora & fa il sogno, che per rispetto di quel moto; all'hora si comprende il tempo, & tanto dura la cognitione del tempo, quanto il movimento di quel sogno. | |
[92v.3] RO L'havete voi anco inteso Conte? |
|||
[92v.4] CO Meno che prima. |
|||
Chivalric declaration of what tempo is in strikes. ROD: I see that the conte does not understand well; and therefore in order to give it to him perhaps to understand, speaking chivalrically: you see, conte, the philosophers have proven that prior to a body moving itself it will remain at rest, and ceasing its motion again remains at rest; so that a motion (provided that it be single) will lie in the middle of two rests. |
[92v.5] ROD. Con sopportatione (Dottore) glie lovo dare ad intendere io per quello, che chiamiamo noi tempo, e sodisfarò al suo secondo quesito insieme. Udite Conte, essi philosophi hanno provato, che innanzi, che un corpo si muova stava in quiete, e cessando il moto anchora stà in quiete, di modo ch'un moto, pure che sia un solo, stà nel mezo di due quieti. |
Dichiaratione cavalleresca che cosa sia tempo nel ferire. [63v.3] ROD. Io conosco che il Conte non ben da intende: & però glie la darò io forse ad intendere, cavallerescamente parlando: udite Conte, essi Filosofi hanno provato che innanzi ch'un corpo si muova stà in quiete, & cessando il moto anchora stà in quiete; di modo ch'un moto (pur che sia un solo) stà nel mezo di due quieti. | |
BOC: In the Seventh and Eighth Physics Aristotle proved it; Rodomonte speaks the truth. |
[92v.6] BOC. Nel settimo, et ottavo della Phisica l'ha provato Aristotile; dice il vero Rodomonte. |
[63v.4] BOC. Nel settimo, & ottavo della Fisica l'ha provato Aristotile: dice il vero Rodomonte. | |
[92v.7] RO. Lasciatemi dir di gratia Dottore, et perdonatemi. |
|||
[92v.8] BOC. A'me farete piacere. |
|||
ROD: I have heard it said by physicians that the motion of the pulse as well lies in the middle of two rests; is it not so, Dottore? |
[92v.9] ROD. Ho udito dir da Medici, che il mo- [93r.1] to del Polso anchora stà in mezo a due quieti, non è vero Dottore? |
[63v.5] ROD. Ho udito dire da'Medici, che il moto del polso anchora stà in mezo a due quieti, non è vero Dottore? | |
BOC: So proves Galen, and claims to have endured great labor for a long time in order to discern by touch the motion of the pulse when it lowers and raises, and divides itself into systole and diastole, that is to say into elevation and depression. |
[93r.2] BOC. Lo prova Galeno, et dice haver durato gran fatica longo tempo in discernere col tatto il moto del polso quando s'abbassa si sommerge, e dividono quel moto in sistole, et Diastole, cio è in elevatione, & depressione. |
[63v.6] BOC. Lo prova Galeno, & dice haver durato gran fatica lungo tempo in discernere co'l tatto il moto del polso quando si abbassa, & si eleva, & dividono quel moto in sistole, & diastole, cioè in elevatione, & depressione. | |
Between two blows lies a guard, and between two guards, a blow. ROD: All right, it suffices that each motion that is single and continuous lies between the preceding and subsequent rest; look, then, conte: before you throw a mandritto, a rovescio, or a punta, you are in some guard; having finished the blow, you find yourself in another guard; that motion of throwing the blow is a tempo, because that blow is a continuous motion; thus the tempo that it accompanies is a single tempo; when you rest in guard, having finished that motion, you find yourself once again at rest; it is therefore a tempo, a motion, which instead of calling a “motion”, we call a “tempo”, because the one does not abandon the other; and the guard is the rest and the repose in some place and form. In conclusion it is as much to say “tempo” and “guard”, as it is to say “motion” and “rest”. Whereby it is necessarily so, that as between two motions there is always a rest, and between two rests there is interposed a motion, apparently between 59 two thrown blows, or two tempos, or two motions, is found a guard. And between two guards, or rests (as you wish to say) are interposed some blow and tempo. |
[93r.3] ROD. Horsù basta, ch'ogni moto, che sia uno, et continuo giace tra la precedente, et susseguente quiete, hor ecco Conte avanti, che meniate un mandritto, un rovescio, ò una punta voi sete posto sotto qualche guardia finito ch'avete il colpo vi ritrovate sopra un'altra guardia, quel moto di menare il colpo è un tempo; perche quel colpo è un moto continuato, cosi il tempo che l'accompagna è un sol tempo, quando restate in guardia finito quel moto, vi ritrovate un'altra volta in quiete è dunque un tempo, un moto, ch'in vece di chiamarlo moto lo chiamiamo tempo; perche l'uno non abbandona l'altro, et la guardia è la quiete et il riposo sopra qualche sito et forma: In conclusione tanto viene à dir tempo, et guardia, quanto moto et quiete. Dove è di necessità che come sempre [93v.1] trà due moti che vogliamo dire si ritrovi una guardia, e tra le due quiete s'interpone un moto. Parimente tra due colpi menati ò due tempi ò due moti si ritrovi una guardia, e tra due guardie ò quieti come dir volete v'interpongasi un qualche colpo e tempo, |
Tra due colpi stà una guardia, & tra due guardie un colpo. [63v.7] ROD. Horsu basta ch'ogni moto che sia uno, & continuo; giace tra la precedente, & susseguente quiete: hora ecco (Conte) avanti che meniate un mandritto, un rovescio, o una punta, voi siete posto sotto qualche guardia: finito ch'havete il colpo; vi ritrovate in un'altra guardia: quel moto di menar il colpo, è un tempo: perche quel colpo è un moto continuato, cosi il tempo che l'accompagna, è un sol tempo: quando restate in guardia, finito quel moto, vi ritrovate un'altra volta in quiete: è dunque un tempo, un moto, ch'in vece di chiamarlo moto, lo [64r.1] chiamiamo tempo, perche l'uno non abbandona l'altro; & la guardia è la quiete, & il riposo sopra qualche sito, & forma. In conclusione tanto viene à dire tempo, & guardia, quanto moto, & quiete. Dove è di necessità, che come sempre tra due moti è una quiere, & tra due quieti s'interpone un moto; parimente tra due colpi menati, o due tempi, o due moti, si ritrovi una guardia. Et tra due guardie, o quieti (come dir volete) vi si interponga un qualche colpo, & tempo. | |
What is a full tempo and mezo tempo in striking. Thus a full tempo is a full perfect blow, because that would be a perfect motion and tempo. And a mezo tempo would then be (as you said) a mezo rovescio, a mezo mandritto. And every bit of movement of the body is called a mezo tempo; and if you see it said sometimes that one strikes in mezo tempo, do not believe nevertheless that this is always true; because now one strikes with a full blow, in full tempo, and now one strikes with a half blow, in mezo tempo; |
[93v.2] un tempo intiero è un colpo perfetto et intiero, perche quello sarà un moto, et un tempo perfetto: Un mezzo tempo sarà poi come diceste un mezo rovescio, un mezo mandritto. Et ogni poco di movimento della persona chiamasi mezo tempo. |
Che cosa sia nel serire tempo intiero & mezo tempo. [64r.2] Cosi un tempo intiero è un colpo perfetto, & intiero: perche quello sarà un moto, & un tempo, perfetto; & un mezo tempo sarà poi (come diceste) un mezo rovescio, un mezo mandritto: Et ogni poco di movimento della persona chiamasi mezo tempo: & se udite tal volta dire, che si ferisce in mezo tempo; non crediate però che questo sia sempre vero: perche hora si ferisce con colpo intiero, intempo intiero; & hora si ferisce con mezo colpo, in mezo tempo; | |
One does not always strike in mezo tempo, but does so the majority of times. it is true, that the majority of striking is in mezo tempo, it being necessary that when there are two well-schooled in the art, he who wishes to strike deceives his companion in the fashion that when the adversary is about to make a blow, he must enter with dexterity and speed, and strike in the middle of the blow of the adversary, with his half blow; hence we can say, that the majority of times the strike will be in mezo tempo with a half blow. |
Non sempre
si serisce
inmezo tempo,
ma il
piu delle
volte. [64r.3] è vero, che per lo piu si ferisce in mezo tempo, sendo di necessità, che quando sono due intelligenti dell'arte; chi vol ferire, inganni il compagno in modo, che quando l'aversario cerca di fare un colpo; egli deve con destrezza, & prestezza entrare, & ferire in mezo al colpo dell'aversario, co'l suo mezo colpo: onde possiam dire, che il piu delle volte il ferire sia in mezo tempo con mezo colpo. | ||
[93v.3] BOC. In fatti sete pure un grand'huomo Rodomonte. |
|||
A blow gives rise to a guard, and a guard to a blow. CON: I believe that I understand it now, when you say to me that between two blows is found a guard, and between two guards a blow; whence perhaps derives that which you say, that each blow gives rise to a guard, and that each guard gives rise to a blow. |
[93v.4] CO. Adesso la intendo, di qui forse nasce quello, che si dice, ch'ogni colpo partorisce una guardia, e ch'ogni guardia partorisce un colpo. |
Un colpo partorisce una guardia, & una guardia un colpo. [64r.4] CON. Credo hora d'intenderla, & quando mi dite che tra due colpi si ritrova una guardia, & tra due guardie un colpo; di qui forse nasce quello che si dice, che ogni colpo partorisce una guardia, & ch'ogni guardia partorisce un colpo. | |
From a particular guard is commodiously generated a particular blow, and not another. ROD: Thus it is, more or less saying that following each blow one finds oneself in some guard, and that following the guard, the blow succeeds it. And as the rest of a particular motion is different from the rest of another varying motion (since these are the natural dispositions which they desire) thus a guard is apt to generate a particular blow commodiously and not another; which I will make you to see better, beginning our schermo. |
[93v.5] RO. Cosi è. quasi dicendo, che dopo ogni colpo vi ritrovate in qualche guardia, et che dopo la guardia ne succede il colpo. Et come la quiete d'un moto particolare, e differente dalla quiete d'un altro diverso moto, secondo vogliono questi naturali: cosi una guardia è atta à generare un colpo particolare commodamente, et non un altro. |
Da una guardia particolare si genera un colpo particolare commodamente, et non l'altro. [64r.5] ROD. Cosi è, quasi dicendo che dopo ogni colpo vi ritrovate in qualche guardia, & che dopo la guardia, ne succede il colpo. Et co- [64v.1] me la quiete d'un moto particolare è differente dalla quiete d'un'altro diverso moto (secondo vogliono questi naturali) cosi una guardia è atta a generare un colpo particolare commodamente, & non un'altro: | |
[93v.6] CO Come io non la intendo. |
|||
[93v.7] ROD. Adesso ve'l farò vedere cominciando lo schermo nostro. |
[64v.2] il che vi farò veder meglio, cominciando lo schermo nostro. | ||
|
[93v.8] BOC. [94r.1] Pur adesso cominciate ad essercitarvi? che havete fatto in questo mezo? |
|||
[94r.2] RO. Sempre quasi habbiamo ragionato circa la notitia de i termini. |
|||
[94r.3] BOC. Al corpo della vita mia, che mi è caro molto et molto di vedervi. |
|||
CON: When I think over that which you have said to me just now, I find a clear example in the Germans, who, coming to an armed brawl, deliver a blow per man, and delivering the blow, stop in guard in order to wait for their companion to deliver his, and withhold theirs, and then redouble; behold the two rests with a motion in the middle. |
[94r.4] CO. Quando penso sopra quel, che m'havete detto adesso ritrovo un chiaro essempio ne i tedeschi, liquali, venendo à rissa d'arme menano un colpo per huomo, e menato il colpo s'affermano in guardia per aspettar, che'l compagno meni il suo, et ritenerlo, et poi raddoppiano: ecco le due quiete col moto in mezo. |
[64v.3] CON. Quando penso sopra quel che m'havete detto adesso, ritrovo un chiaro essempio ne' Tedeschi, i quali, venendo à rissa d'arme, menano un colpo per huomo, & menato il colpo si fermano in guardia, per aspettare che'l compagno meni il suo, & ritenerlo, & poi raddoppiano; Ecco le due quieti co'l moto in mezo. | |
[94r.5] BOC. Questo è uno assai acconcio essempio Rodomonte, dice il vero il Conte, et l'ho veduto piu volte mentre era in questa Città L'Imperatore. Horsù di gratia cominciate il vostro giuoco. |
|||
[94r.6] RO. Il mio Schermo volete dir voi. |
|||
[94r.7] BOC. Signor si. |
|||
ROD: This is a fairly fitting example; but we give the principal place to my schermo, beginning with the first guard. |
[94r.8] RO. Horsù state attento Conte, cominciamo dalla prima guardia. |
[64v.4] ROD. Questo è uno assai acconcio essempio: ma diamo principio al mio schermo, cominciando dalla prima guardia. | |
BOC: And I will silence myself, and will watch you, reserving for myself however the liberty to be able to ask of you at times some thing that I desire to know. |
[64v.5] BOC. Et io tacito me ne starò à vedervi, riservandomi però la libertà di potere tal volta dimandarvi qualche cosa, che io desideri sapere. | ||
