|
|
You are not currently logged in. Are you accessing the unsecure (http) portal? Click here to switch to the secure portal. |
Difference between revisions of "Die Blume des Kampfes"
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
{{hidden begin | {{hidden begin | ||
| − | | title = <span style="font-size:130%;"> | + | | title = <span style="font-size:130%;">Spear, Sword and Shield in Armor</span> |
| titlestyle= background:#f2f2f2; border:1px solid #aaaaaa; padding:10px; text-align:center; vertical-align:middle; width:60%; | | titlestyle= background:#f2f2f2; border:1px solid #aaaaaa; padding:10px; text-align:center; vertical-align:middle; width:60%; | ||
| bodystyle = display:block; width:140em; | | bodystyle = display:block; width:140em; | ||
Revision as of 19:03, 28 March 2014
| “Die Blume des Kampfes” | |
|---|---|
| The Flower of Battle | |
| Author(s) |
|
| Ascribed to |
|
| Illustrated by | Unknown |
| Date | before 1420s |
| Genre | |
| Language | Early New High German |
| State of Existence | Original hypothetical; multiple incomplete copies exist |
| Manuscript(s) |
|
| Concordance by | Michael Chidester |
Die Blume des Kampfes (“The Flower of Battle”) is a nickname given to a group of three German manuscripts that share a common technical syllabus and set of illustrations. It might be based on the tradition of 14th century Italian master Fiore de'i Liberi, from whose treatise Fior di Battaglia it derives its nickname, given that his works include considerable technical overlap. It is equally likely, though, that they represent an earlier German tradition of which Fiore was himself an initiate. Fiore mentions in his prefaces that he owned books on the art and he also names two older masters in his tradition, Johane Suveno and Nicholai de Toblem; it is possible that either or both of those masters authored texts which inspired both this tradition as well as Fiore's own writings.
The oldest manuscript in the Blume des Kampfes group is the Cod. 5278, which dates to the late 1420s and contains only crude line drawings somewhat reminiscent of the art of Fiore de'i Liberi, though lacking many signature characteristics such as garters and crowns and generally less organized than the Friulian master's work. The second entry was completed in ca. 1500 by Ludwig VI von Eyb, and contains a significant degree of overlap with the 5278 but also a wealth of new material. While the artwork, though colored, is of similar quality, Eyb's treatise improves on its predecessor by including detailed German descriptions of the devices in most of its sections. Whether this text was authored by Eyb or present in the sources upon which he based his work cannot currently be determined.
The final manuscript, Cod. 10799, dates to 1623 and is again textless. Unlike its fellows, though, it is illustrated with watercolors of high quality; it is also the most extensive of the three by far, encompassing nearly every device from both works as well as a number of unique devices that suggest that it was either not derived directly from the other two known manuscripts or that it used additional sources currently lost to us. The two older manuscripts include war books derived from Konrad Kyeser's famous treatise on siege warfare Bellifortis, and the copyist of the 10799 also included the few Bellifortis illustrations that seem to portray knights and soldiers, perhaps indicating that he did not understand what he was copying.
There is a fourth Germanic manuscript potentially connected to this tradition, the Cod.Guelf.78.2 Aug.2º. This manuscript, dating to between 1465 and 1480, includes a version of Johannes Liechtenauer's record, a complete set of illustrations from Gladiatoria, and a heavily-abridged version of Bellifortis. Tucked away amidst these works are illustrations of fencing with sword, spear, axe, and dagger that parallel the teachings of the Blume des Kampfes but only occasionally replicate them exactly. While this may simply be a case of an overambitious artist reinterpreting the manuscript art he was copying, the differences are too many to include the manuscript in the concordance below.
Contents
Treatise
Like Fior di Battaglia, die Blume des Kampfes treats grappling, dagger (including dagger against sword), sword both armored and unarmored, poleaxe/halberd, spear, and mounted fencing; it also includes unique content such as armored sword and shield and dueling with longshields. In comparison to its Italic counterpart, the Germanic works place a much greater emphasis on armored fencing, doubling or tripling the number of devices, and also dwarf Fiore's own rather brief treatment of unarmored grappling. The dagger, sword, and polearm material is all more or less consistent across both traditions, and where available the explanatory text, though unconnected to that of Fiore, demonstrates a similar understanding or interpretation of the techniques.
Images |
Erlangen Version (1500) |
Vienna Version I (1420s) (?) |
Vienna Version II (1623) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
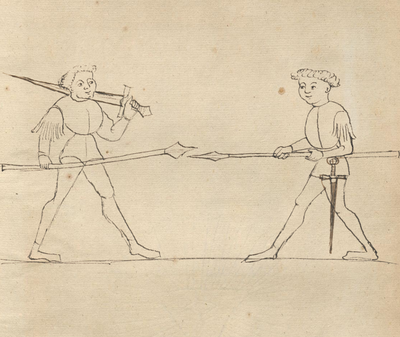
[1] [No text] |
[182r-a] [No text] |
[007r] [No text] | ||
[2] Note: a good deceptive duelling technique (kampffstuck) on foot, in armour. When you are in the Arena and want weapons and want the end to be promptly given—then take your sword exposed by the blade in your left hand so that the point stands upright and your [spear]spike ascending in your right hand.And if he then steps toward you with his spear, and he proceeds to charge at you, then prepare to throw [yours] at him, and yet you do want to exchange throws with each other, then profur him at the third moment throw the Spear strongly at him and so you run at him while the shot causes him concern and he must parry the spear away—then seize your sword by the hand and hilt, and shove it strongly at him, and whilst he attempts to recover, then go at him and fall in under him to penetrate in with both hands and arms onto his, or by the arse, and pull him strongly toward you. During the pull, place your head low on his chest, and penetrate and break him high on his chest with the head quickly, over your arm on to his back, and do this bravely and quickly with your force, so you will freely succeed, so must you also learn well how to shoot forward with the spear and sword. |
[21r-a] [I]Tem ein gut tewsch kampffstuck zu fuss In harnisch Wan dw dich Ring wilt wappen / vnd pald endt wilt geben – So nym dein swert plos bey der klingen In dein lincke hant das das ort vbersich stee / vnd dein spitz In dein Rechte handt auf stigen vnd trit ainer gegen dir mit seinem spiess / vnd will sich mit dir stechen / so dro Im zu schiessen / vnd thue doch zwir sam dw In an schiessen wollest so versticht er zu dem dritten mall scheus den spies starck In In vnd Im den schus lauff mit Im ein / dieweil er den schus besorgt so lauff dw In seinem spies ab vnd In dem lauffen So ergreiff dein schwert bey der hand hab vnd dem gehiltz vnd schews es auch starck In In / vnd In dem schus ee er sich des erhole / So bist bey Im vnd fall In unten mit drin baiden henten vnd armen an bey seiner mit Oder bey dem ars / vnd zuck In starck zu dir / vnd In dem zucken setz Im dein kopff vnten an sein prust vnd dringt vnd priche in oben mit dem kopff gar reschlich bey seiner prust vber dein arm an seinen Ruck / vnd thue [da]s als kunlich vnd reschlich mit deiner krafft / So gelingt dir freylich auch mustw vor schiessen lern gar woll mit dem spies vnd schwert |
[165r] [No text] | ||
[3] A shot[1] with the spear: take your sword by the blade in your left hand and spear in the right hand. Angle the [spear-]shaft forward, and raise the hilt of the sword to place them together[2] to quite spontaneously[3] charge at him. And if he runs in directly at you whilst you are justly charging, then thrust upwards quickly with the sword and with the shaft hand, and shoot in at him. And whilst there is this protection (schutz), then run in at him with the sword and stab. With this action yet he cannot yet come around to his sword, and thereby tackle (unterlauff[4]) his spear as well so that he may not have a shot at you and thus stab at him quite hard until he comes in to the sword. |