CON: That is well reasoned, and we likewise will look to you for that (as you know more than we) when such occasions occur. But speak of the first guard, Rodomonte. |
[64v.6] CON. E'ben ragione, & noi parimente ricercaremo voi di quello, che sapete meglio di noi, quando verranno le occasioni. Ma dite della prima guardia Rodomonte. | ||
|
Prima guardia difensiva, imperfetta; formed from girding the sword at the left side, from whence originates the rovescio ascendente. [95v] Prima Guardia difensiva Imperfetta formata dal cingersi la Spada al manco lato da cui nasce il Rovescio Ascendente. [65v] PRIMA GUARDIA DIFENSIVA, IMperfetta; formata dal cingersi la spada al manco lato, da cui nasce il rovescio ascendente. |
First guard, called “difensiva imperfetta”, derives from having the sword girded at the hip. ROD: It is supposed (conte) that the carrying of the sword at the hip is for defense, and as a guard of man, and nature invites man to carry it for his defense; the carrying of the sword thus bound to the left hip, and resting firmly in this form and at that place, will be the first guard, called by us “guardia difensiva, imperfetta”. |
[94r.9] Si suppone, Conte, che'l portar della spada al fianco sia sempre per difesa, et guardia dell'huomo, la natura invita esso huomo à portarla per sua difesa, non è egli il vero? |
Prima guardia detta difensiva imperfetta tolta dall'haverla spada cinta al fianco. [64v.7] ROD. Si suppone (Conte) che'l portar della spada al fianco sia per difesa, & guardia dell'huomo, & la natura invita esso huomo a portarla per sua difesa: |
[94r.10] CO. E'vero. |
|||
|
[94r.11] ROD. Il portar dunque la spada cinta al fianco sinistro, e star fermo in quella forma, et in quel sito, [94v.1] sarà la prima guardia chiamata da noi guardia defensiva imperfetta. |
[64v.8] il portar dunque la spada cinta al fianco sinistro, & star fermo in quella forma, & in quel sito sarà la prima guardia, chiamata da noi guardia difensiva, imperfetta. | ||
CON: For what reason do you call it thus? |
[94v.2] CO. Per qual cagione cosi la chiamate voi? |
[64v.9] CON. Per qual cagione cosi la chiamate voi? | |
Why it is named “guardia difensiva imperfetta”. ROD: It is a guardia through being a still placement and pose; it is called “difensiva” through being for defense of that side where the sword is positioned; “imperfetta” I call it, because lying within the scabbard it only defends, frightening the enemy; but it is an imperfect defense, as it does naught else. |
[94v.3] ROD. Per esser un sito et una figura quieta; difensiva chiamasi per esser per difesa in quel lato posta la spada: Imperfetta la dico, perche stando la dentro il fodro difende solo, facendo paura al nimico, ma è difesa imperfetta s'altro non facesse. |
Perche sia nominata guardia difensiva imperfetta. [64v.10] ROD. E'guardia per essere un sito, & una figura quieta: difensiva chiamasi, per essere per difesa in quel lato posta la spada: imperfetta la dico, perche stando ella dentro il fodro difende solo, facendo paura al nimico: ma è difesa imperfetta, s'altro non facesse. | |
CON: What blows arise from this first guard? |
[94v.4] CO. Et questa è la prima guardia, ma che colpo partorirà questa guardia? |
[64v.11] CON. Questa prima guardia che colpo partorirà ella? | |
Advice that all the guards be done with the right foot, and with the right side, toward the enemy. ROD: The rovescio, but you are advised that all seven guards must be done with the right foot and the right side advance toward the enemy; because they are less mortal and have greater strength and faculty than the left, as much in the offending as well as in the defending. Watch, therefore, conte, now I hold this sword at my left hip; if I wish to avail myself of it, and use it against you, either to offend you or to defend myself, it will be necessary that I put my right hand here at the hilt of the sword, in order to draw it forth, |
[94v.5] RO. Il rovescio. |
Avvertimentoche tutte le guardie si faccino col piè destro, & con le parti destre verso il nimico. [64v.12] ROD. Il rovescio, | |
[94v.6] CO. Come? |
|||
[94v.7] RO. Avvertite che queste sette guardie tutte voglio si facciano col pie destro, et le parti destre innanzi verso il nimico. |
[64v.13] ma avvertite [65r.1] che queste sette guardie tutte voglio si facciano co'l pie destro, & le parti destre innanzi verso il nimico: | ||
[94v.8] CO. Perche cosi? |
|||
[94v.9] RO. Perche sono meno mortali et hanno maggior forza et uso delle sinistre, tanto nell'offendere come anco nel difendere. |
[65r.2] perche sono meno mortali, & hanno forza, & uso maggiore delle sinistre, tanto nell'offendere, come anchora nel difendere. | ||
[94v.10] CO. Faccisi. |
|||
[94v.11] RO. Vedete dunque Conte adesso io tengo questa spada al fianco sinistro, s'io voglio valermene, et usarla contra di voi, ò per offendervi, ò per difendermi, fa di bisogno (vedete) c'he io ponga questa mia destra mano quivi all'elzo della spada per trarla fuori |
[65r.3] Vedete adunque, Conte, hora io tengo questa spada al fianco sinistro: s'io voglio valermene, & usarla contra di voi ò per offendervi, ò per difendermi; fà dibisogno ch'io ponga questa mia destra mano qui all'elzo della spada, per trarla fuori, | ||
The rovescio ascendente originates from the first guard. whereby I do this rovescio ascendente with strength, and this is the first blow, originated from the left side, guardia prima, et difensiva imperfetta. |
[94v.12] dove faccio per forza questo ro= [95r.1] vescio ascendente. Ecco il primo colpo nato dal fianco stanco guardia prima, et difensiva imperfetta, fatelo mo voi Conte? |
Nasce dal la prima guardia il rovescio ascendente. [65r.4] dove faccio per forza questo Rovescio ascendente, & questo è il primo colpo, nato dal fianco stanco, guardia prima, & difensiva imperfetta. | |
CON: Do you see whether I do it, too? Look, I draw my sword, and here’s the rovescio; I’m standing with my right side and with my right foot advanced toward you. |
[95r.2] CO. Che cosa? di trar la spada? |
[66r.1] CON. Vedete se lo faccio anch'io? ecco il trar della spada, | |
[95r.3] RO. Si. |
|||
[95r.4] CO Ecco, et ecco il rovescio. |
[66r.2] & ecco il rovescio, | ||
[95r.5] RO Non fate bene à far cosi Conte. |
|||
[95r.6] CO Come no? non è questo un rovescio? non istò io con le parti destre, et col pie destro innanzi verso di voi? |
[66r.3] stando io con le parti destre, & co'l pie destro innanzi verso di voi. | ||
How one must hold the hand during the unsheathing of the sword, and how the body is to be moved in order to execute the rovescio ascendente. ROD: Yes, but you do it nonetheless, I know not why, turning your wrist as you draw it forth, which does not please me; hold your wrist in such a fashion while you draw it forth that you do not make a turning; and do it so that your hand rises high, and to the rear on your right side, so that the point of your sword is aimed at my chest, and downwards somewhat toward the ground, and stop it there, with the true edge of the sword facing the sky, and the false toward the ground, taking care in the selfsame tempo that the rovescio travels, that you make with your body a little turn in such a way that your left shoulder is found somewhat more forward than your right, and that your left arm follow the right through the forward side, so that it is found toward the right side; and make additionally a slight turn of your left leg on the point of your foot through the draw, and the heel should be somewhat lifted from the ground; and together with this make your right leg lie extended, with the body somewhat erect: you see how I do it? |
[95r.7] RO. Si; mà fate però non so che volta della mano nel trarla fuore, che non mi piace. |
Come si debba tenere la mano'nello sfodrare la spada, & come si mova la persona per fare il rovescio ascendente. [66r.4] ROD. Si, ma fate però non so che volta della mano nel trarla fuori, che non mi piace: | |
[95r.8] CO. Come debbo fare? |
|||
|
[95r.9] RO Tenete modo, che il nodo della mano nel trarla fuore non faccia alcuno volgimento, et fate, che la mano vada tanto alta, et à dricto verso le destre parti, che la punta della spada guardi al Petto mio, et declini alquanto verso terra, et ivi si fermi, e che il drritto filo della spada guardi verso [96r.1] il cielo, et il falso verso terra. |
[66r.5] tenete modo che'l nodo della mano nel trarla fuori, non faccia alcun volgimento, & fate che la mano vada tanto alta, & adietro verso le destre parti, che la punta della spada guardi al petto mio, & declini alquanto verso terra, & ivi si fermi, & che'l dritto filo della spada guardi verso il cielo, & il falso verso terra, | ||
[96r.2] CO. à questo modo? |
|||
[96r.3] ROD. Non vedete come facc'io, in questo tempo medesimo, che camina il rovescio fate con la persona un poco di volta di modo, che la spalla sinistra si ritrovi alquanto piu innanzi della destra, e che la destra non manchi, che sia piu alta alquanto della sinistra, e che'l braccio stanco segua il destro per la parte dinanzi, di sorte, che si truovi verso il destro fianco, et fate ancora girare la gamba sinistra sù la punta del piede un poco per difuori, et che il calcagno sia alquanto levato da terra, et fate insieme, che la gamba diritta stia distesa con la persona alquanto diritta: vedete come faccio io? |
[66r.6] avertendo che in questo tempo medesimo, che camina il rovescio, facciate con la persona un poco di volta; di modo che la spalla sinistra si ritrovi alquanto piu innanzi della destra, & che la destra sia piu alta alquanto della sinistra, & che'l braccio stanco segua il destro per la parte dinanzi; di sorte che si truovi verso il destro fianco: & fate anchora girare la gamba sinistra sù la punta del piede un poco per di fuori, & che il calcagno sia alquanto levato da terra, & fate insieme che la gamba dritta stia distesa con la persona alquanto dritta: vedete come faccio io? | ||
CON: I’m watching, but I cannot settle this right leg with the body well, and if I lift the heel of my left foot, I cannot support myself on it well, nor have my right leg extended and somewhat raised. |
[96r.4] CO. Troppo il veggio, ma non posso rassettar bene questa gamba diritta con la persona. |
[66r.7] CON. Veggio, ma non posso rassettar bene questa gamba dritta con la persona: | |
[96r.5] ROD. Come no? io non saprei pur fare altrimenti quasi: pare, che la natura formi tal figura ritrovandovi in quel sito con le parti destre innanzi, et volendo menar ben alto quel rovescio quanto si possa, senza volta ò giro di mano. |
|||
|
[96r.6] CO. In fatti s'io alzo quel calcagno del piè stanco, che è di dricto non mi vi posso poi sostentare sopra, ne tenere la gamba destra distesa [97r.1] et alquanto levata. |
[66r.8] & s'io alzo il calcagno del piè stanco; non mi vi posso ben sostentare sopra, ne tenere la gamba destra distesa, & alquanto levata. | ||
ROD: I would not know how to do it otherwise; it seems that nature forms such a figure finding yourself in that place with your right side forward, and wanting to throw that rovescio quite high, as much as can be done, without pivoting or turning the hand; but do it several times, paying attention to all the particulars of which I have told you. |
[66r.9] RODOM. Io non saprei far pur altrimenti quasi: pare che la natura formi tal figura ritrovandovi in quel sito con le parti destre innanzi, & volendo menar ben alto quel rovescio quanto si possa, senza volta, o giro di mano: | ||
CON: Look. |
[66r.10] ma fatelo piu volte, avertendo a tutti i particolari che io v'ho detto. | ||
ROD: Lift the heel of your left foot a bit more, and extend your right leg. |
|||
CON: Like so? |
[66v.2] & distendete ben quella vostra gamba destra. | ||
|
Seconda guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta; formed from the rovescio ascendente, from which originates the punta sopramano offensiva, either complete or incomplete. [96v] Second Guardia alta offensiva perfetta formata dal Rovescio ascendente da cui nasce la Punta sopramano offensiva ò intera, ò non intera. [67r] SECONDA GUARDIA ALTA, OFFENsiva, perfetta; formata dal rovescio ascendente, da cui nasce la punta sopramano offensiva, ò intiera, ò non intiera. |
Second guard, called “alta, offensiva, perfetta”. ROD: Just so; this is our second guard, called “guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta”. |
Seconda guardia detta alta, offensiva, perfetta. [66v.3] CON. Così? | |
CON: I know why it is called “guardia alta”, but I do not know the reason why you call it “offensiva” and “perfetta”. |
[67v.1] CON. Guardia alta, sò perche si chiama; ma non sò la cagione, perche la chiamate offensiva, & perfetta. | ||
Rules to recognize which guards are defensive and which offensive. ROD: I will tell it to you: every guard formed on the left side will be called “difensiva”, and all of those on the right side will have the name “offensiva”; accordingly any time that the sword will be found on the left side (with the right foot in front, nonetheless, which we always assume, as much in guardia larga, as in stretta), still, whether the arm be found higher, or less narrow, or lower than it between the stretta, and the larga, that will be understood as a defensive guard, and will be for defense; and all the times in which the sword will be found by the right side (also with the right foot forward) both in guardia alta perfetta and in imperfetta, both in guardia stretta and in larga, either were it then among the alta, and the stretta, or between the stretta, and the larga, provided that the sword should be by the right side, such a guard will always be understood as offensive, and will be in order to offend. This will be our rule, and hold it fixed in your memory. |
Regole di conoscere qual sia guardia difensiva & quale offensiva. [67v.2] RO. Dirollovi; ogni guardia formata nelle sinistre parti, si chiamerà difensiva, & quelle tutte dalla banda destra haveranno nome di offensive: dove tutte le volte che si troverà la spada nelle parti stanche (co'l piè destro avanti però, che questo sempre supponiamo, cosi in guardia larga, come stretta) anchora, che si trovasse piu alta un braccio, ò meno della stretta, ò piu bassa di essa fra la stretta, & la larga; s'intenderà quella tal guardia difensiva, & staranno per difesa, & tutte le volte che si troverà la spada nelle parti destre (pur co'l piè destro avanti) tanto in guardia alta perfetta, quanto imperfetta; tanto in guardia stretta, quanto in larga; ò fosse poi tra l'alta, & la stretta, ò fra la stretta, & la larga; pur che la spada sia nelle parti destre; s'intenderà tal guardia sempre offensiva, & starà per offendere. Questa sarà nostra regola, & tenetela fissa nella memoria. | ||
CON: I would ground it better in my memory, if I understood the basis of these “alte”, “strette” and “larghe” guards of yours. |
[67v.3] CON. La terrei à memoria meglio, s'io intendessi la forza di queste vostre guardie alte, & strette, & larghe. | ||
Why the second guard is called “offensiva” and “perfetta”. ROD: We will do them all soon, and then you will better understand the rule. This guardia alta is accordingly offensive, the sword being on the right side. |
Perche la seconda guardia si chiami offensiva, et perfetta. [67v.4] ROD. Le faremo prima tutte, & poi intenderete meglio la regola. Questa guardia alta adunque è offensiva, sendo la spada nella dritta parte. | ||
CON: Why is it called “perfetta”? |
[67v.5] CONTE. Perche chiamasi perfetta? | ||
ROD: Because the point of the sword uncovers the enemy more, and looks more toward him in this form, than in some other in which one can be; this guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta is born from the rovescio, the doing of which you have in the drawing forth of the sword. |
[67v.6] RODOM. Perche la punta della spada piu scuopre il nimico, & piu lo mira in questa forma, che in alcun'altra, in che si possa stare: questa guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta, è partorita dal rovescio, che fatto havete nel cavar fuori la spada. | ||
BOC: And if in that tempo, Rodomonte, in which you pull forth your sword, and in which the rovescio travels from low to high, the conte were to deliver some blow in order to harm your head or upper body, what would you do? |
[67v.7] BOCCA. Et se in quel tempo, Rodomonte, che voi tirate fuori la spada, & che'l rovescio camina da basso ad alto, il Conte menasse qualche colpo per [68r.1] offendervi la testa, ò le parti superiori, come fareste voi? | ||
ROD: With the very same rovescio I would beat aside the blow of his sword toward the air, and toward my right side, and then settling into the said guardia alta, perfetta, et offensiva, I would thrust the readied point into his chest. |
|||
BOC: If you were quick, and he slow. |
|||
ROD: If one has understanding, then there is no need for him to already be asleep. |
|||
BOC: Do it a bit, conte. |
|||
CON: Look. |
|||
What must be done coming to blows with the enemy, either at close range or at a distance. ROD: And behold the response, and when you come to blows with your enemy at close range, this is the shortest defense and offense that you can make; because having finished drawing forth your sword, you address it toward the enemy, and not otherwise, in order to offend him, and defend yourself. |
|||
CON: And if I am at a distance from my enemy, then what must I do? |
|||
ROD: The very same: again, put yourself in this alta guardia offensiva perfetta, and here you will give to him that you intend to thrust the point of your sword into his eyes. |
|||
CON: Isn’t it better to target it so as to thrust into his chest? |
|||
It is better to present the point of the sword to the eyes of the enemy than elsewhere. ROD: No Sir, because if you elevate the punta sopramano such that you point to his eyes, in the extension your arm lowers, and drops to his chest; but if you point to his chest, it will descend to his thigh, and without pretending to hit him in his eyes, by which you would give him more terror (the eyes being the noblest parts of the body) and make him lose more spirit. |
|||
BOC: You speak the truth, Rodomonte; some of those who are armored in full jousting harness, when the opponent lowers his lance, looking to the visor of their helm in order to offend it, I have seen that they happen to have a little helmet hanging from a band, well advanced from the face, to avoid the enemy’s point for fear of their eyes. And there are some that close their eyes out of fear, and these never make worthy blows, except by luck. Now if these armored men are in such fear of the point finding their eyes, how then will one unarmored be, seeing the very point of a sword directed straight at his eyes? |
|||
ROD: A most excellent argument from the least to the greatest. |
|||
CON: And if finding myself at a distance from the enemy, I were to make a sign that I wished to do offense to his head with some blow from high to low using the edge, and not the point? |
|||
ROD: You would induce less terror thereby; because his left arm holds the care and safekeeping of head in taking the blow with his hand, or in restraining its force with his arm;[11] thus the point is always more perfect and offensive than the edge. |
|||
CON: Thus we make use only of the strike of the point in the Roman fashion, and not of the edge, as much in close range as in far. |
|||
Advisement that one strike with the point into the depth of the nobler parts. ROD: And we see as well that we thrust it into the depth of the nobler parts, where the wounds are crueler and more deadly. |
|||
Praise for the Most Illustrious Signor Duca Hercole IV di Ferrara. CON: Very well, so this is your second guard; I have understood it, and if I practice it, I will do it well before too much time passes. I have heard it said that this guard is well liked by the Signor Duca Hercole Quarto di Ferrara, who in addition to his many other virtues, is extremely delighted by the military art, and that of the unaccompanied sword. |
|||
ROD: That is quite reasonable, because as this guard is quickest to offend it is fitting to a knight most quick, and desirous of striking his enemy, as it is seen that the Signor Duca was in the joust and in the public combats when he was exercising; then had he always well accomplished the keeping of the peace for his people. |
|||
CON: I have always heard him celebrated as such, and infinitely commended, and I hear that in writing he is hailed greatly as well. |
|||
ROD: Hailed certainly, and it is no wonder, for he is among the ideal and wisest Princes that this age has. |
|||
CON: Now teach me the third. |
|||
|
Terza guardia alta, offensiva, imperfetta; formed from the rovescio ascendente, from which originates a mandritto descendente, either full or half. |
Third guard, called “guardia alta offensiva imperfetta”. ROD: Willingly; do the rovescio from low to high in drawing forth your sword so that it goes so high that the point of the sword looks to the sky, and that your wrist makes a half turn, in such fashion that the true edge faces up toward the sky, and the false, together with the point of your sword, faces toward the right side of your body over your right shoulder, and the pommel of your sword faces me, making all of those turns of the body, the hand, and the feet, of which I taught you in the other guard. This will be our third guard, called “guardia alta, offensiva, imperfetta”. |
||
The third guard gives rise to a mandritto discendente. You see how I do it? And how I pull this rovescio up high, and how as the rovescio travels I make a half turn with my wrist; look how the point of the sword together with the false edge faces behind me. This guard does not give rise to a thrust, but rather a mandritto to your upper body, if I allow it to fall. |
|||
CON: Let me do it a bit; would that be all right? |
|||
ROD: Raise your arm then as high as you can. |
|||
CON: And if you had been in the way beneath me? |
|||
ROD: Let the blow fall, and you would have contacted me forcefully in the head, if I had not otherwise made a defense. |
|||
CON: Why is it called “imperfetta”? |
|||
Why the third guard is called “imperfetta” and “offensiva”. ROD: Because it does not give rise to a thrust, but only a cut, and therefore is of less offense, and I will avoid it more easily. |
|||
CON: “offensiva”, because it originates from the right side, correct? |
|||
ROD: Yes Sir, and “imperfetta”, as such a blow offends imperfectly, as I have said, and also because when you want to deliver a blow from high to low, your right side would be uncovered to my eye, and thus you could be stuck in the body with this thrust; and I might find myself with my sword advanced and could easily defend myself. |
|||
BOC: And then, although it happens that the blow falls from high to low with a great onslaught, it does not always kill, because the bones of the skull are extremely strong and doubled in some places; in addition if you contact some other place, such as the shoulder, there are other very hard bones; and sometimes they are armored with good arms of defense, which abate the fury of the cut, but not the thrust. |
|||
ROD: This is a good and natural argument. |
|||
CON: Up to this point we have the third guard, called “alta offensiva, imperfetta”; now let’s come to the fourth. |
|||
|
Quarta guardia larga, difensiva, imperfetta; formed from the full punta sopramano, and from which originates the rovescio ritondo. |
How one must reset and move the body in order to make the fourth guard. ROD: Reset yourself in guardia alta offensiva, perfetta, and fix all of your weight firmly on your left foot, body elevated, so that the right one may be more agile, and likewise all your right leg, in order to be able to pass forward, and come toward me. |
||
CON: I cannot, if I don’t support part on the right leg as well. |
|||
ROD: You won’t do anything, because if your right leg is weighed down, you can’t come forward to me with the side that holds your offensive arms. But if you find yourself with your right foot unencumbered, you can pass forward with a big step in this fashion. |
|||
CON: Now watch whether I satisfy you. |
|||
ROD: Excellent; now fix yourself in that pose, and take the big step, and make your right shoulder drive your arm as far forward as you can, and with your sword hand direct the aim of your point at my breast without making any turn of your hand, until it comes forward as far as it can come, and then, turn there the true edge of the sword toward the left side, and from here you descend finally to the ground, and it is necessary that you make a half turn with your body at the same time that the blow is traveling, so that your right shoulder is somewhat lower than your left, and that it faces my chest; and the right foot trailing behind somewhat, bring yourself to rest again in good stride, and settle your feet, which are on the diagonal, and bend your knees a bit, and cause your sword hand to be located halfway between your knees, and your left arm to lower from high to low during that tempo in which the point will travel, and it will go back and by the outside with the left leg somewhat extended. Do you see how I do it? And how I lower myself down to the ground? |
|||
CON: I see it, and I believe that in the space of a year I would still never give to it the beautiful agility, and such elegance of body as you do, Rodomonte; but continue on, as it will take me more time to practice it. |
|||
ROD: This is “guardia larga, difensiva, imperfetta”. |
|||
CON: For what reason is it called “guardia larga”? |
|||
Why the fourth guard is called “larga difensiva, imperfetta”. ROD: It is called “larga”, in consequence of the point of the sword being distanced from the enemy in such fashion that it does not target his body in any place. It is called “difensiva” from being posted on the left side, from whence all the defensive guards take form, as I told you; and it is “imperfetta” because it produces a cut yielding a rovescio tondo. |
|||
The fourth guard takes form from the punta sopramano offensiva. CON: This guard takes form then from that punta sopramano offensiva. |