[16v-a] [E]in schiessen mit dem spiess Nym dein swert In dein lincke handt bey der klingen vnd den spiess In die rechte handt vnd ker den schafft fur sich vnd leg In auf das swert gehiltz sam dw gar Torlich gen Im laufst vnd wen er dir In dein Rechten rennen sey / so stoss mit dem swert vnd der handt den schaft reschlich vbersich vnd scheus In an vnd In dem schutz so lauf mit dem swert In In vnd stichen so kan er aber / zu seim swert nicht kemen hat ers vor nicht heraussen vnd vnterlauff Im den spies auch das er dich nit ge / schissen mag vnd stich In gar hart bis er zu dem swert kimbt |
[146r] [No text] | ||
[4] Either a shot with the spear or with the sword, such that someone cannot be guarded from it, and also someone cannot be sure whether you will shoot. Thus take the spear or the sword in hand and turn the point (spike, spitz) towards him, and shoot low in front of you, so that you may well dissipate a strong shot. Also do not pull it upwards because the opponent will rightly want to take a shot. And similarly, if you notice that he wants to do, then tread yourself away. |
[17r-a] [O]der ein schiessen mit dem spiess oder mit dem swert das [m]an sich darvon nicht gehutn kan vnd / man merck sein auch nit ob dw schiessen wilt / So nym den spies oder das swert In die handt vnd ker die spitz gegen Im / vnd scheus vnten fur dich / so magstw wol ein starcken schuss verpring[e]n vnd zeug auch nit vbersich auff als man von rechts wegen schiessen soll wan das selb merck man woll / vnd trit dir auss |
[148r] [No text] | ||
[5] A good shot or stabbing blow with the spear, and in this you go quite maliciously and discretely against someone:[5] So take the spear forward to wield in both forearmed upturned[6] hands. Angle your right side arm and leg forward, so that if someone steps toward you with a sword or spear it is then that you want to reveal your spear, and in doing so you may well allow him to run right up to the half-spear, then at that point, step back quickly with your right leg so that you let your spear go around above the head in your right hand, so you may have your spear sufficiently ahead of you and thus may your spear strike him well with the iron[-point], or else shoot it in whatever way you want. That means you go quite level and proceed directly. |
[16v-c] [E]in guter schuss oder schlag stich aus dem spiess / vnd get gar schlechtlich vnd verholen zw das dw gegen ainem [?] so nym den spiss In paid gewappent verwant hendt / vnd ker dein Rechte seitten pain vnd arm fur trit den[?] ainer gegen dir mit einem swert oder spiess vnd will dir dein spies ausweisen / so magstw In woll lassen lauff[?] biss zw halben spiess / so trit dan gar Reschlich mit dein rechten pain zu ruck vnd In dem trit so las dein spies vber dein kopff vmb gen yn deiner rechten handt / so wirt dein spies kurtz gennug vor dir vnd magst also dein spis woll In In schlahen mit deiner eissen oder schiessen was dw wilt / das get dir gar eben vnd geradt darauss |
[147r] [No text] | ||
[6] If you want to take a shot at someone with the spear, then jump or step always outside him on your left side, so he cannot then hit you if the shot is always struck at your right side and at his left hand. |
[17r-c] [W]ill dich ainer schiessen mit dem spiess / so spring oder drit Im aus albeg auf dein lincke seitten / so drifft er dich nit wan der schuss albeg slugt auf dein rechte seitten vnd auf sein lincke hanndt |
[149r] [No text] | ||
[7] [No text] |
[182r-c] [No text] |
[008r] [No text] | ||