|||
|
Quinta guardia stretta, difensiva, perfetta, formed from the meza punta sopramano, offensiva, from which originates a mezo rovescio tondo. |
ROD: That it does, and that thrust is a perfect blow, sticking it as far as you can reach with your arm. If you find yourself, then, conte, in the guardia alta offensiva perfetta (also with the right foot forward) and from here throwing an imbroccata sopramano offensiva, and How one must do the fifth guard. making those same turns of the body, of the hands, and of the feet (except for the turning of the true edge toward your left side, as I taught you), do not pass your sword hand past yourself nor cross your right knee, and make the point aim at my chest; this will be the fifth guard, which we call “guardia stretta, difensiva, perfetta”. |
[103r.1] col pie destro innanzi) e che di quiui spingendo la imbroccata sopramano offensiva, e facendo quelli stessi volgamenti della persona, delle manim e de' piedi (eccetto, che nel voltare il dritto filo verso le parti stance, come u' insegnai) facciate che la mano della spada non vi passi, ò trascorra il ginocchio destro, et, che la punta di essa riguardi il petto mio. questa sarà la quinta Guardia da noi chiamata. Guardia stretta difensive perfetta. |
|
CON: Do it, Rodomonte. |
[103r.2] CO. Fatela voi Rodomonte. |
||
ROD: Behold it; you see that my hand does not pass my right knee, and how the point is aimed at your chest? |
[103r.3] RO. Eccola vedete, che la mano non mi passa il ginocchio destro? et come la punta guarda il petto vostro? |
||
CON: Why do you name it thus? |
[103r.4] CON. Il veggio, et bene: ma perche cosi la nominate voi? |
[73r.1] CON. Perche cosi la nominate voi? | |
Why the fifth guard is called “stretta, difensiva perfetta”. ROD: I call it “stretta” on account of the sword being close to the enemy; and he cannot be an assailant without great contest, in respect of the point, which is aimed at the enemy’s chest, and your left side finds itself again distant from him, such that it cannot be offended, it still being the more mortal. |
[103r.5] ROD. Stretta la chiamo io per essere la spada astretta con il nimico, e non puo essere assalita senza grandissima contesa per rispetto della punta, che guarda il petto del nimico, e le parti stanche ritrovansi anco lontane da lui talmente, che non ponno esser offese anchor che sieno le piu mortali. |
Perche la quinta guardia sia detta stretta difensiva perfetta. [73r.2] ROD. Stretta la chiamo io, per essere la spada stretta co'l nimico, & non può essere assalita senza grandissima contesa, per rispetto della punta, che guarda il petto del nimico, & le parti stanche ritrovansi anchor lontane da lui talmente, che non ponno essere offese, anchor che siano le piu mortali. | |
BOC: Finding the right side forward, which appears to have the duty of defense, and the sword hand advanced, it is found to be as much for defending oneself as offending others; I believe that in this guard the conte and anyone else will be defended more easily and with less fatigue than in any other guard in which they place themselves. |
[103r.6] BOCC. Credo io, che trovandosi le parti destre innanzi, lequali par c'habbino cura della difesa et, che la mano della spada alla presenza si ritruovi [103ar.1] tanto per difendere se, come per offender poi, credo (dico) che in questa guardia si difenderà il Conte piu facilmente, et con minor fatica, che in qualunque altra guardia si ponesse. |
[73r.3] BOC. Trovandosi le parti destre innanzi, le quali pare c'habbiano cura della difesa, & che la mano della spada alla presenza si ritrovi tanto per difendere se, quanto per offendere altrui, credo io, che in questa guardia si difenderà il Conte, & ciascun altro più facilmente, & con minor fatica che in qualunque altra guardia si ponesse. | |
CON: Why is it called “perfetta”? |
[103ar.2] CON. Perche la chiamate perfetta? |
[73r.4] CON. Perche la chiamate perfetta? | |
ROD: Oh, didn’t I tell you that you need to turn the point of your sword toward my chest? Look, because it engenders the thrust, one calls it “perfetta”; but if indeed it principally engenders the thrust, nonetheless from it is easily born the mezo rovescio tondo, with which we will be able to serve ourselves as well in our schermo. |
[103ar.3] RO. O' non vi dico, che bisogna, che voltiate la punta della spada verso il petto mio? Ecco, che perche partorisce la punta chiamasi perfetta. |
[73r.5] ROD. O non vi dico che bisogna che voltiate la punta della spada verso il petto mio? Ecco perche partorisce la punta, chiamasi perfetta: ma se ben partorisce punta principalmente, nondimeno da lei agevolmente nasce il mezo rovescio tondo, delquale noi potremo servirci poi tanto nello schermo nostro. | |
CON: And “difensiva”? |
[103ar.4] CON. E difensiva? |
[73r.6] CON. Et difensiva? | |
ROD: Don’t you see whether this thrust would originate from the left side, and that it would be a punta rovescia ascendente? |
[103ar.5] ROD. Non vedete se quella punta nascerebbe dalle vostre parti sinistre, e sarebbe punta rovescia ascendente? |
[73r.7] ROD. Non vedete se quella punta nascerebbe dalle vostre parti sinistre, & sarebbe punta rovescia ascendente? | |
Praise of the S. Giovanni de Medici, and of the Sig. Conte Guido Rangone. CON: It is true; this seems to me the finest guard among the defensive, and this (if I recall correctly) was much used by the Signor Giovanni de Medici and the Signor conte Guido Rangone, rare men, and excellent in the wielding of arms. |
[103ar.6] CON. E vero, questa mi par buonißima guardia tra le difensive, e questa se ben mi raccordo molto usavano il Sig. Giovanni de'Medici et il Conte Guido Rangone huomini rari, et eccellenti nell' essercitio dell' Armi. |
Lode del S. Giovanni de Medici, & del Sig. Conte Guido Randone. [73r.8] CON. E' vero: questa mi par buonissima guardia tra le difensive, & questa (se ben mi ricordo) molto usavano il Signor Giovanni de'Medici, & il Sig. Conte Guido Rangone, huomini rari, & Eccellenti nell' essercitio delle Armi. | |
From the guardia alta, offensiva, imperfetta originates a full mandritto, offensivo, imperfetto. ROD: You speak the truth; I have seen it used by the Signor conte Guido, a man not very tall of body (although towering in valor), and chiefly with the unaccompanied sword. Now when you are in the guardia alta, offensiva, imperfetta, such that the point of your sword points to the right (still with the right foot forward), you can make a mandritto thus, that descends down to the ground, and do all those turns of the body, of the hands, and of the feet, that I told to you in the punta sopramano, offensiva, perfetta; and this mandritto will be a full blow, and a full, offensive, imperfect tempo. |
[103ar.7] RO. Voi dite il vero, e massime il Sig. Conte Guido huomo non molto alto di persona, altissimo però di valore, et massimamente nella spada sola: Hor quando sarete nella guardia alta, offensiva, imperfetta. |
Dalla guardia alta offensiva, imperfetta nasce un mandritto intiero, offensivo, imperfetto. [73r.9] RODO. Voi dite il vero, io l'ho veduta usare al Signor Conte Guido, huomo non molto alto di persona (altissimo però di valore) & massimamente nella spada sola. Hor quando sarete nella guardia alta, offensiva, imperfetta, | |
[103ar.8] CON. Cio è che la punta della spada guardi al di dietro? |
[73r.10] cioè che la punta della spada guardi al di dietro, | ||
[103ar.9] ROD. Signor si, ritrovandovi, dico, in quella guardia, pur co'l pie destro avanti. |
[73r.11] ritrovandovi in quella guardia (pur co'l pie destro avanti) | ||
[103ar.10] CO. Si: questo lo presupponiamo sempre. |
|||
|
[103ar.11] RO. Potrete far nascere un mandritto, cosi [103av.1] che discenda insino à terra, et far quei volgimenti tutti della persona, delle mani, et de' piedi, che vi dissi nella punta sopramano offensiva perfetta. Et questo Mandritto sarà un colpo intiero, et un tempo intiero offensivo imperfetto. |
[73v.1] potrete far nascere un mandritto cosi, che discenda sino a terra, & far quei volgimenti tutti della persona, delle mani, & de' piedi, che vi dissi nella punta sopramano, offensiva, perfetta: & questo mandritto sarà un colpo intiero, & un tempo intiero, offensivo, imperfetto | ||
CON: Why “full”? |
[103av.2] CON. Perche intiero? |
[73v.2] CON. Perche intiero? | |
Why the mandritto is called “full, offensiva, imperfetta”. ROD: Because it originates from on high, to finish low to the ground; and “offensiva” because it originates from the right side, from whence originate all the offenses. |
[103av.3] ROD. Perche, nasce dall'alto al basso fin à terra. Et offensivo perche nasce dalla banda destra, d'onde nascono le offese. |
Perche esso mandritto sia detto intiero, offensivo imperfetto. [73v.3] ROD. Perche nasce dall'alto al basso fin'à terra, & offensivo, perche nasce dalla banda destra, donde nascono l'offese. | |
CON: “Imperfetta”, then, through being the delivery of a cut, and not a thrust. |
[103av.4] CO. Imperfetto poi per esser menato di taglio, et non di punta. |
[73v.4] CON. Imperfetto poi per esser menato di taglio, & non di punta. | |
[103av.5] RO. Ecco, che la cominciate ad intendere Conte. |
|||
[103av.6] BOC. La comincio ad intendere anch'io. |
| ||
[103av.7] CO. La intenderete ben Dottore forse meglio di me; ma la fareste forse anchor peggio, che non facc'io. Si come io peggio di voi intenderei un testo del vostro Aristotile. |
| ||
[103av.8] RO. Esso ve l'ha pur cinta questa volta ah Dottore'. |
| ||
[103av.9] BOC. O' che miracolo ha detto; questo sapevo anch'io prima, che hora Rodomonte. |
| ||
ROD: You speak the truth; behold you, conte, that the said full blow will have formed the guardia larga difensiva. |
[103av.10] ROD. Eccovi Conte, che'l detto colpo intiero harà formato la guardia larga difensiva. |
[73v.5] ROD. Dite vero: Eccovi Conte che'l detto colpo intiero havrà formato la guardia larga difensiva. | |
|
|
From guardia alta offensiva imperfetta can originate a mezo mandritto offensivo, imperfetto. CON: And if in this same guardia alta, offensiva, imperfetta, I delivered a mezo mandritto, which did not reach the ground, but that stopped halfway through its path, not passing myself at the knee in this way, with all the aforesaid turns of the body, the hand, and the feet, ending with the sword held firm; tell me then what blow would that be? |
[103av.11] CO. Et se in questa medesima guardia alta offensiva imperfetta, io menassi un mezo Mandritto solo, ilquale non giungesse à Terra, ma che [104v.1] à mezo del camino si fermasse non passandomi il ginocchio à questa guisa, con tutti i sudetti volgimenti di vita, di mano, e di piedi fin che fosse ferma la spada (ditemi) che colpo sarebbe questo? |
Dalla guardia alta offensive imperfetta può nascere un mezo mandritto offensivo imperfetto. [73v.6] CON. Et se in questa medesima guardia alta, offensiva, imperfetta io menassi un mezo mandritto solo, il quale non giugnesse a terra, ma ch'a mezo del camino si fermasse, non passandomi il ginocchio a questa guisa, con tutti i sudetti volgimenti di vita, di mano, & di piedi, fin che fosse ferma la spada; ditemi che colpo sarebbe questo? |
Why it is called a mezo mandritto offensivo, imperfetto. ROD: It would be a mezo mandritto, offensivo, imperfetto; it would be offensive, falling from the right side; imperfect, being a cut and not a thrust; and this mezo mandritto places you in the guardia stretta, difensiva, perfetta, you see? |
[104v.2] ROD. Sarebbe un mezzo mandritto, non lo vedete voi? |
Perche sia detto mezo mandritto offensivo, imperfetto. [73v.7] ROD. Sarebbe un mezo mandritto, | |
[104v.3] CO. Si bene ma come lo chiamereste? |
|||
[104v.4] RO. Lo chiamerei un mezzo mandritto offensivo imperfetto. |
[73v.8] offensivo, imperfetto: | ||
[104v.5] CON. Et perche cosi? |
|||
[104v.6] RO. Offensivo sarebbe calando dalle parti destre; imperfetto sendo egli, Taglio, et non punta. |
[73v.9] offensivo sarebbe calando dalle parti destre, imperfetto sendo egli taglio, & non punta: | ||
[104v.7] CO. Benissimo. |
|||
[104v.8] RO. Et questo mezo mandritto vi forma la guardia stretta difensiva perfetta; Lo vedete? |
[73v.10] & questo mezo mandritto vi forma la guardia stretta, difensiva, perfetta, lo vedete? | ||
CON: I’m watching. |
[104v.9] CO Come s'io lo vedo, e di che sorte. |
[73v.11] CON. Veggio. | |
|
Sesta guardia larga, offensiva, imperfetta; formed from the full rovescio difensivo; from which originates the resetting into guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta. |
How one must do the sixth guard, called “larga offensiva imperfetta”. ROD: Now let’s step ahead a little, conte; if you found yourself in one of those two described defensive guards, either stretta or larga, still with the right foot forward, and you wanted to do a rovescio, you would be forced to turn your right hand in order to rotate the true edge toward your right side; where the point of your sword will turn toward the rear by the outside of your left side, and from low, rise to high finally to your left shoulder, and from here fall from high to low through the right side, finishing at the ground; in that same tempo make your body do a half turn and yet make your left shoulder be somewhat advanced, and higher than the right, and your left arm follow the right, and the left leg cause its foot to turn a little to the outside of the left side, the heel a bit raised from the ground; so that the sword hand finds itself outside the right leg, and back a half of a braccio[12] and a bit distant from the thigh; I say that this rovescio will be a full, and a defensive blow: “full”, you see; “defensive”, because the rovescio is a defensive blow, originating from the left side. And this blow creates for you a sixth guard, called by us “guardia larga, offensiva, imperfetta”. |
[104v.10] RO. Hora passiamo un poco innanzi Conte; se vi ritrovaste in una di queste due guardie difensive narrate, ò stretta, ò larga (pur col pie destro avanti) e che voleste fare un rovescio vi sarà forza di voltar la destra mano per voltare il dritto filo verso le vostre parti destre, Dove se la punta della spada voltarassi verso le vostre parti di dietro per di fuori al lato sinistro, et il suo principio sia da basso ad alto per insino alla spalla sinistra, e di quiui calando [105v.1] d'alto à basso verso le destre parti insino a terra facciate, che in quello stesso tempo la persona vostra faccia una meza volta, et che però la spalla stanca sia alquanto inanzi, e piu alta della destra, e che il braccio sinistro segua il destro, e che la gamba stanca faccia, che il piede giri un poco per di fuori alle parti sinistre, che il calcagno sia un poco sollevato da terra, tal che la mano della spada si truove di fuori dalla gamba dritta, et à dietro un mezzo braccio, e discosto dalla coscia un poco, dico, che questo rovescio sarà colpo intiero, e difensivo. Intero lo vedete, difensivo, perche'l rovescio è colpo difensivo nascendo dalle parti sinistre. Et questo colpo vi partorisce una Sesta guardia chiamata da noi guardia larga offensiva? |
Come si debba sare la sesta guardia detta larga offensive imperfetta. [73v.12] ROD. Hora passiamo un poco innanzi (Conte) se vi ritrovaste in una di queste due guardie difensive narrate, o stretta, o larga, pur co'l pie destro avanti, & che voleste fare un rovescio; vi sarà forza di voltar la destra mano per voltar il dritto filo verso le vostre parti destre: dove se la punta della spada si voltarà verso le vostre parti di dietro per difuori al lato sinistro, & il suo principio fia da basso ad alto per sin'alla spalla sinistra, & di qui calando d'alto a basso verso le destre parti insin'a terra; facciate che in quello istesso tempo la persona vostra faccia una meza volta, & che però la [74r] spalla stanca sia alquanto innanzi, & piu alta della destra, & che'l braccio sinistro segua il destro, & che la gamba stanca faccia che'l piede giri un poco per di fuori alle parti sinistre, che'l calcagno sia un poco sollevato da terra; talche la mano della spada si truovi di fuori dalla gamba dritta, & a dietro un mezo braccio, & discosto dalla coscia un poco; dico che questo rovescio sarà colpo intiero, & difensivo: intiero, lo vedete; difensivo, perche'l rovescio è colpo difensivo, nascendo dalle parti sinistre. Et questo colpo vi partorisce una sesta guardia chiamata da noi guardia larga, offensiva, imperfetta. |
CON: Why “larga”? |
[105v.2] CO. Per che larga? |
[75r.1] CON. Perche larga? | |
Why the sixth guard is called “larga, offensiva”. ROD: For the same reason that we called our fourth guard “larga”; “offensiva”, for being on the right side. |
[105v.3] RO. Per le ragioni medesime, per le quali chiamassimo la quarta nostra guardia, larga, offensiva per esser nelle parti destre. |
Perche la sesta guardia sia detta larga, offensive. [75r.2] ROD. Perle ragioni medesime, per le quali chiamassimo la quarta nostra guardia larga, offensiva per esser nelle parti destre. | |
[105v.4] CO. Questa è ella la sesta Guardia? |
|||
[105v.5] RO. Questa è. |
|||
[105v.6] CO. Dunque à quello, che comprendo io, noi siamo da capo hormai. |
|||
[105v.7] RO. Fermatevi ve n è un altra. |
|||
|
[105v.8] CO. Io le haverò ben con l' udito, e con tutti gli occhi [106v.1] capite ma il fatto starà poi à farle. Per Dio che vi durarò grandissima fatica. |
|||
[106v.2] RO. Eh, non già |
|||
[106v.3] CO. Per mia fede, che à mio credere non le farò in un anno ben come voi, che con una certa destrezza, Agilità, et Prontezza gli date un garbo mirabilissimo. |
|||
CON: Very well, on to the seventh guard. |
[106v.4] R·Horsu alla Settima guardia |
[75r.3] CON. Horsù alla settima guardia. | |
|
Settima guardia stretta, offensiva, perfetta, formed from the mezo rovescio difensivo, from which one will be able to reset into guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta. |
How one must do the seventh guard, named “stretta offensiva, perfetta”. ROD: Wishing, conte, from some defensive guard, either stretta or larga, to make the same rovescio with all of those turns (still with the right foot forward) of the body, the hands, and the feet, as you know; it will be necessary for your sword hand in descending to not pass lower than your knee, but that you stop it outside and a span forward thereof, and that the point of your sword aim toward my chest (you see how I do it?) and this blow will be a mezo rovescio, not having made other than half the path of an entire rovescio, and it will frame you in a guardia stretta, offensiva, which will be our seventh. |
[106v.5] volendo voi Conte di alcuna guardia difensiva, ò stretta, ò larga far nascere il medesimo rovescio con quei volgimenti tutti (pur col pie destro innanzi) della vita delle mani, e de i piedi, come sapete, bisogna che la mano della spada nel discendere à basso non trascorra piu giù del ginocchio, ma che di fuori, e d'avanti di esso un palmo si fermi, et che la punta della spada guardi al petto mio (vedete come facc'io?) et questo colpo sarà mezo rovescio, non havendo fatto altro, che mezo il camino del intiero rovescio, et vi formerà una guardia stretta offensiva |
Come si debba far la settima guardia, nominata stretta offensiva, perfetta. [75r.4] ROD. Volendo voi, Conte di alcuna guardia difensiva, o stretta, o larga far nascere il medesimo rovescio con quei volgimenti tutti (pur co'l pie destro innanzi) della vita, delle mani, & de piedi, come sapete; bisogna che la mano della spada nel discendere a basso; non trascorra piu giù del ginocchio: ma che di fuori, & davanti di esso un palmo, si fermi, & che la punta della spada guardi al petto mio (vedete come faccio io?) & questo colpo sarà mezo rovescio, non havendo fatto altro che mezo il camino dell'intiero rovescio, & vi formerà una guardia stretta, offensiva, che sarà la settima nostra. |
CON: Why “stretta”? |
[106v.6] CO. Perche stretta? |
[76r.1] CON. Perche stretta? | |
Why the seventh guard is called “stretta, offensiva”. ROD: Don’t you see whether the sword is hindered in the way it is advanced toward the enemy, that to offend him it is very close? “offensiva” it is, then, through being on the right side, from whence (as I have told you many times) are born all the offensive guards and blows. |
[106v.7] RO. Non vedete voi se la spada è ristretta in modo alla presenza del nimico, che ad offenderlo è molto vicina? Offensiva è poi per esser nelle parti destre dalle quali (come piu volte u'ho detto) nascono le guardie e colpi tutti offensiva. |
Perche la settima guardia sia detta stretta, offensiva. [76r.2] ROD. Non vedete voi, se la spada è ristretta in modo alla presenza del nimico, che ad offenderlo è molto vicina? offensiva è poi per essere nelle parti destre, dalle quali (come molte volte u'ho detto) nascono le guardie, & i colpi tutti offensiva. | |
Praise of the Most Excellent S. Francesco Maria, Duca d’Urbino. CON: The Most Excellent Francesco Maria, Duca di Urbino, of his age a man of valor, knowledge, and prudence (according to a few), praised beyond measure this final guard of yours, and placed it before nearly all others. But let’s return all over again, please, Illustrious Rodomonte, and do these seven guards, as an epilogue, telling along with them the origin of each one. |
[106v.8] CO. Sia laudato Nostro Signore, [107v.1] che questa è l'ultima vostra Guardia: L'Eccellentissimo Duca d'Urbino huomo nella sua età di valor, di sapere e di prudenza, à pochi secondo: lodava oltre modo questa vostra ultima Guardia, et quasi à tutte l'altre la preponeva; ma ritorniamo di gratia da capo Rodomonte illustre e facciamo di queste sette guardie, come un Epilogo nominandole di nuovo per li proprii nomi, e dicendo insieme l'origine di ciascuna. |
Lodi dell'Eccellentissimo S. Francesco Maria Duca d'Urbino. [76r.3] CON. L'Eccellentissimo Francesco Maria Duca di Urbino huomo nella sua età di valor, di sapere, & di prudenza (a pochi secondo) lodava oltra modo questa vostra ultima guardia, & quasi a tutte l'altre la preponeva. Ma ritorniamo di gratia da capo Rodomonte Illustre, & facciamo di queste sette guardie, come uno epilogo, nomandole di nuovo per li proprii nomi, & dicendo insieme l'origine di ciascuna. | |
Epilogue of the seven guards with proper names. ROD: I am happy to do this, and every other thing for you, conte. The first guard is “difensiva, imperfetta”, generated from girding the sword at the hip, and it is a tempo, or motion, defensive and imperfect. The second is “guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta”, made from the rovescio, which is done in the drawing forth of the sword to on high, a full, defensive blow. The third is “guardia alta, offensiva, imperfetta”, made from the same full rovescio. The fourth is called “guardia difensiva, imperfetta, larga”, born from the full punta sopramano perfetta, or alternately from the mandritto sopramano, descendent down to the ground, and full. The fifth is called “guardia difensiva, perfetta, stretta”, formed from the incomplete punta sopramano, or alternately from the mezo mandritto sopramano, descendent down only as far as the right knee. The sixth is called “guardia offensiva”,[13] born from the second full rovescio difensivo. The seventh and last is called “guardia offensiva stretta, perfetta”, formed from the mezo rovescio difensivo. Behold each in order, according to how we have done them. You see now, conte, how each blow, or motion lies in between two guards, or rests, and each guard in between two blows? |
[107v.2] RO. Son per farvi questo piacere Conte mio generoso. |
Epilogo delle sette guardia co' proprinomi. [76r.4] ROD. Son per farvi questo, & ogni altro piacere, Conte. | |
[107v.3] CO. Lo vedo, e vene rin gratio. |
|||
|
[107v.4] RO. La prima Guardia è difensiva imperfetta generata dal cingersi la spada al fianco, et è tempo, o moto difensivo imperfetto. La seconda è guardia alta offensiva perfetta fatta dal rovescio, che si fa nel tirar fuore la spada ad alto, colpo difensivo intiero. La terza è guardia alta offensiva imperfetta fatta dal medesimo rovescio. La quarta chiamasi guardia difensiva imperfetta larga, nata dalla punta sopramano perfetta, et intiera, overo dal mandritto sovramano discendente fin à terra, et intiero. La quinta è chiamata Guardia difèsiva perfetta stretta formata dalla punta sopramano non [108r.1] intiera, overo dal mezo mandritto sopramano discendente fin al ginocchio destro solamente. La Sesta dicesi guardia offensiva nata dal rovescio intiero difensivo secondo. La Settima, et ultima chiamasi Guardia offensiva stretta perfetta partorita dal mezo rovescio difensivo. Eccole tutte per ordine secondo che l' habbiamo fatte noi; vedete adesso Conte qualmente ogni colpo overo moto stia in mezo di due guardie ò quieti, et ogni guardia in mezo di due colpi. |
[76r.5] La prima guardia è difensiva, imperfetta, generata dal cingersi la spada al fianco, & è tempo, o moto difensivo imperfetto. La seconda è guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta, fatta dal rovescio, che si fa nel tirar fuori la spada ad alto, colpo difensivo intiero. La terza è guardia alta, offensiva,imperfetta, fatta dal medesimo rovescio intiero. La quarta chiamasi guardia difensiva, imperfetta, larga, nata dalla punta sopramano perfetta, & intiera, overo dal mandritto sopramano, discendente fin'a terra, & intiero. La quinta è chiamata guardia difensiva, perfetta, stretta, formata dalla punta sopramano non intiera, overo dal mezo mandritto sopramano, discendente fin' al ginocchio destro solamente. La sesta dicesi guardia offensiva, nata dal rovescio intiero, difensivo secondo. La settima, & ultima chiamasi guardia offensiva stretta, perfetta, partorita dal mezo rovescio difensivo. Eccole tutte per ordine, secondo che l'habbiamo fatte noi. Vedete hora (Conte) qualmente ogni colpo, o moto, stia in mezo di due guardie, o [76v.1] quieti, & ogni guardia in mezo di due colpi? | ||
CON: I observe it plainly. |
[108r.2] CON. Lo veggio apertamente. |
[76v.2] CON. Lo veggio apertamente. | |