[8] A good charge (einlauffen) when in armour with the spear: Take the spear and the sword together in both hands and wield the sword discretely so that someone will not notice it. And when someone steps toward you with a spear and has his sword separate when he charges lancingly (stecken[7]), and he attempts to stab at the same time as you, then strike his spear away and run in at him with the sword and stab him. And also stab him upwards from below four times, so is he disarmed with a break against his armour. Then you try to stab him to death, until he goes to draw his sword, and then you jump backward so that he cannot retaliate, and go again towards him according to your advantage. |
[17v-a] [E]in gut einlauffen In harnisch mit dem spies Nym den spies vnd das swert zusamen In paid hendt / vnd nym das swert verhollen das man es nit wol merckt vnd drit ainer zu dir mit einem spies vnd hat sein swert In der schaiden stecken / vnd sticht sich mit dir / so slag Im den spiess aus vnd lauff mit dem swert zu Im vnd stich Im auch vier stich vnten auf / ist er nit gewappent mit ainer harnasch pruch / so stich dw In zu todt bis er zv seim swert kumbt / vnd spring den hinter dich das er dich nicht ergrewff / vnd gee dan wider zu Im nach deim fortaill |
[150r] [No text] | ||
[9] Yet again quite a good technique against forearmed hands using the Spear:If you step towards someone with the spear, then reduce the distance between your hands [nym In kurtzer In die handt] than his is, and if he wants to stab at you this way, then rebuke[8] (parry) his stab away with the spear, and whilst you parry, step toward him and stab him with your spear through the surcoat between his legs and let it slope down [hangen], during whatever you then drive at him. So twist in the spear firmly, release your rear grip to seize it over your back, so as to reach in with the spear through his legs. Allow the point to go to the ground and lift the shaft up strongly in front of you. And so, with it in the ground between his legs, throw him on his back. |
[17v-b] [A]ber ein gar gut stuck zu gewappenter handt aus dem spies / wen dw zu einem dritzt mit dem spies so nym In kurtzer In die handt den er den sein vnd wen er dich will anstechen so weiss In den stich aus mit dem spies vnd in dem weisen vnd trit zu vnd stich Im dein spies durch den wappenrock zwischen sein pain / vnd las In hangen / was dw den mit Im treibst / so ret In der spies gar fast felst dw aber des rucks so far Im mit dem spies durch sein pain / vnd las den ort auf die erden gen vnd heb den schafft vor dir starck auf vnd auch In mit dem zwischen sein pain der erden vnd wurf in an den Ruck |
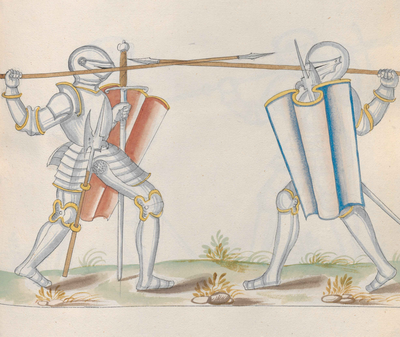
[185r-b] [No text] |
[151r] [No text] | |
[10] Note; Here there are three techniques described in sequence:The first is a throw with the spear, the other a low stab with the sword, the third is a high stab with the sword and these three deceptive techniques are for when duelling with someone in armour and forearmed in accordance with the German customs of duelling. So take your spear in your right hand in order to throw. In your left hand take together both a Pavise[9] and a sword with a heavy pommel held upright by the blade. Cover your openings and peer out and from there with the Pavise. Also, step toward him and from this position, throw the spear strongly in at him. Whilst he attempts to parry the shot, then grasp your sword by the hilt and run in at him. Thus you run his spear away and give him an unexpected low lead-thrust while approaching from your centre-of-gravity (balance) pushed and shoved, with a similar stab at his helmet. You stab someone through any [form of] Arena armour. |
[18v-a] [I]Tem ess sind hie drey stuck nacheinander geschriben Das erst ein schuss mit dem spies das ander ein vnter stich mit dem swert / das drit ein ober stich mit dem swert vnd sind drey tewsche stuck wen einer In rinck harnisch nach Tewtschem siten ring gewappent ist / So nym dein spies auf schiessen In dein rechte handt vnd ein Pauessen / vnd ein swert mit einem sweren knopff ploss bey der klingen beyss zwsamen In dein lincke handt vnd deck dein ploss vnd antlitz auss vnd aus mit der pauessen / vnd drit also zw eim vnd schewss den spies starck In In vnd in dem schuss er sich des erholt so ergreiff dein swert / bey dem gehiltz vnd lauff zu Im ein / So laufst dw Im sein spies ab vnd gib Im ein vntern swanckenten vor stich mit eim zutrit aus der wag sein helm weg gestossen vnd geschossen mit eim solichem stich Sticht man durch allen Rinck harnisch |
[152r] [No text] | ||
[11] The other [2nd] technique is when you have thrown your spear, and during the shot, thus grasp your sword by the hilt for a low fore-thrust and charge in, so you run his spear away. Yet if he recovers from it, then also step towards him with a varied entry [schwanken zutritt] from below to his stomach or done with a strong shot by punching the stab. And if his sword has been harmed by the stechen and cannot proceed, then allow your Pavise to drop down to strike him at the head, on the arm and hand, for as long as possible until he is hurt by you. And don’t let him come no more to his sword. |
[18v-c] [D]aS ander stuck wen dw dein spies also verschossen hast vnd in dem schuss / So ergreiff dein swert bey dem ge / hiltz auf ein vntren vor stich vnd lauff ein so laufst dw Im sein spiess ab ee er sich des schus erholt / vnd gib Im also mit eim swanckenten zudrit vo[n] vnten an auf sein pauch oder gemacht ein starcke[n] schus stoss stich / vnd het er den sein swert In der schaiden stecken / vnd nit heraussen so las dein pauessen fallen / vnd slag In an den kopff / vnd auf die arm vnd hendt / als lang bis er dir an schaden sey vnd las In zu seim swert nit mer kumen |
[153r] [No text] | ||
[12] The third is for when you have thrown your spear and run in towards him and given him a strong thrusting stab with a varied approach from the Balance [your stance][10] so that you go through his armour; then stand your ground against him at the sword, if he has withdrawn and exposes the hands, to then cover your openings well with the Pavise. Step towards the back and so it misses your sword hand, moving up with a high thrust blow and step towards him, always keeping your openings covered quite well, and give him yet another high thrust blow under his neck, strengthened using your legs,[11] and step back yet again and always perform [treib, drive] that as long as possible with low stabs and with high stabs, until you overcome him, so that he is hurt by you. |
[18v-d] [D]as drit wen dw in also mit dem spies geschossen hast vnd zu Im laufst vnd Im gibst ein starcken sch[w]s stich mit eim swanckente[m] zu trit aus der wag das get durch als harnasch so steh Im auf das swert hat er das auss gezogen vnd plos In der hendt so deck dein Ploss mit der Pauessen wol vnd drit wider zu ruck vnd verbessol dein swert In der handt auf ein obern schuss schlag stich vnd trit den wider zu / vnd deck albeg dein plos gar woll vnd gib Im aber ein obern schus schlag stich vnter sein hals starck aus d[er] wag / vnd drit den aber wider zurück / vnd treib das alles als lang mit vnter stichen vnd mit obern stichen bis das dw In wuntes das er dir an schaden ist |
[154r] [No text] | ||
[13] |
[050v] WEr ein kampff soll fechten / der soll sein vortail suchen mit stant vnd vechten gen der sonnen vnd man sol Im geben Sander[?]haw / gibt das auch lauffenden Pferden oder ainem hundt es laufft fuer / vnd wirt des der stercker / dw solt auch kein sollen an dein fussen haben an dein schuchen |
[145r] [No text] | ||
[14] [No text] |
[160r] [No text] | |||
[15] [No text] |
[190r] [No text] |
- ↑ Presently, a term more commonly associated with firearms evidently originated with throwing of javelins. Schiessen means ‘shooting’, but it is also indicative of ‘throwing’, ‘launching’, ‘discharging’ etc.
- ↑ A similar method of holding the weapons together is found in Talhoffer.