BOC: It could additionally be said that each action is between two potentialities, and each potentiality is between two actions, because the strike, while it is being a guard, is not yet an action, it is a potentiality; then, once the blow is actually thrown, it is an action. |
[108r.3] BOC. Potrebbesi dire anchora, che ogni atto è in mezo di due potenze, et ogni potenza in mezo di due atti: perche il ferire mentre è guardia, che anchora non è atto sarà potenza. Quando poi attualmente si tira il colpo è atto. |
La guardia è potenza, & il ferire è atto. [76v.3] BOC. Potrebbesi dire anchora, ch'ogni atto è in mezo di due potenze, & ogni potenza in mezo di due atti: perche il ferire, mentre è guardia, che anchora non è in atto; sarà potenza: quando poi attualmente si tira il colpo; è atto. | |
ROD: You speak most excellently, Dottore, that the guard is nothing else than the potential of a blow; and each particular potentiality refers to its own particular action; thus the particular guard corresponds to its own particular blow. |
[108r.4] ROD. Dice benißimo il Dottore che essa guardia altro non è, che potenza del colpo, e come ogni potenza particolare corrisponde al suo atto proprio, e particolare, cosi la Guardia particolare corrisponde al suo colpo particolare et proprio. |
[76v.4] ROD. Dice benissimo il Dottore, che essa guardia altro non è, che potenza del colpo: & come ogni potenza particolare si riferisce al suo atto proprio, & particolare; cosi la guardia particolare corrisponde al suo colpo particolare, & proprio. | |
CON: You would do for me a gracious thing, Rodomonte, if you would put these guards of yours in the form of a Tree, and divide them, as you did in the manner of the strikes, by which I retained them with more facility, and you put them in their places with more order. |
[108r.5] CON. Se la intendete voi Rodomonte, gia non la intendo io. A' me fareste piu grata cosa se mi poneste in forma d' Albero [108v.1] queste vostre guardie, e le divideste come nelle maniere di ferir faceste accioche con piu facilità io le riserbassi, et voi piu ordinatamente le poneste ne luoghi suoi. |
[76v.5] CON. Mi fareste (Rodomonte) grata cosa, se mi poneste in forma d'Albero queste vostre guardie, & le divideste, come faceste nelle maniere di ferire, accioche con piu facilità io le riserbassi, & voi piu ordinatamente le poneste ne' luoghi loro. | |
|
Tree of the Guards |
ROD: I will do it, but you will not have such copious divisions, and such a fruitful tree, as you had in that one, because then I compressed nearly all of the types of strikes simply and naturally, but here I make for you only seven guards (and all with the right foot forward), more important and useful with which to come to arms with the enemy; because all the guards that want counting are nearly infinite. |
[108v.2] ROD. Farollo, ma non havrete si copiosa divisione, e si fruttifero Albero come haveste in quello; perche ivi compresi quasi tutte le spetie di ferire semplici, et naturali, ma qui vi faccio solo sette guardie (e tutte col pie destro innanzi piu importanti, et utili à colvi che viene all' arma col nimico, le guardie tutte sono quasi infinite. |
[76v.6] ROD. Farollo, ma non havrete si copiosa divisione, & si fruttifero Albero, come haveste in quello; perche ivi compresi quasi tutte le spetie di ferire semplici, & naturali, ma qui vi faccio solo sette guardie (& tutte co'l pie destro innanzi) piu importanti, & utili a colvi che viene all'Arme co'l nimico; perche le guardie tutte chi volesse contarle; sono quasi infinite. |
CON: Divide only these seven good guards with order. |
[108v.3] CONT. Nò nò dividete pur queste sette buone guardie con ordine. |
[76v.7] CON. Dividete pur queste sette buone guardie con ordine. | |
Division of the classes of guards into seven kinds named according to their differences. ROD: Behold: a man can have his arms either on the right side, or on the left side. If on the right side, it will be called an offensive guard; if on the left side, it will be called an defensive guard. The guardia offensiva, perfetta gives rise to a thrust or a cut; if it gives rise to a thrust, it will be called “offensiva perfetta”; if a cut, “offensiva imperfetta”. The guardia offensiva perfetta will either be done high or low. If it is done high, it is said to be “offensiva perfetta, alta”; if it is done low, “offensiva, perfetta, stretta”. The offensiva imperfetta will either be done high or low. If it is done high it will be called “offensiva, imperfetta, alta”; if low, “offensiva imperfetta larga”. Now we go to the defensive guards; either they give rise to a thrust, or a cut; if a thrust, they are called “perfect”, and have a single type which we call “difensiva, perfetta, stretta”. If they give rise to a cut, it will either be wide, or less wide; if quite wide, it will be holding the sword girded at the side, and we say that it is “guardia difensiva, imperfetta”. If it is less wide, we call it “difensiva, imperfetta, larga”. |
[108v.4] RODO. Ecco; ò serà l'huomo con l'arme nelle parti destre, ò nelle parti sinistre; se nelle parti destre si chiamerà guardia offensiva se nelle parti sinistre sarà guardia difensiva. La guardia offensiva perfetta partorirà una punta ò un taglio; se partorirà una punta chiamerassi offensiva perfetta, se un taglio offensiva imperfetta. La guardia offensiva perfetta ò sarà in alto, ò sarà a basso; se sarà in alto si dirà offensiva perfetta alta; se sarà à basso offensiva perfetta stretta la offensiva imperfetta ò sarà alta o sara bassa; Se sarà alta chiamerassi offensiva imperfetta alta; se bassa [109r.1] offensiva imperfetta larga, hora andiamo alle guardie difensive ò che partorirà punta ò Taglio. Se punta, chiamerassi perfetta, et ha una specie sola, quella chiamiam noi diffensiva, perfetta, stretta, Se partorirà taglio ò sarà larga ò meno larga, se sarà ben larga serà tenendo la spada allato cinta, e la diciamo guardia difensiva imperfetta; se sarà men larga la chiamiamo difensiva imperfetta larga. |
Divisione del genere delle guardie nelle sette spetie dette per le sue differenze. [76v.8] ROD. Ecco, o sarà l'huomo con l'arme nelle parti destre, o nelle parti sinistre. Se nelle parti destre; si chiamerà guardia offensiva: se nelle parti sinistre; sarà guardia difensiva. La guardia offensiva, perfetta partorirà una punta, ò un taglio: se partorirà una punta; si chiamerà offensiva perfetta: se un taglio offensiva, imperfetta: la guardia offensiva perfetta o sarà in alto, o sarà a basso. Se sarà in alto, si dirà offensiva perfetta, alta: se sarà a basso, offensiva perfetta, stretta. La offensiva imperfetta, o sarà alta, o bassa. Se [77r.1] sarà alta, si chiamerà offensiva, imperfetta, alta: se bassa, offensiva, imperfetta larga. Hora andiamo alle guardie difensive: o che partorirà punta, o taglio: se punta; chiamerassi perfetta, & ha una spetie sola laquale chiamiam noi difensiva, perfetta, stretta. Se partorirà taglio; o sarà larga, o meno larga: se sarà ben larga; sarà, tenendo la spada a lato cinta: & la diciamo guardia difensiva, imperfetta. Se sarà men larga; la chiamiamo difensiva, imperfetta, larga. | |
The guardia difensiva imperfetta, larga is called “imperfetta” even though it produces a thrust. CON: Won’t this last guard give rise to a thrust? Why do you therefore want to call it “imperfetta”? |
[109r.2] CO. Questa vostra ultima guardia non partorirà punta? Perche la volete chiamar dunque imperfetta? |
La guardia difensensiva imperfetta, larga è detta imperfetta anchor che produca punta. [77r.2] CON. Questa vostra ultima guardia non partorirà punta? perche la volete chiamare dunque imperfetta? | |
ROD: You are correct; but we call it “imperfetta” because you uncover your body too much to the enemy, and through being very wide, you can use it in other ways than in delivering a thrust. |
[109r.3] RO. Dite il vero; ma la chiamiamo imperfetta, perche vi scoprite con la persona troppo al nimico, et per esser molto larga potete anco usarla in altro, che n menar di punta. |
[77r.3] ROD. Dite il vero: ma la chiamiamo imperfetta, perche vi scoprite con la persona troppo al nimico, & per esser molto larga, potete anco usarla in altro, che in menar di punta. | |
CON: Give to me, please, the making as a figure of this Tree, copious in such good fruits. |
[109r.4] CO. Deh digratia fatemi in figura quest'albero copioso di tante buone frutte. |
[77r.4] CON. Deh di gratia fatemi in figura questo albero copioso di tante buone frutte. | |
ROD: I am happy to please you, and here it is. |
[109r.5] ROD. Per farvi piacere son contento |
[77r.5] ROD. Per farvi piacere son contento, & eccolo. | |
[109r.6] CON. Basciolavi. |
|||
[109r.7] ROD. Eccolo. |
|||
CON: Yes, now I recall all the names; I knew that thereby I would do them well, as I intend for them. Which of these guards is the most perfect? Which is the most excellent? |
[109r.8] CON. Adesso si, che mi raccordaro de i nomi tutti, sapesio cosi ben farli come gli hò nella mente, quale di queste guardie è la più perfetta? quale è la piu Excellente? |
||
ROD: Which do you think to be of greater valor, the offensive, or the defensive? |
[109r.9] RO. Lo farò dire à voi, qual pensate che sieno di piu valore le offensive ò le difensi= |
||
The most excellent guard is the alta, offensiva, perfetta. CON: I would believe it to be the offensive. |
|||
ROD: Among the offensive isn’t the perfect more excellent than the imperfect? |
|||
CON: The name says it. |
|||
ROD: Among the offensiva perfetta, the high or the low? |
|||
CON: It seems the high, which uncovers more of the enemy’s body, and can offend it more with all of one’s strength united, with all of the body, with all the muscles, and that can offend it in the more vital and nobler parts. |
|||
Praise of the guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta. ROD: You have spoken excellently. You see therefore that the guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta is of greater perfection, and more valorous. This is the most apt guard with which to offend the enemy with grave harm, and to defend oneself marvelously at the same time. Requirement that a knight consider well the equality or inequality of his adversary. If it happens then that the enemy should be smaller than you, and you place yourself in this guard, he will never put himself at risk by coming against your directed 99 point; and if he is clever, he will remain well distant, because this is a necessary condition of a good knight, to consider well the equality, or the inequality of his adversary. |
|||
Praise of the Illustrious Signor Conte Ugo Pepoli. CON: If the Illustrious Signor conte Ugo, house holder, man of such valor, art, and knowledge that he is the chief Italian close to His Most Christian Majesty, has this guard for his favorite, and is well practiced in it, being large of frame, and well proportioned, he has good reason; because he has thereby among other knights (allow me to say) the greatest advantage. |
|||
ROD: You are correct, conte; it is of great consequence to be of large stature, and have good proportion of limbs, and then to have cunning and great learning, as has conte Ugo. |
|||
BOC: Our conte Ugo in truth has done a thousand beautiful enterprises, and has brought excellent fame to his country in distant lands. He is certainly a man with a great heart, and of perfect judgment. |
|||
CON: This guard is marvelously even more pleasing to the Most Serene S. Duca Alberto di Baviera, than whom it is not possible to find another more judicious, and more supportive of all the belles artes and the noble disciplines. |
|||
ROD: If for no other attribute and virtue were this Serene Prince to deserve to be praised and exalted, he would merit it for his constant and steadfast firmness in defending the Holy Catholic Religion in the midst of so many others who contradict, and do not wish to accept it. And to me it seems that this praise exceeds every greatness, and every glory, which has come to his house from so many Emperors, that he has had. |
|||
BOC: After this you must put in second place the favor that he has done to letters, and to the lettered; which I understand, being among the favored, and highly awarded. |
|||
CON: Not only the lettered, but all the nobly learned have refuge and entertainment under this high and generous Prince. And I would like, Signor Dottore, for you to see his library, and then you would genuflect, for he has stocked it in every way at incredible expense, and I say as much, that here is my final opinion, that he has assembled books in every faculty for more than twelve thousand scudi. |
|||
ROD: I understand that he has apparently innumerable abundances of jewels of inestimable worth. |
|||
CON: If I said to you that I had seen about him cases full, you would think me lying; and only of a knight could you believe what I have seen. But you know that all the greatness of this great prince is achieved by another, not one point less. |
|||
BOC: And which is this? |
|||