- ↑ Lexer equates “Torlich” with temerarius: accidental, rash, thoughtless. I have used the term ‘spontaneous’ in order to avoid an undesirable connotation in English.
- ↑ Lit: “run under”, “pass under”, “undermine”
- ↑ This is evidently Talhoffer’s second position for throwing (MS XIX.17-3, 6r; MS 78.A.15, 10r; MS KK5342, 6r)
- ↑ Gewappent can mean “armed” whilst verwant can mean “relatively”.
- ↑ Ebers, Vol.5 (1799, 354-355) “Stecken, signifies also, to pitch, to drive or thrust in, to stick”. Pfahle stecken “to set Pales, to drive or thurst them into the ground” also referring to “auf einen Pfahl stekcen, spießen: to impale”. It also follows the implication to Plant, i.e. trees into the ground. Also consider the meanings of “einer Sache das Ziel stecken: to stop the Course of a Thing”, “ein Ziel stecken: to set an Aim or a Mark to aim at”, “sich in Noth stecken: to engage, embark or intangle in a dulle Piece of Trouble”. “Ich weiß wo es steckt: I know the Difficulty of it”. The term stëchen means to Stab, but with a driving action. Such a meaning caused it to be used variously as a synonym for tournament jousting (das turnieren), particularly in poetic works (http://woerterbuchnetz.de/Lexer/?lemid=LS07141 : WIG. SUCH. LIEHT. 71,26. VIRG. 75,5. 546,8. REINFR. B. 27113. ANTEL. 185. 87. FASN. 646,25. CHR. 4. 323,15; 9. 859,2; 10. 375,17). Talhoffer makes use of the term appealing to such chivalric epics in his exordium to Liutold von Koenigsegg. Here we see the logic for why a the sword and spear are to be taken together, as per the preliminary instructions.
- ↑ wîʒen stv. II. (BMZ III. 781b) beachten, bemerken s. die partic. adj. gewiʒʒen, ungewiʒʒen; mit dat. u. acc. (oder präp. umbe DIEM. BÜCHL. WALTH. WIG.) jemand einen vorwurf woraus od. weshalb machen, ihm es schuld geben, verweisen, allgem. z. b. waʒ wîʒest dû mir? RUL. 50,1. waʒ wîʒet ir mir Hildebrant? BIT. 7655. 980.waʒ wîʒet ir disem wîbe? GLAUB. 2174. daʒ ne darf man ire nicht w. GR.RUD. 21,15. vgl. noch GEN. D. 62,15. ER.6303. BÜCHL. 2,15. MSF. 40,35. 113,17. NEIDH. XXXVII, 4. XXXIX, 12. LIEHT. 48,9. TROJ. 45829 (lies im statt in). AMIS L.1937. CRAON 1720. MART. 148,79. ALBR. 1,318. 24,9. HEINR. 4041. SSP. prol. 14. mit abh. s. der vater weiʒ in, daʒ GEN.65,12; bestrafen KCHR. D. 153,29. REINH. 307,445. ENGELH. 1670. mit ent-, ge-, ver-. gt. veitan nhd. sehen (in gt. in-, fraveitan) zu skr. vid, lat. videre, gr. ἰδεῖν GSP. 321. Z. 154. CURT.3 227. FICK2 189. vgl. wiʒʒen.
- ↑ The Bohemian Pavise, a form of shield as shown in the illustration named after the city of Pavia, Italy. It became the quintessential duelling weapon, being featured heavily in the Weisskunig. Here it takes the German form of the noun, Pavessen. Because of its size (up to a yard wide, and four or more feet tall) it often became grouped to form a shield-wall known as a Pavisade. It also tended to be used heavily by archers in the English wars with France (Fosbroke 1843, 880)
- ↑ The implication seems to be that the body stands evenly, and using ponderation, the body-weight is transferred forward to take the opponent by surprise.
- ↑ starck aus d[er] wag, lit: “strong from the balance”, or in other words, with strength from your stance, or derived from the legs. A good example of kinetic linkage perhaps?