CON: The Principe Guglielmo, his son. Now here I would like, Dottore, that you fixate yourself to contemplate this noble young man, full of holy and Catholic zeal, entirely ardent of charity against poverty, wholly given over to pondering things abstract and remote from the common science of others. And without doubt you will judge that this must turn out to be a most clear example of virtue, of goodness, of generosity, and of humanity above all others. But tell me, Rodomonte, now that we have seen the seven guards, don’t you wish to teach me the schermo you proposed to me? |
|||
ROD: As you like. |
|||
CON: It would delight me greatly to know it, if it did not trouble you to show me. |
|||
ROD: And I take the greatest delight in showing you. |
|||
BOC: The sign of the wise man is the ability to teach others, as does Rodomonte today; he both can, and wants to teach you. |
|||
Who knows how to do the punta sopramano well, knows that which matters more in employing one’s hands, either suddenly or thoughtfully. ROD: I tell you, conte, that whoever will want to know well how to use the schermo to offend, and defend himself, will need to know how to do that punta sopramano well, with all those turns of the body, and of the hands, and of the feet, as I have shown you, and with all those gestures, and with that refined bodily grace, to such extent that he does it with great facility. And if he does this, he can indeed claim to have that understanding, which is of greater need in employing one’s hands, either suddenly, or thoughtfully. Way of doing the proposed schermo. And so that you can understand this safe schermo of ours well, behold, I repeat, and say, How from guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta one must execute the punta sopramano. that finding yourself with your right foot forward in guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta, and with your weight on your left side, How one can do the punta sopramano perfectly. and wanting to execute the punta sopramano, and do it perfectly, you must always accompany the sword hand with the right foot together with the entire body, as much with the upper parts as with the lower, and not allow the lower right parts to go forward without the company of the upper right parts. |
|||
CON: Why? |
|||
ROD: In order that you be able to put all the strength of your body to your service; but when you have in mind to do the punta sopramano, make the right foot move itself, and go forward a big step, and immediately make the left arm begin to descend, and the right shoulder to propel the arm forward, dropping with the point from high to low, taking aim at my chest, without making any turn of your hand, pushing it so far forward and so long as you are able. How from the punta sopramano one must go into guardia difensiva, larga, imperfetta. In this tempo the heel of the left foot will follow the right, not moving, however, the point of the left foot from its place, then turning the wrist of the sword hand together with the true edge toward the left side, and immediately descending down to the ground, withdrawing the right foot somewhat back, and making the point of your sword draw a line on the ground and travel behind you on the left side, and after the right foot finally is a span from the left foot, the right shoulder then will find itself very low, and the left arm will be behind, and high, and extended forth toward the left side; the feet remain even, but the point of the right foot will point out toward the right side, and the point of the left foot out toward the left side, your shoulders will be looking at the enemy more than your forward side, and your weight will be placed on your left side; thereby you will find yourself in this guardia difensiva, larga, imperfetta. Advisement that one not rest much in some defensive guard in this schermo. But I advise you well, conte, that you not make a long stay in one of the defensive guards, low, or wide, or narrow that it may be; but make your right hand turn the point of the sword somewhat to the rear by the outside on your left. How one must do the rovescio tondo from the guardia difensiva, larga, imperfetta. And traveling from low to high as far as your left shoulder, the true edge will turn toward me, and the false edge will face your left shoulder; and here you must unite all the strength of your body together with both arms somewhat bent and pulled in, from which you can immediately deliver a rovescio, almost tondo; but do not uncouple the right arm from the strength of the body, and make the rovescio go no higher than your shoulders, the point not be higher than the pommel, nor the true edge higher than the false, but the flat of the sword to face toward the sky; the right leg along with the foot does not move, but the left turns somewhat on the point of the foot with the heel lifted up a bit from the ground; How from the rovescio tondo one turns into guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta. the rovescio does not have to pass through the guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta, rather, stop in the said guard, and the right arm must be bent, going with the elbow back as far as you can to the outside on the right side, and the right hand is not higher than the right shoulder, and the point of the sword aims at my face, the left shoulder remains somewhat ahead of the right, and the left arm will be in front of your chest with your hand toward your right side. And place your weight on your left side, in order to have your right leg free and agile. How, having done the schermo once in order to address the enemy, one must then repeat it in order to strike. And wanting from the said guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta, to do again the above said thrust, you must lift your sword hand up somewhat high, and turn the true edge toward the sky, and the point will then be lower than your hand; and immediately, with your right foot forward, take a big step toward me, and in the same tempo, drop that point from high to low toward my chest. And in the lowering of the sword toward your left side, you must not let it stop long in some low defensive guard, but make it travel from low to high toward your left shoulder, making immediately the rovescio tondo, which terminates in the guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta; but make the flat, or plane, of the sword be face up, and not the true edge, not forgetting to do all those turns of the body, of the hand, and of the feet mentioned above. And thus doing these many turns you will very well comprise the punta sopramano, offensiva, perfetta, together with the rovescio tondo with all those gestures and turns of the body. But take heed, that if you were smaller than your enemy, you would have a great disadvantage settling yourself in this manner. Do you see how I do this whole schermo entirely with ease? |
|||
CON: I’m watching, but I will not be able to do it soon. |
|||
Praise of the Most Illustrious S. Duca Ottavio Farnese. ROD: You will be able to do it sooner than you believe, having judgment and disposition in arms, as did the Most Excellent Signor Duca Ottavio Farmese, who, hearing it, and hearing it from me, imagined himself to have to toil long before he would learn it well, and then in the shortest time he became a more perfect master of it than I. |
|||
Praise of the Most Illustrious House of Farnese. CON: I believe it, because he is of the most subtle and acute wit, and apt to every work of judgment, as though he and all of his most illustrious house were favored beyond custom by nature in every enterprise wherein is required agility of body and strength of mind. |
|||
What entirely comprises this schermo. ROD: If we live, conte, we will see this Signore the chief of all the knights and Signori, he being blessed with valor, virtue, and knowledge. But returning to our proposition, I tell you that this is my schermo, composed of the most perfect offense, and of the most perfect guards that there are, namely the guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta, and the punta sopramano, offensiva, perfettissima. There you have also the rovescio tondo, a good defensive blow, and the guardia difensiva larga. |
|||
CON: It is not, therefore, a tempo, as you said. |
|||
Although it does well appear that this schermo is not done in one tempo, nonetheless by the speed of defending and offending it is in a single tempo. ROD: On the contrary, as the schermo is one, thus is the tempo that accompanies it one; and as the schermo has two blows done successively without an intervening guard, namely the rovescio tondo and the punta sopramano, and has two guards; thus this tempo of yours is in turn composed of two tempos, successively issued, and two rests. |
|||
BOC: You speak excellently, Rodomonte, except that the rest is measured by the tempo, and it seems that you distinguish the tempo by the rest. |
|||
ROD: In accord with our discussion, by “tempo” I intend “motion”, not the number of the motion, as you mean. |
|||
CON: Listen to me a bit, please, Rodomonte; if you came against me wishing to offend me, what should I do? |
|||
ROD: Come against me always in guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta; but not, however, in a mind to offend me immediately; because if we were both of equal height, then we would offend each other equally, using the same offense in the very same tempo, and if I were taller than you, it could easily occur that my point offended you, I remaining without any harm, or at least with much less. |
|||
CON: So you want me to always use this guard? |
|||
One should always use the guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta, appropriate to defend oneself in every case. ROD: Yes Sir, because it is always the most perfect, and better than others in order to defend yourself in every dangerous case. Look; if I were settled in guardia alta, offensiva, imperfetta, wanting to offend your head with a mandritto from high to low, what protection would you find, conte, from that fendente? |
|||
In order to defend the head from a mandritto, discendente. CON: I would reset myself in guardia stretta, difensiva, formed from the meza punta sopramano with the right foot forward; and when your mandritto fell, I would lift my sword going against yours, as if I wanted to form another mandritto, but in such a fashion that the point of my sword did not fall, but rather went higher than my pommel, holding my arm well extended. In this fashion the swords would connect each other true edge to true edge, in the manner of a cross. |
|||
One defending oneself from a mandritto discendente with a mandritto ascendente cannot in any way offend his enemy without great danger. ROD: This is the common schermo that all the Masters teach, and the greatest part of combatants use; but this is not a good protection for defending your head, because you cannot deny, conte (following reason) that the blows which fall from high to low are superior to those contrary ascending blows; hence with my falling blow I could so encumber your sword that you could still be harmed. And if it happened that you did defend yourself, how would you escape that thicket of my having wanted to harm you? CON: I would turn the point of my sword to my left side, over yours, and from there I would offend your head with a rovescio. |
|||
ROD: While your rovescio travels, my sword, which remains in descent, will soon fall and offend you in the head in this fashion. |
|||
CON: I would therefore lower the point of my sword toward my right side in such a way that yours had to take a path to drop by my right side down to the ground; because such would be its travel; where lowering, or not lowering your sword, I would send it toward my left side without moving the fist that holds my sword, and then I would drop from high to low with a rovescio to the right side of your head, and do it like so. |
|||
ROD: And I, in that very same tempo, would turn my true edge against yours, encumbering it, and I would remain defended, and what is more, I could offend you with a rovescio to your right arm, like so. |
|||
CON: Therefore I would cross the swords as I did earlier, that is, true edge to true edge, and distancing mine from yours somewhat, I would drop with a mandritto to the leg on your left side in this fashion. |
|||
ROD: But during all that, couldn’t my sword finish falling, and offend you indeed in your upper body, in the tempo in which you drop to my leg? See? |
|||
CON: In fact this is true. |
|||
ROD: Return at ease to guardia stretta difensiva. |
|||
CON: Here you are. |
|||
Various feints against he who wished to defend himself from a mandritto discendente with a mandritto ascendente. ROD: If you don’t make some other block than this earlier one of yours, then I, settled in guardia alta, offensiva, imperfetta, as you see, could feign to offend you with a mandritto discendente to your head, and you defending yourself with another mandritto of your own, I will then be able, in dropping from high to low, to make my sword not to touch yours (in this fashion) and offend your right arm near the hand, and then retreat, so that you remain with your arm struck. I could also go to find your right leg instead of your arm, and then retreat; I could make a feint that I want to offend you on the right side of your head, by making only a half turn of my wrist; I could also feign to want to offend you from high to low with a mandritto, and immediately turn the point of my sword forward, into the manner of the guardia alta, offensiva, perfetta, and from here drop from high to low, and stick this punta sopramano into the middle of your chest, and then promptly retreat. Do you see, conte, how many feints I could make, only as a result of you being settled in guardia stretta, difensiva, against my guardia alta offensiva, imperfetta? And through defending yourself from my mandritto discendente with your opposite mezo mandritto? This is, therefore, not the good parry. |
|||
CON: What, then, should I do? |
|||
A better defense to all the enemy’s blows is to beat aside with a mezo rovescio tondo and in one tempo offend, thrusting the punta sopramano. ROD: It behooves you (to deliver your enemy some desired blow) that (being in that guardia stretta, difensiva with your right foot forward) you turn the point of your sword toward your left side, diagonally, so that the point faces that same side, and the pommel is on your right, as if you wanted to lay hand to the sword, and from here uniting all the strength of your body together, do the same rovescio tondo with those same turns of the hand and the feet of which I have told you, and in the same manner; When it is possible to break the enemy’s sword. but pay heed that in this delivering of the rovescio, the swords meet each other true edge to true edge, but that the forte of your sword will have met the debole of mine, whereby mine could be easily broken by virtue of the disadvantage of such a meeting, and also because of the fall of the cut; and you will also be more secure, being shielded by the forte of your sword. |
|||
CON: How should I avenge myself of the insult? |
|||
The punta sopramano is called “Great blow”. ROD: While my mandritto is beat aside by your rovescio tondo, it will go by your right side; lift up your sword hand somewhat, and turn the true edge toward the sky, and make the point of the sword drop somewhat, and move yourself toward me with your right foot forward with a big step, and then immediately drop your left arm, and make your right shoulder throw your right arm forward, declining toward me from high to low, with that punta sopramano offensiva, accompanying it in all of the said manners; and if I do not give you a response with some blow, do not halt there, but lift your sword, and going with it a span forward of your right knee, you will fix yourself in guardia stretta offensiva, perfetta; this is a perfect offense, which you must do following the insult received from me, and following your defense. But if I turned to some other blow in order to offend you, then you, with the same rovescio tondo, will always be able to beat back my sword toward your right side, and return to offend me in the chest with the same punta sopramano, offensiva, perfetta; and thus after you defend yourself, you will always be able to offend me again in the chest with the punta sopramano perfetta; therefore it is the most perfect and secure blow that can be found, and to express it succinctly, this is called “Great blow”, because it is necessary to make a conjoining and a union of all the strength of the body, of the wits, of the senses, and of the art; and accompanying the said blow, reveals one to be endowed with knowledge, with heart, and with temperance. Watch, I pray you, how I do it. |
|||
CON: I am watching, and with great happiness. |
|||
BOC: You have done the same schermo that you taught him a little ago, having said it anew, part by part. |
|||
ROD: And you philosophers, will you not make to the limit of your abilities, an epilogue, containing in brief the substance of the entire work? And accordingly, I, in order to show him how good and perfect this, my schermo, is for offending and for defending, have shown him in this particular case of how much power it is; tomorrow, then, I will show him of how much importance it is in every way that can be done, both of offense and of defense; but now I am ever so wearied, and we have already had swords in hand for nearly two hours; I would not like the conte Ugo to wait for me overlong, for we have to ride together for recreation. Oh, have you nothing to say, conte? |
|||
This schermo can be reduced to a perfect guard and offense. CON: I am full of amazement, seeing how utterly perfect is this schermo of yours, and fundamental to all wielding of the sword; but how have you reduced everything to a perfect offense, and to a perfect guard? |
|||
BOC: If our Aristotle entirely reduces the ten Predicaments under two headings, “substance” and “accident”, or, we wish to say better, under “action” and under “potentiality”, as each thing will be either an action or a potentiality, similarly does the unvanquished Rodomonte reduce under these two headings all his art: that is, under “offense”, which is action, and under “defense”, or “guard”, which is potentiality; and in taking the most perfect action and the most perfect potentiality, has therein enclosed every other inferior action, and every other inferior potentiality. |
|||
CON: Rodomonte could have struck me a thousand times today with that thrust, yet he wanted that I might make some parry thereto, and this although I have learned something from many most skillful men, and Masters, and have practiced now and then. |
|||
BOC: It may be that if you were earnestly at blows, that Rodomonte would have the worse, if he lacked luck. I have seen the most skillful and practiced men many times do worse than others unpracticed in battle. As I could clarify to you by many examples, ancient and modern. |
|||
CON: This I do not believe. |
|||
Why he who does this schermo more, often fares worse in the quarreling. ROD: The Dottore speaks truly; I believe that this happens for one of two reasons: the first is that the man blessed in this art is wanting in courage, or in choleric temperament; the other is, that many times the man, through excessive courage and art, is sensed to make an error, as a result of which he is overcome and vanquished. It may also be said that fortune may be the cause of this; she, as the enemy of virtue, cannot endure that one who is virtuous advances himself with aid other than hers, fearing that the people will abandon her and thereby have recourse to virtue. Luck most often aids the ignorant. Do you not see, conte, that if the virtuous advance themselves, it would be believed that they were advanced through their virtue, and not through the benefit of fortune, so that every man would give himself to virtue, abandoning fortune entirely? And thereby it is seen that she most often aids the ignorant. |
|||
BOC: This is most lovely reasoning. I will therefore remain without learning this virtue of arms of yours, placing myself in the hands of fortune, which will aid me in such occasions. |
|||
Although luck is the enemy of virtue, one must not, however, remain without learning. CON: And who knows whether fortune will succor you? Hence who can swear thereunto one jot? Whereof, being thus uncertain, it will be necessary that you, fearing, undertake to succor yourself with virtue and with art. |
|||
ROD: It is time that we go, because there waits the conte Ugo; tomorrow, then, we will do another bit of practice, conte, and we will talk over this schermo, as much as we haven’t been able to talk today. |
|||
CON: You are right; indeed, let’s go. |
|||
BOC: And I will return to see you again tomorrow. |
|||
ROD: And we will look forward to it. |
For further information, including transcription and translation notes, see the discussion page.
| Work | Author(s) | Source | License |
|---|---|---|---|
| Illustrations (Cod.10723) | Österreichische Nationalbibliothek | Österreichische Nationalbibliothek | |
| Illustrations (Book) | |||
| Translation | W. Jherek Swanger | Document circulated online | |
| Transcription | Index:Trattato d'uno Schermo (Cod.10723) | ||
| Transcription | Index:Lo Schermo (Angelo Viggiani) |
Additional Translation Terms: All rights reserved. Copyright 2002 by William Jherek Swanger. No part of this work (excepting images, which are in public domain) may be reproduced or transmitted by any means or in any form, electronic or mechanical, without prior written consent of the author/translator, subject to Fair Use in the Copyright Act of the United States of America.
Or, to put it more bluntly, feel free to make a thousand printouts of this work for individual and group study, as long as you leave the copyright and credits on it. But trying to make any money off of it is strictly out of the question.
Additional Resources
The following is a list of publications containing scans, transcriptions, and translations relevant to this article, as well as published peer-reviewed research.
- Gotti, Roberto (2023). "The Dynamic Sphere: Thesis on the Third State of the Vitruvian Man." Martial Culture and Historical Martial Arts in Europe and Asia: 93-147. Ed. by Daniel Jaquet; Hing Chao and Loretta Kim. Springer.
- Runacres, Rob (2022). "The Bolognese Tradition: Ancient Tradition or Modern Myth?." Acta Periodica Duellatorum 10(1): 1-18. doi:10.36950/apd-2022-002.
- Viggiani, Angelo (2017). The Fencing Method of Angelo Viggiani: Lo Schermo, Part III. Trans. by W. Jherek Swanger. Self-published.
- Viggiani, Angelo (2019). Angelo Viggiani: Lo Schermo (Book III, English Translation). Trans. by Tom Leoni. Self-published.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Unspecified service to Charles is mentioned in his brother's dedication on page 3.
- ↑ Literally, “Braggart”.
- ↑ Literally, “Iron Mouth”.
- ↑ It is conspicuous that in every other instance in the present text, (at least, in the sections translated here) Viggiani uses the term “da giuoco” (of play/practice) to refer to practice arms. Sydney Anglo (The Martial Arts of Renaissance Europe p.324, footnote 102) refers to evidence showing that in late 16th century Spain the spada da marra was considered to be an Italian equivalent of the spada negra, a blunted weapon with a button, and discusses the significance of the different terms. “Marra” in modern Italian is “hoe, fluke of an anchor”, and is given by Florio (A Worlde of Wordes, 1598) to mean “a mattock, a spade, a shovell, a rake to mingle sand and lome together, a pickaxe, or such rusticke instrument.” Thus “spade da marra” may simply mean “swords of blunt metal”, and represent a standard type of practice weapon. Of possible relevance, “smarra” is used to refer to the practice rapier by Marcelli (Regole della scherma, 1686) and others, presumably as a linguistic descendent of “spade da marra” (Gaugler, The History of Fencing, 1998, p. 92); turning again to Florio, “smarrare” is given as “to pare or shave down” and so “smarra” may simply derive from the meaning of “a sword whose point has been pared down”, rather than a contraction of “spada da marra”. It is intriguing to speculate that the term was originally pejorative, suggesting something akin to “swords like shovels”.
- ↑ Psalm 45:3.
- ↑ The word for which I substitute the phrase “dull edge” is, in the original, “costa”; the relevant meaning given in Florio is “the back of a knife”. Viggiani uses it to refer, first, to a dull false edge (as in a backsword); and second, to a dull portion of either the false, or, more likely, both edges (as an extended ricasso). I am unaware of a discrete word in English that could stand in adequate stead.
- ↑ Psalm 149:6-7.
- ↑ This is almost certainly an error in the original. The text reads “se nascerà la punta dalle parti dritte, chiamerassi punta rovescia”. This is, of course, the complete opposite of what is meant by “punta rovescia”, and Viggiani immediately contradicts this statement on pg. 56V, endnote immediately following.
- ↑ Here the correct definition (contrary to the preceding endnote) is given: “Se si ferirà con la punta, o nascerà dalle parti diritte, & chiamerassi punta diritta, o dalle parti stanche, & chiamerassi punta rovescia…”
- ↑ "C" is upside down.
- ↑ Interpreting this maneuver is problematic. It may refer to the practice of arresting a fendente by meeting it at the agent’s hand, hilt, or at worst, forte; yet no mention is made of the patient closing distance to do so, creating the impression of simply putting a hand or forearm in harm’s way rather than take the blow in the head. The relevant passage in the original is “…il suo braccio stanco tien cura, & custodia della testa in pigliare il colpo con la mano, o in ritener co’l braccio la forza sua…”
- ↑ A braccio is a unit of length of approximately 60 centimeters. The specified distance is therefore about 30 cm, or one foot.
- ↑ This is, of course, in full, “guardia larga, offensiva, imperfetta”.